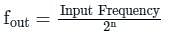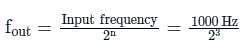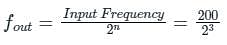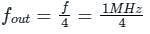Test: T Flip Flop - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Analog and Digital Electronics - Test: T Flip Flop
Three T flip flops are connected to form a counter. The maximum states possible for the counter will be:
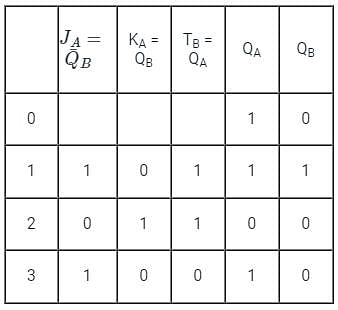
A two-bit counter circuit is shown below

If the state QA QB of the counter at the clock time tn is ‘10’ then the state QA QB of the counter at tn + 3 (after three clock cycles) will be
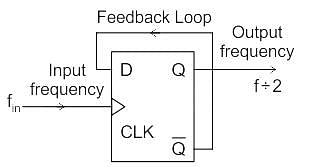
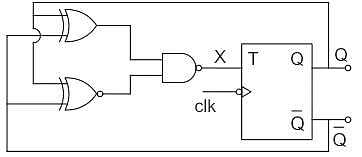
The clock frequency applied to the digital circuit shown in the figure below is 1KHz. If the initial state of the output of the flip-flop is 0, the frequency of the output waveform Q in KHz is
If the input to T-flipflop is 200 Hz signal, the final output of the three T- flipflops in cascade is
Determine the output frequency of the given circuit if the input CLK frequency is 1 MHz.

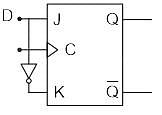
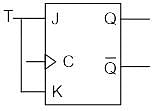
In J-K flip-flop, the function K=J is used to realize _____________
The only difference between a combinational circuit and a flip-flop is that _____________
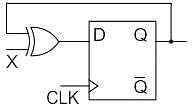
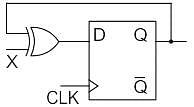
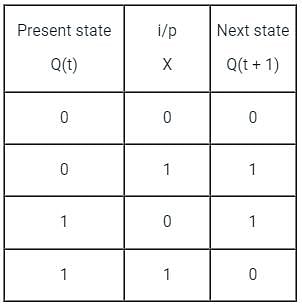
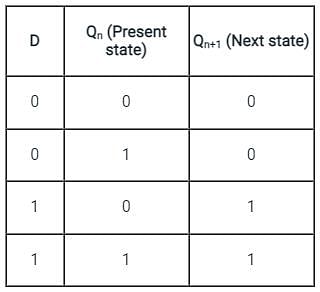
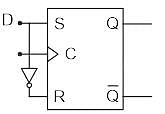
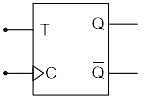
Both the J-K & the T flip-flop are derived from the basic _____________
___________ only allows for one master and one slave and is limited to distances of up to 15 meters.
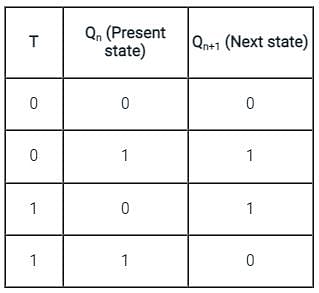
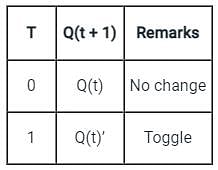
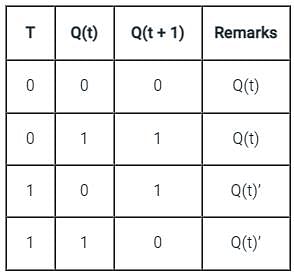
In Digital Circuits, which of the following options represent the synchronous control inputs in a T flip flop?
|
137 videos|144 docs|71 tests
|