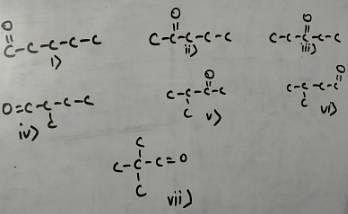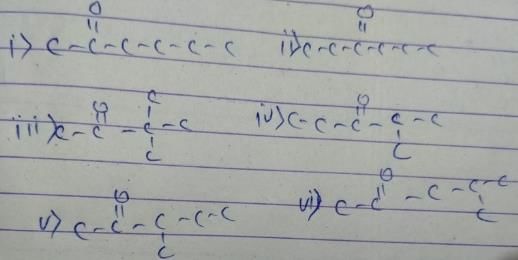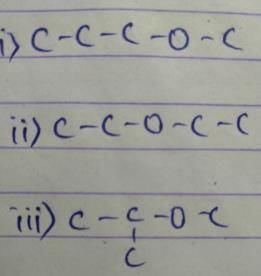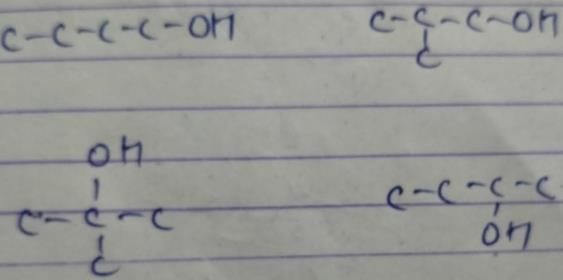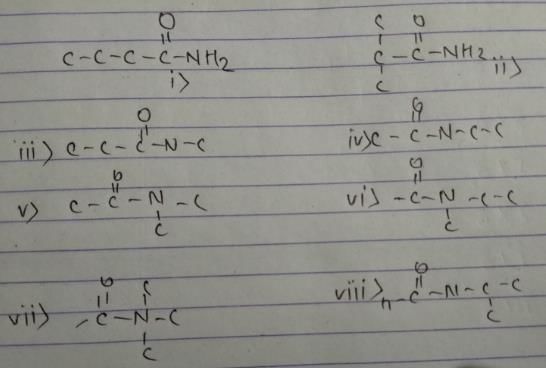Test: Structural Isomerism - 2 - JEE MCQ
18 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Structural Isomerism - 2
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
how many structural isomers (aldehyde + ketone) are possible for C5H10O ?
An organic acid containing carbon, oxygen and hydrogen only has molar mass of 132 g. 6.6 g of this acid require 80 mL 1.25 M NaOH for complete neutralisation. How many carboxylic groups are present in one molecule of this acid?
An organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen has molar mass 100. How many structural isomers satisfy this condition which are also simultaneously ketones?
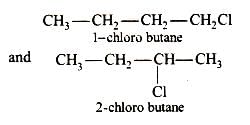
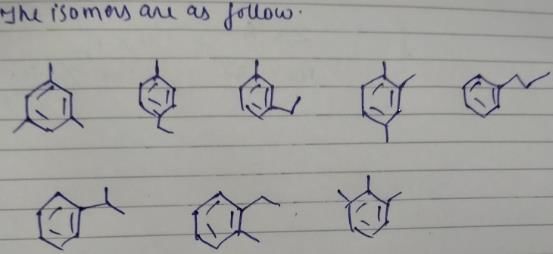
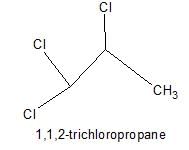
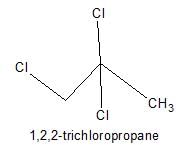
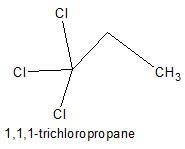
Only two isomers of monochloro product is possible of
Which of the following compounds will exhibit cis-trans isomerism?
An organic compound has three ether isomers and it is the smallest ether which satisfy this condition. Which of the following is true regarding this compound?
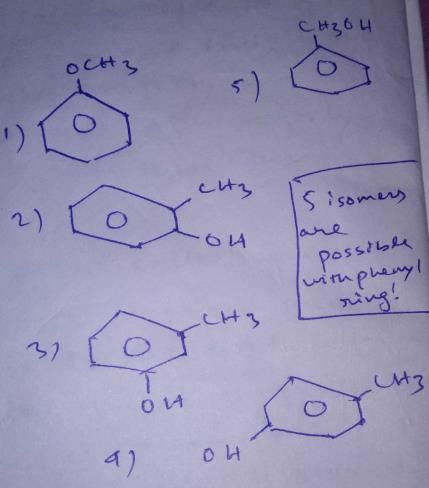
How many structural isomers exist for C7H80 where each isomer contain a phenyl ring?
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-12) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
Organic compound with molecular formula C2H4O2 can have which of the functional isomer(s)?
The correct statement(s) about structural isomers of compounds having chemical composition C5H12O is/are
What is/are correct deduction regarding compounds with their composition C3H60?
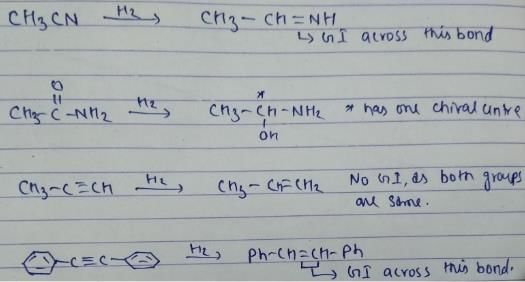
Which of the following on adding one molecule of hydrogen (H2) per molecule of the compound can result in compound capable of exhibiting stereoisomers?
Direction (Q. Nos. 13 and 14) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q.
Column I has some molecular formula and Column II has some organic functional groups. Match the functional group from Column II with the formula from Column I that may contain this functional group. Additional functional groups may also be present. There may also be more than one same functional groups present.
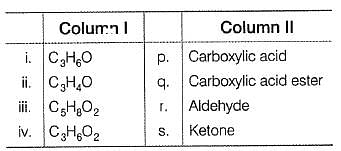
Codes

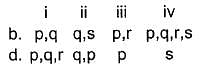
Match the formula from column I with their possible identity from Column II
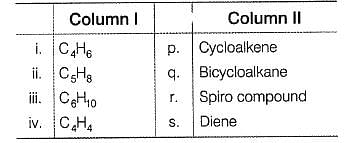
Codes

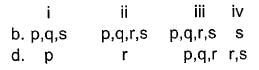
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-18) This section contains 4 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q.
How manyisomers, each contaning a phenyl ring, are possible for C9H12 ?
How many enols (mono plus dienols only) excluding stereomers are possible for heptane-2,4-dione?
How many ester isomers are possible for compound with molecular formula C5H10O2?
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|