Test: Alkynes Reaction - NEET MCQ
24 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Alkynes Reaction
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
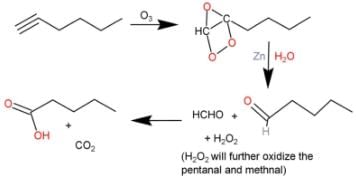
Q. Which of the following reaction would not give atleast one aldehyde product?
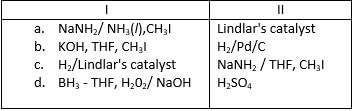
Which set of reagent(s) in correct order would accomplish the following transformation?
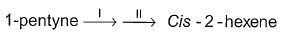

What is true about the final major product of the reaction?
A chiral hydrocarbon has molar mass 82 and it gives effervescence when heated with Na metal. What is true about the original hydrocarbon?
A hydrocarbon X (C14H22)o n treatm ent with H2/Pt gives C14H26. Also X on treatm ent with alkaline KMnO4 followed by hydrolysis of products yields C7H12O2 which on further heating with soda lime gives cyclohexane. Hence, X is
Direction (Q. Nos. 9 - 12) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has fo ur choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. What is/are true about ozonolysis of 1-hexyne followed by aqueous work-up?
Which reagent(s) below results in a visible change withl-butyne and can be used to differentiate it from 2-butyne?
Which of the following sets of reagent when applied sequentially, on 2-butyne will produce a meso product?
The correct statement(s) regarding relative reactivity of an alkyne and an aklene is/are
Direction (Q. Nos. 13 - 14) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q. Column I has some alkynes and Column II has their corresponding reaction products. Match them appropriately.
Column I has some reactions and Column II has the characteristics of reactions and products of Column I. Match them appropriately.
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 - 20) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Six questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
Unlike alkenes, alkynes undergo nucleophilic addition as well as electrophilic addition as :
Q. Which of the following best describes what happens in the first step in the mechanism of reaction shown below?
Passage I
Unlike alkenes, alkynes undergo nucleophilic addition as well as electrophilic addition as :
Q. Rates of Br2 addition were measured for a series of alkynes, giving the data shown.
Assuming that Br2 addition to alkynes proceeds through rate determining formation of cyclic bromonium ion, what generalisations can you make about the structure of rate determining transition state?
Passage I
Unlike alkenes, alkynes undergo nucleophilic addition as well as electrophilic addition as :
Q. Nucleophilic addition can occur on alkynes that bear strong electron withdrawing group such as — CF3 on the triple bond. Predict product of the following reaction :
Passage II
Two isomeric alkynes A and B have molecular formula C8H14 A on treatment with ammoniacal AgNO3 solution forms a white precipitate while B on similar treatment formed no precipitate. Also both A and B are chiral and hydrogenation of either A or B with H2/Pt gives the same achiral hydrocarbon C(C8H18). Treatment of A with HgSO4 /H2SO4 (aq) gives D(C8H16O) a s major product while sim ilar treatment of B, mixture of D and E in comparable amounts are formed.
Q. The structures of A and B are respectively
Passage II
Two isomeric alkynes A and B have molecular formula C8H14 A on treatment with ammoniacal AgNO3 solution forms a white precipitate while B on similar treatment formed no precipitate. Also both A and B are chiral and hydrogenation of either A or B with H2/Pt gives the same achiral hydrocarbon C(C8H18). Treatment of A with HgSO4 /H2SO4 (aq) gives D(C8H16O) a s major product while sim ilar treatment of B, mixture of D and E in comparable amounts are formed.
Q. The correct statement regarding A and B is
Passage II
Two isomeric alkynes A and B have molecular formula C8H14 A on treatment with ammoniacal AgNO3 solution forms a white precipitate while B on similar treatment formed no precipitate. Also both A and B are chiral and hydrogenation of either A or B with H2/Pt gives the same achiral hydrocarbon C(C8H18). Treatment of A with HgSO4 /H2SO4 (aq) gives D(C8H16O) a s major product while sim ilar treatment of B, mixture of D and E in comparable amounts are formed.
Q. What is true regarding A and B?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21 - 24) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. How many different isomeric alkynes on catalytic hydrogenation can give 2, 3, 4 -trimethyl heptane?
is treated will 2 moles of Br2, how many different isomers of products would be obtained?
In the reaction below :
Q. How many different isomers of tetrabromides are formed?
How many reagents from the list below would give effervescence when reacted with 1-pentyne?
NaOH(l), CH3CH2ONa(ll),
CH3CH2MgBr(lll), NaH(IV),
NaNH2(V), Na(VI)
NaHCO3(VII), [(CH3)2CH]2NLi(VIII),
CH3CH2 Li(IX), C6H5Li(X).
|
119 videos|338 docs|74 tests
|