31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Breathing & Exchange of Gases - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Breathing & Exchange of Gases
Select the favorable conditions required for the formation of oxyhemoglobin at the alveoli. [2021]
Select the correct events that occur during inspiration. [2020]
(i) Contraction of diaphragm
(ii) Contraction of external inter costal muscles
(iii) Pulmonary volume decreases
(iv) Intra pulmonary pressure increases
(i) Contraction of diaphragm
(ii) Contraction of external inter costal muscles
(iii) Pulmonary volume decreases
(iv) Intra pulmonary pressure increases
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Tidal Volume and Expiratory Reserve Volume of an athlete is 500 mL and 1000 mL respectively. What will be his expiratory capacity if the residual volume is 1200 mL? [2019]
Which of the following options correctly represents the lung conditions in asthma and emphysema, respectively? [2018]
Lungs are made up of air-filled sacs, the alveoli. They do not collapse even after forceful expiration, because of [2017]
Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in
The alveolar epithelium in the lungs is[1990]
Carbon dioxide is transported from tissues to respiratory surface by only [1993]
Oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin is[1994]
Air is breathed through [1994]
Although much CO2 is carried in blood, yet blood does not become acidic, because [1995]
The carbon dioxide is transported via blood to lungs as [1995]
People living at sea level have around 5 million RBC per cubic millimeter of their blood whereas those living at an altitude of 5400 metres have around 8 million. This is because at high altitude [1995, 2006]
The quantity 1200 ml in the respiratory volumes of a normal human adult refers to [1996]
In alveoli of the lungs, the air at the site of gas exchange, is separated from the blood by
[1997]
The exchange of gases in the alveoli of the lungs takes place by [1998]
The process of migration of chloride ions from plasma to RBC and of carbonate ions from RBC to plasma is [1999]
Which one of the following organs in the human body is most affected due to shortage of oxygen? [1999]
When CO2 concentration in blood increases, breathing becomes [2004]
Blood analysis of a patient reveals an unusually high quantity of carboxyhaemoglobin content. Which of the following conclusions is most likely to be correct?The patient has been inhaling polluted air containing unusually high content of [2004]
Which one of the following mammalian cells is not capable of metabolising glucose to carbon-dioxide aerobically? [2007]
Intercostal muscles occur in [1988]
What is vital capacity of our lungs?
Listed below are four respiratory capacities (i–iv) and four jumbled respiratory volumes of a normal human adult: [2010]
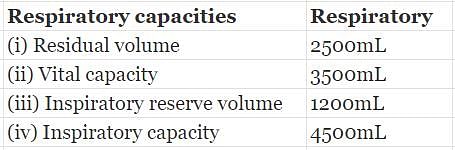
Which one of the following is the correct matching of two capacities and volumes?
Which two of the following changes (a–d) usually tend to occur in the plain dwellers when they move to high altitudes (3,500 m or more)? [2010]
(i) Increase in red blood cell size
(ii) Increase in red blood cell production
(iii) Increased breathing rate
(iv) Increase in thrombocyte count
Changes occurring are:
Which one of the following is a possibility for most of us in regard to breathing, by making a conscious effort? [2011M]
Which of the following are the correct statement for respiration in human [2012]
The figure shows a diagrammatic view of human respiratory system with labels A, B, C and D. Select the option which gives correct identification and main function and/or characteristics. [NEET 2013]
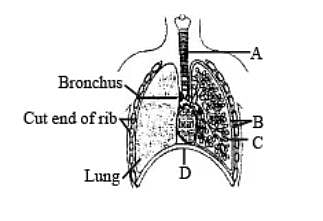
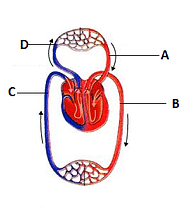
Figure shown schematic plan of blood circulation in humans with labels A to D. Identify the label and give its function’s. [NEET 2013]
Which one of the following is one of the paths followed by air/O2 during respiration in an adult male Periplaneta americana as it enters the animal body? [NEET Kar. 2013]
|
182 videos|365 docs|153 tests
|



















