|
Card: 2 / 96 |
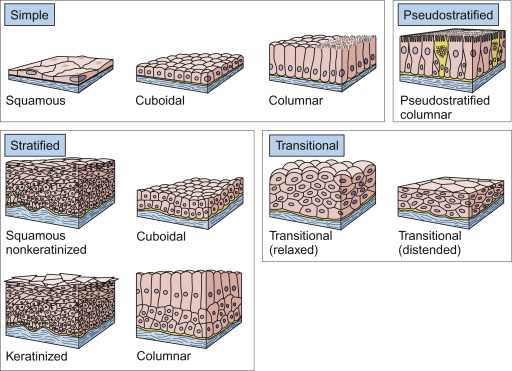
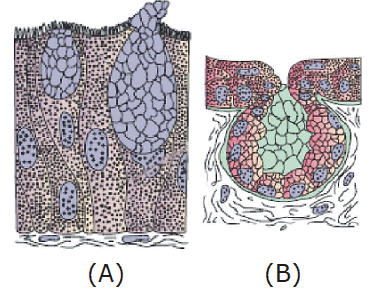
The two main types of epithelial tissue are simple epithelium, which serves as a lining for body cavities, ducts, and tubes, and compound epithelium, which consists of multiple layers and provides protective functions.
|
|
Card: 4 / 96 |
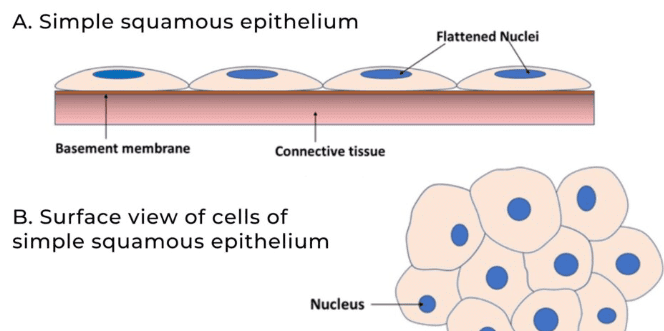
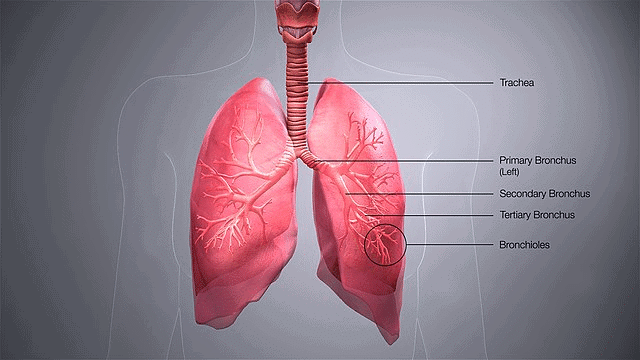
Squamous epithelium is composed of a single thin layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. It is found in the walls of blood vessels and air sacs of the lungs, primarily facilitating diffusion and filtration processes.
|
|
Card: 5 / 96 |
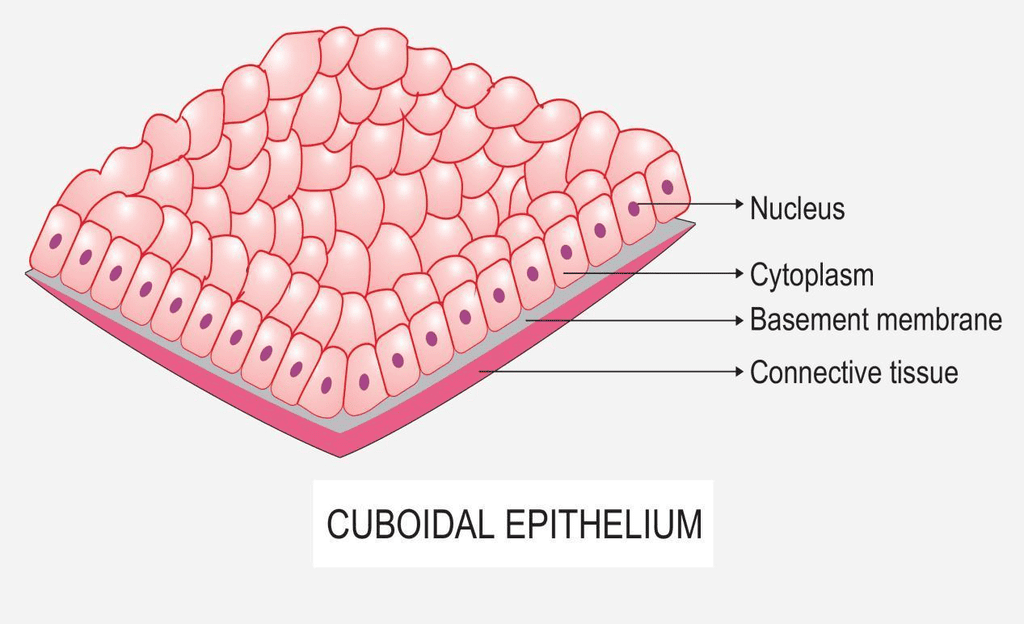
Cuboidal epithelium is primarily involved in ___ and ___ and is commonly found in ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 6 / 96 |
secretion and absorption; ducts of glands and tubular parts of nephrons in kidneys.
|
|
Card: 7 / 96 |
What is the primary function of columnar epithelium in the lining of the stomach and intestine? |
|
Card: 8 / 96 |
The primary function of columnar epithelium in the lining of the stomach and intestine is to facilitate secretion and absorption.
