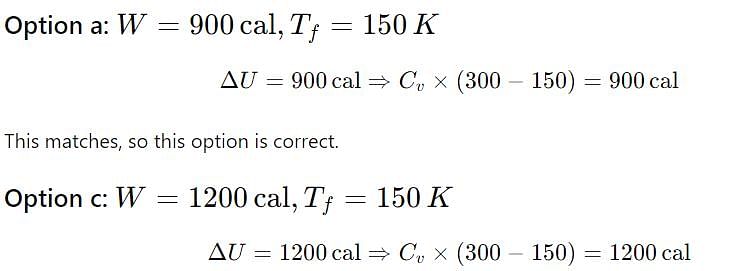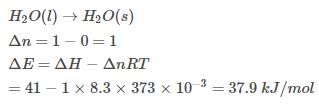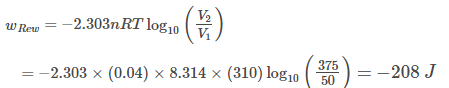Test: First Law of Thermodynamics - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: First Law of Thermodynamics
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
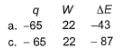
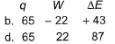
Q. A gas is cooled and loses 65 J of heat. The gas contracts as it cools and work done on the system equal to 22 J is exchanged with the surroundings. Thus, q, W and ΔE (change in internal energy) are (in joules)


Which of the following is true for a steady flow system?
One kg of carbon produces __________ kg of carbon dioxide.
A gas absorbs 200 J of heat and expands by 500 cm3 against a constant pressure of 2 x 105 Nm-2. Change in internal energy is
The pressure-volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated using the expression
This type of work can also be calculated using the area under the curve within the specified limits. When an ideal gas is compressed, (I) reversibly or (II) irreversibly, then
In the following case
Magnitude of work done and Final temperature respectively are:
Assuming that water vapour is an ideal gas, internal energy change (ΔE)when 1 mole of water is vaporised at 1 bar pressure and 100°C will be
(Given, molar enthalpy of vaporisation of water at 1 bar and 373 K = 41 kJ mol-1)
[IIT JEE 2007]
1.0 mole of a monoatomic ideal gas is expanded from state I to state II at 300 K.
Thus, work done is
A " 1/4 HP" electric motor uses 187 W of electrical energy while delivering 35 J of work each second. How much energy must be dissipated in the form of friction (heat)?
1 mole of a diatomic gas is contained in a piston. It gains 50.0 J of heat and work is done on the surrounding by the system is -100 J. Thus,
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. The reversible expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic and isothermal conditions is shown in the following figure. Select correct statement.
[IIT JEE 2012]
A piston filled with 0.04 mole of an ideal gas expands reversibly from 50.0 mL to 375.0 mL at constant temperature of 37.0°C. As it does, it absorbs 208 J of heat. The value of q and W for the process will be (R = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1, In 7.5 =2.01)
[JEE Main 2013]
A sample containing 1.0 mole of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly to ten time of its original volume, in two separate experiments. The expansion is carried out 300 K and at 600 K, respectively. Choose the correct option.
An ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure p1 volume V1 and absolute temperature T1 expands irreversibly against zero external pressure, as shown in the diagram. The final internal pressure, volume and absolute tem perature of the gas are p2, V2 and T2, respectively. For this expansion
[JEE Advanced 2014]
In a certain chemical process, a lab technician supplies 254 J of heat to a system. At the same time, 73 J of work area done on the system by its surroundings. What is the increase in the internal energy (in J) of the system ?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-17) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
A fixed mass m of a gas is subjected to transformation of states from K to L to M to N and back to K as shown in the figure.
Q. The succeeding operations that enable this transformation of states are
[JEE Advanced 2013]
A fixed mass m of a gas is subjected to transformation of states from K to L to M to N and back to K as shown in the figure.
Q. A pair of isochoric processes among the transform ation of states is
Direction (Q. Nos. 18) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
I. A sample of an ideal gas underwent an expansion against a constant external pressure of 1.0 bar from 1.0 m3, 10.0 bar, and 273 to 10.0 m3, 1.0 bar and 273 K. Work done by the system on the surroundings is W1 (in J).
II. The external pressure was increased to 10.0 bar and the gas sample was isothermally compressed from 10.0 m3 and 1.0 bar to 10 m3 and 10.0 bar.
Work done on the system by the surroundings is W2 (in J).
III. Total work done is W3 (in J).
IV. Least amount of work needed to restore the system to the original p-V conditions is W4 (in J) .
Match W1 W2, W3 and W4 in Column I with corresponding values in Column II.
Direction (Q. Nos. 19 and 20) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. About 1 dm3 gastric juice are produced per day in the human body from other body fluids such as blood, whose pH is 7.6021 [H+] = 10-pH] at 53°C. Calculate the minimum work (in kJ) required to produce 1 dm3 gastric juice may be taken as unity.
One mole of an ideal gas, Cp = 4 R at 300 K Is expanded adiabatically to n times the original volume. What is value of n if temperature falls by 150°?
|
127 videos|245 docs|87 tests
|