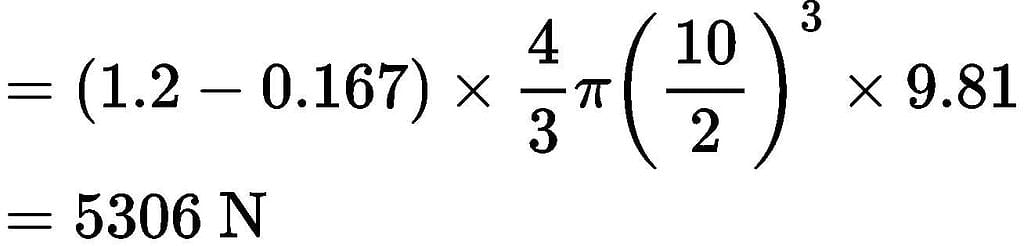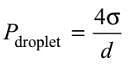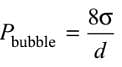Test: Types of Fluids - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Test: Types of Fluids
The relation between shear stress Z and velocity gradient  of a fluid is given by
of a fluid is given by 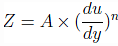 where A and n are constants. If n = 1, what type of fluid will it be?
where A and n are constants. If n = 1, what type of fluid will it be?
The relation between shear stress Z and velocity gradient  of a fluid is given by
of a fluid is given by 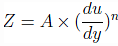 where A and n are constants. What type of fluid will it be if n < 1 and n > 1 respectively?
where A and n are constants. What type of fluid will it be if n < 1 and n > 1 respectively?
For what value of flow behaviour index, does the consistency index has a dimension independent of time?
The relation between shear stress Z and velocity gradient of a fluid is given by
+ B where A, n and B are constants.
Which of the following conditions will hold for a Bingham plastic?
The relation between shear stress Z and velocity gradient of a fluid is given by
+ B where A, n and B are constants. Which of the following conditions will hold for a Rheopectic?
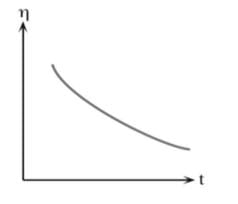
The above graph of viscosity vs time depicts which of the following fluids?
(Hint : This fluid is present in inks and paints)
The relation between shear stress Z and velocity gradient of a fluid is given by
where A and n are constants. The graphs are drawn for three values of n. Which one will be the correct relationship between n1, n2 and n3?
What will be the dimension of the flow consistency index for a fluid with a flow behaviour index of -1?
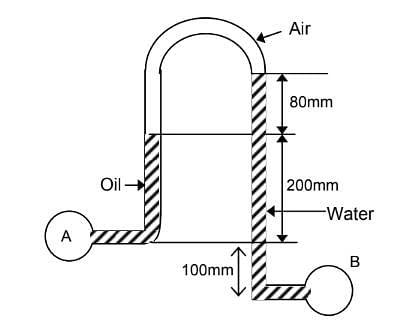
An inverted U-tube manometer is used to measure the pressure difference between two pipes A and B, as shown in the figure. Pipe A is carrying oil (specific gravity = 0.8) and pipe B is carrying water. The densities of air and water are 1.16 kg/m3, respectively. The pressure difference between pipes A and B is kPa.
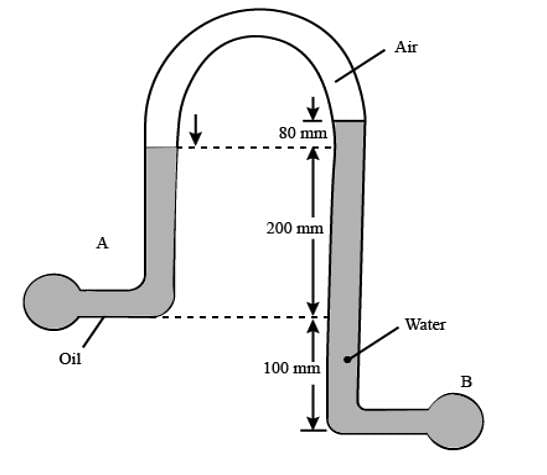
Acceleration due to gravity g = 10 m/s2.
