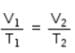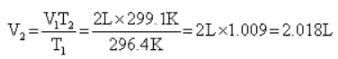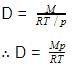Test: The Gas Laws (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: The Gas Laws (Old NCERT)
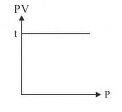
The slope of plot between pV and p at constant temperature is:
Mathematical expression that describes Boyle's law is
At constant temperature, the pressure of a fixed amount of gas varies inversely with its volume, is
At constant volume, pressure of a fixed amount of a gas varies directly with the temperature, is
The vapour pressure of water at 300 K in a closed container is 0.4 atm. If the volume of the container is doubled, its vapour pressure at 300 K will be
Equal volumes of all gases under the same conditions of temperature and pressure contain equal number of molecules, is
A vessel contains 0.16g of methane and 0.28g of nitrogen. The ratio of partial pressures of methane to nitrogen in the mixture is about:
A balloon seller filled a balloon with 2 L air when the temperature was 23.4° C. He sold the balloon at the time when temperature was recorded to 26.1°C. Volume of the balloon at this temperature is
One mole of N2O4 is kept in a close container at 300K and 1 atm pressure. When it is heated to 600 K 20% of it decomposes to NO2 (g). Calculate the resultant pressure exerted on the walls of the container
For a certain reaction PV = 2 dm3 atm and volume is 4 dm3 then corresponding pressure is
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|