Test: Basic Concept - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basic Concept - 2
Which of the following aspect is not true regarding microscopic propertie s of thermodynamic system
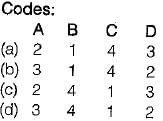
Match List-I with List-I I and select the correct answer:
List-I
A. Interchange of matter is not possible in a
B. Any processes in which the system returns to its original condition or state is called
C. Interchange of matter is possible in a
D. The quantity of matter under consideration in thermodynamics is called
List-ll
1. Open system
2. System
3. Closed system
4. Cycle
List-I
A. Interchange of matter is not possible in a
B. Any processes in which the system returns to its original condition or state is called
C. Interchange of matter is possible in a
D. The quantity of matter under consideration in thermodynamics is called
1. Open system
2. System
3. Closed system
4. Cycle

Which one of the following represents open thermodynamic system?
A thermodynamic system is considered to be an isolated one if
In highly rarefied gases, the concept of this loses validity
Which of the following is an example of heterogeneous system?
Consider the following:
- Entropy
- Viscosity
- Temperature
- Specific heat at constant volume
Which of the above properties of a system is/are intensive














