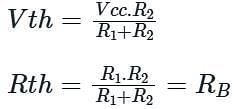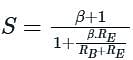Test: Self Bias - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Analog and Digital Electronics - Test: Self Bias
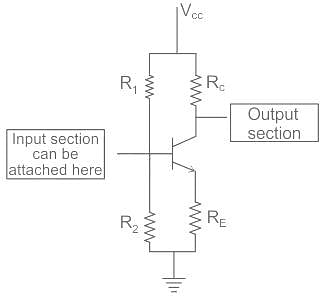
The collector current (IC) that is obtained in a self biased transistor is_________
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What is the Thevenin’s resistance (RTH) in a self bias shown below?
In the circuit, the transistor has a large β value (VBE=0.7V). Find the current through RC.
A silicon NPN transistor is used and it has a large value of β. Find the required value of R2when IC=1mA.
The value of αac for all practical purposes, for commercial transistors range from_________
Directions: Each of the next items consists of two statements, one labeled as the `Assertion (A)' and the other as 'Reason (R)' You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the answers to these items using the codes given below :
Assertion (A): The bias stability of a self-bias amplifier circuit can be improved by increasing the values of both the base resistor (RB) and the emitter resistor (RE).
Reason (R): The base resistor (RB) provides the required voltage to the base terminal and the emitter resistor (RE) provides negative feedback to the amplifier.
|
137 videos|143 docs|71 tests
|
|
137 videos|143 docs|71 tests
|