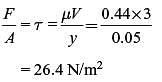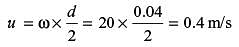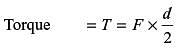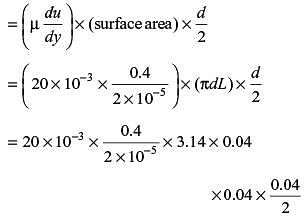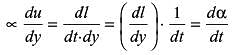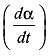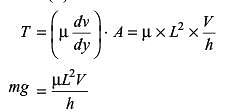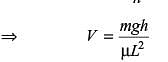Test: Fluid Properties - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Fluid Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering - Test: Fluid Properties - 1
Which one of the following is the unit of specific weight?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Match the following physical quantities in Group 1 with their dimensions in Group 2.
1. Mass Density (p) A. [M0 L 0 T 0 ]
2. Specific Gravity B. [M L– 1 T – 1 ]
3. Specific Volume (v) C. [M1 L -3 T 0 ]
4. Specific Weight (γ) D. [M-1 L3 T 0 ]
5. Dynamic viscosity (μ) E. [M L– 2 T – 2 ]
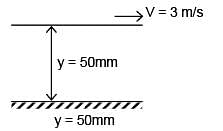
Consider fluid flow between two infinite horizontal plates which are parallel (the gap between them being 50 mm). The top plate is sliding parallel to the stationary bottom plate at a speed of 3 m/s. The flow between the plates is solely due to the motion of the top plate. The force per unit area (magnitude) required to maintain the bottom plate stationary is ______ N/m2.
Viscosity of the fluid µ = 0.44 kg/m-s and density ρ = 88 kg/m3.
Which of the following forces generally act on fluid while considering fluid dynamics?
1. Viscous force
2. Pressure force
3. Gravity force
4. Turbulent force
5. Compressibility force
Which property of the fluid offers resistance to deformation under the action of shear force?
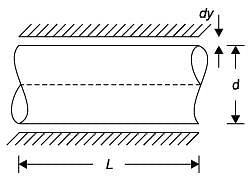
A journal bearing has a shaft diameter of 40 mm and a length of 40 mm. The shaft is rotating at 20 rad/s and the viscosity of the lubricant is 20 MPa-s. The clearance is 0.020 mm. The loss of torque due to the viscosity of the lubricant is approximately
The study of force which produces motion in a fluid is called as
The difference in pressure (in N/m2) across an air bubble of diameter 0.001 m immersed in water (surface tension = 0.072 N/m) is _____
Two fluids 1 and 2 have mass densities of p1 and p2 respectively. If p1 > p2, which one of the following expressions will represent the relation between their specific volumes v1 and v2?
A beaker is filled with a liquid up to the mark of one litre and weighed. The weight of the liquid is found to be 6.5 N. The specific weight of the liquid will be
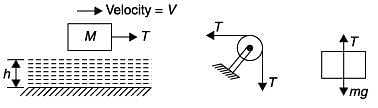
A cubic block of side ‘L’ and mass ‘M’ is dragged over an oil film across table by a string connects to a hanging block of mass ‘m’ as shown in figure. The Newtonian oil film of thickness ‘h’ has dynamic viscosity ‘μ’ and the flow condition is laminar. The acceleration due to gravity is ‘g’. The steady state velocity ‘V ’ of block is
|
56 videos|104 docs|75 tests
|
|
56 videos|104 docs|75 tests
|