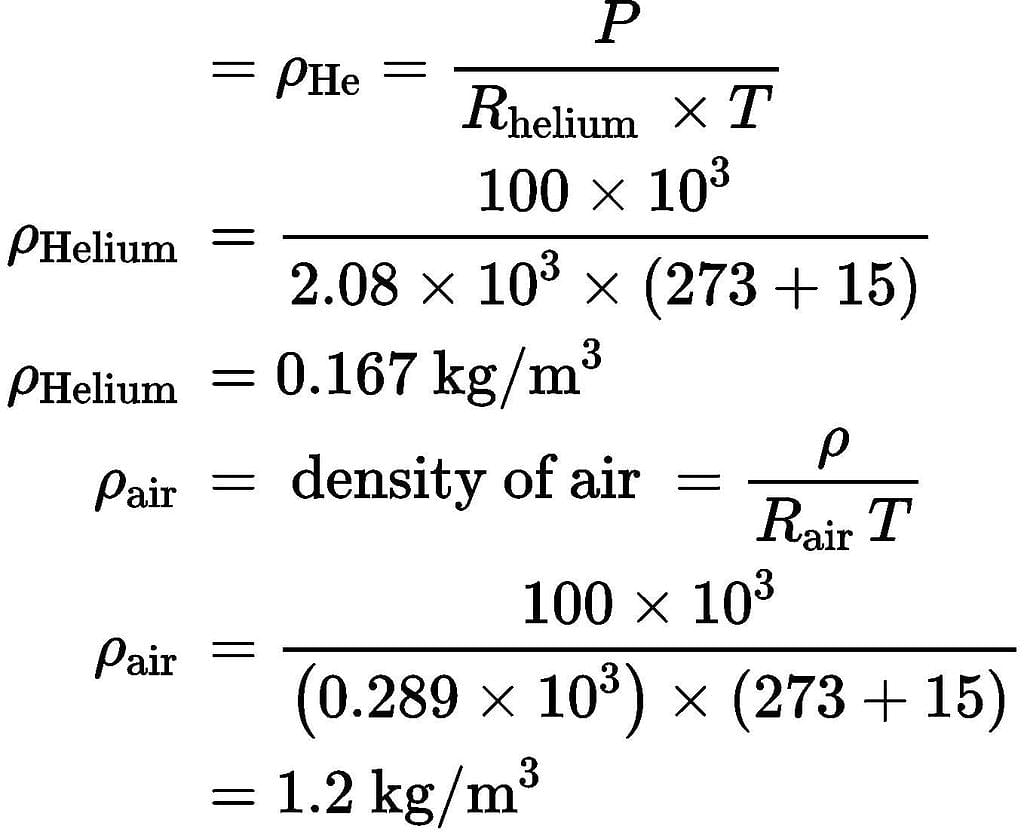
A spherical balloon with a diameter of 10 m, shown in the figure below is used for advertisements. The balloon is filled with helium (RHe = 2.08 kJ/kg⋅K) at ambient conditions of 15°C and 100 kPa. Assuming no disturbances due to wind, the maximum allowable weight (in Newton) of balloon material and rope required to avoid the fall of the balloon (Rair = 0.289 kJ/kg ⋅K) is _____

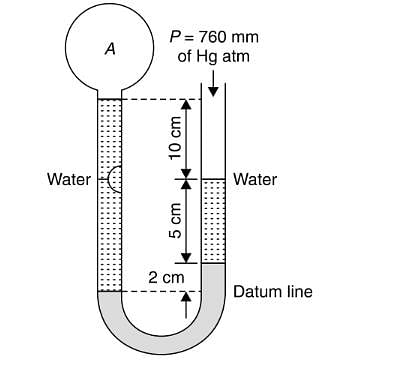
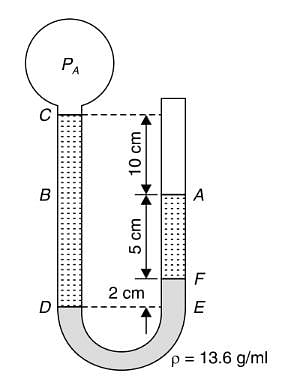
Refer to figure, the absolute pressure of gas A in the bulb is
If ‘P’ is the gauge pressure within a spherical droplet, then gauge pressure within a bubble of the same fluid and of same size will be
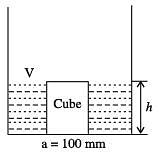
A cube of side 100 mm is placed at the bottom of an empty container on one of its faces. The density of the material of the cube is 800 kg/m3. Liquid of density 1000 kg/m3 is now poured into the container. The minimum height to which the liquid needs to be poured into the container for the cube to just lift up is _____ mm.
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|



 of a fluid is given by
of a fluid is given by