Test: Crystal Field Theory (CFT) & Colour of Complexes - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Crystal Field Theory (CFT) & Colour of Complexes
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Among the following complexes the one which shows zero crystal field stabilisation energy is
The wavelength of light absorbed is highest in
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The CFSE for octahedral [CoCI6]4- is 18000 cm-1. Then the CFSE for tetrahedral [CoCI4]2- will be
The crystal field splitting energy (Δo) of
I. [CoBr6]3- II. [CoF6]3-
III. [Co(NCS)6]3- IV. [Co(CN)6]3- is in the order of
A magnetic moment of 1.73 BM will be shown by one among the following
The correct order o f ligand field strength is
The crystal field splitting energies (CFSE) of high spin and low spin d6 metal complexes in octahedral complex in terms of Δo respectively are
The Δt of the following complexes follows the order
I. [CoCI4]2-
II. [CoBr4]2-
III. [Co(NCS)4]2-
In which of the following coordination entities, the magnitude Δo (CFSE in octahedral field) will be maximum ?
The increasing order of wavelength of absorption for the complex ions
I. [Cr(NH3)6]3+
II. [CrCI6]3-
III. [Cr(H2O)6]3+
IV. [Cr(CN)6]3-
is :
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which of the following metal ions cannot form both high spin and low spin octahedral complexes?
Which is/are the correct statements?
CFSE is zero for the complexes with
Octahedral complex of Cr (III) will be
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have.
Passage
In octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g. The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.
Q.
The CFSE for d7 configuration for strong ligand field is
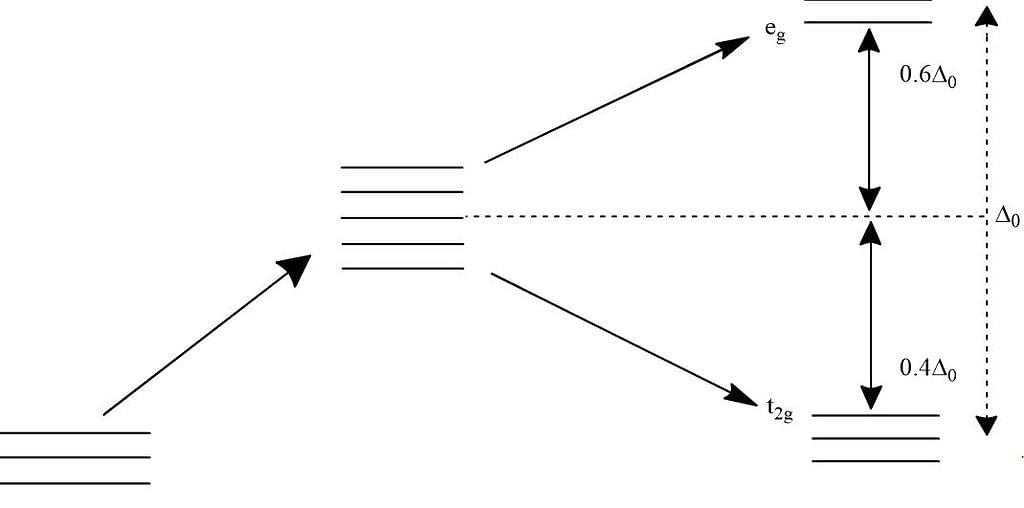
In octahedral complexes due to repulsion between the ligands and d-orbitals, there is splitting of d-orbitals into two sets, i.e. two orbitals of higher energy called eg and three orbitals of lower energy called t2g. The difference of energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is called crystal field stabilisation energy denoted by Δo. For any given metal cation, the magnitude of Δo depends on the nature of ligands.
Q.
In the following complexes of manganese, the distribution of electrons in d-orbitals of manganese
i. [Mn(H2O)6]2+
ii. [Mn(CN)6]4-
Matching List Type
Direction (Q. No. 18-19) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
Number of unpaired electrons in d6, low spin octahedral complex.
The number of ligands which have strong crystal field splitting than
H2O among SCN-, NCS-, EDTA4- , ,
, Br-, PPh3, F-
The total number of unpaired electrons in the two complexes [Cr(H2O)6]2+ and [Cr(CN)6]4- having octahedral geometry are
Number of unpaired electrons in t2g and eg orbitals in weak octahedral ligand fields with d7 configuration.
In tetrahedral complexes having weak field ligand, pairing starts with ...... electron.
Statement Type
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : The value of CFSE for the octahedral complex [Co(NH3)6]3+ is - 2.4Δo.
Statement II : The ammonia molecule is strong field ligand.
|
102 videos|282 docs|123 tests
|


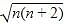 BM
BM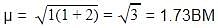
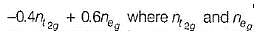 are the number of electron occupying the t2g and eg orbitatls respectively.
are the number of electron occupying the t2g and eg orbitatls respectively.