|
|
Card: 9 / 96 |
Ciliated epithelium is primarily found in the inner surfaces of hollow organs like ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 11 / 96 |
What are the main types of glands in glandular epithelium and how do they differ in secretion methods? |
|
Card: 12 / 96 |
The main types of glands in glandular epithelium are unicellular glands, like goblet cells, which secrete mucus, and multicellular glands, like salivary glands, which release secretions through ducts (exocrine glands) or directly into the surrounding fluid (endocrine glands).
|
|
Card: 13 / 96 |
What are the main components secreted by connective tissue cells, and what roles do they play? |
|
Card: 14 / 96 |
Connective tissue cells secrete structural proteins like collagen and elastin, which provide strength, elasticity, and flexibility to the tissue, as well as modified polysaccharides that form the matrix or ground substance between cells and fibers. |
|
Card: 15 / 96 |
Dense connective tissue can be classified into two types based on fiber orientation. Name these types and provide an example for each. |
|
Card: 16 / 96 |
The two types of dense connective tissue are dense regular connective tissue, which is exemplified by tendons and ligaments, and dense irregular connective tissue, which is found in the skin. |
|
Card: 17 / 96 |
Loose connective tissue serves as a support framework for epithelium and contains various cell types. Name two cell types found in areolar tissue and their functions. |
|
Card: 18 / 96 |
Two cell types found in areolar tissue are fibroblasts, which produce and secrete fibers, and macrophages, which are involved in immune responses and the removal of debris. |
|
Card: 19 / 96 |
What are the primary components that give bone its strength and structural integrity? |
|
Card: 20 / 96 |
The primary components that give bone its strength and structural integrity are calcium salts and collagen fibers. |
|
Card: 21 / 96 |
Cartilage is characterized by its ___ and ___, which allows it to resist compression. |
|
Card: 23 / 96 |
Describe the role of osteocytes and where they are located within bone tissue. |
|
Card: 24 / 96 |
Osteocytes are bone cells located in small cavities called lacunae within the bone matrix, and they play a crucial role in maintaining bone tissue. |
|
Card: 25 / 96 |
What are the three types of muscle tissue, and where is each type primarily located? |
|
Card: 26 / 96 |
The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle is attached to skeletal bones, smooth muscle is found in the walls of internal organs such as blood vessels, stomach, and intestines, and cardiac muscle is present only in the heart. |
|
Card: 27 / 96 |
Describe the structural characteristics and functions of cardiac muscle tissue. |
|
Card: 28 / 96 |
Cardiac muscle tissue is characterized by intercalated discs that fuse plasma membranes of cardiac muscle cells, allowing them to contract as a unit. This tissue is responsible for heart contractions and is involuntary, meaning it operates without conscious control. |
|
Card: 29 / 96 |
Smooth muscle fibers are described as ___ and are primarily found in ___ organs. |
|
Card: 30 / 96 |
Smooth muscle fibers are described as fusiform and are primarily found in internal organs such as the blood vessels, stomach, and intestines. |
|
Card: 31 / 96 |
What role do neuroglia play in neural tissue, and how do they compare in volume to neurons? |
|
Card: 32 / 96 |
Neuroglia make up more than one-half of the volume of neural tissue, providing support, nourishment, and protection for neurons. |
|
Card: 33 / 96 |
Describe the relationship between tissues, organs, and organ systems in multicellular organisms. |
|
Card: 34 / 96 |
In multicellular organisms, basic tissues organize to form organs, which then combine to create organ systems, enabling efficient and coordinated activities among millions of cells. |
|
Card: 36 / 96 |
Morphology focuses on the form or external appearance of organisms, while anatomy concentrates on the internal structure of animal organs. |
|
Card: 37 / 96 |
What are the three main body parts of a cockroach, and what is the primary function of the exoskeleton? |
|
Card: 38 / 96 |
The three main body parts of a cockroach are the head, thorax, and abdomen. The primary function of the exoskeleton, made of chitin, is to provide protection and support to the cockroach's body. |
|
Card: 40 / 96 |
The head region of a cockroach is triangular and features compound eyes, long antennae, and a mouth equipped with mandibles and other mouthparts, along with a flexible tongue-like structure. |
|
Card: 41 / 96 |
In which segments of the cockroach's abdomen are the reproductive organs located, and what structures are found at the end of the abdomen? |
|
Card: 42 / 96 |
The reproductive organs of the cockroach are located in segments 7 to 9 of the abdomen, and at the end of the abdomen, there are filamentous structures called cerci. |
|
Card: 44 / 96 |
The gizzard in the cockroach's alimentary canal functions as a grinding organ that mechanically breaks down food before it enters the midgut for digestion. |
|
Card: 45 / 96 |
What is the significance of the Malpighian tubules in the excretory system of cockroaches? |
|
Card: 46 / 96 |
Malpighian tubules are crucial for the excretory system of cockroaches as they absorb nitrogenous waste from the hemolymph and convert it into uric acid, which is then expelled through the hindgut, allowing for water conservation. |
|
Card: 47 / 96 |
In the reproductive system of cockroaches, what is the function of the spermatheca in females? |
|
Card: 48 / 96 |
The spermatheca in female cockroaches serves to store sperm after mating, enabling the female to fertilize her eggs over time, which is essential for reproduction. |
|
Card: 49 / 96 |
Frogs are classified under which phylum and class, and what does this classification indicate about their habitat? |
|
Card: 50 / 96 |
Frogs are classified under the phylum Chordata and the class Amphibia, indicating that they can live both on land and in freshwater. |
|
Card: 51 / 96 |
The ability of frogs to change their skin color for camouflage serves what primary purpose? |
|
Card: 52 / 96 |
The primary purpose of frogs changing their skin color for camouflage is to help them hide from predators. |
|
Card: 53 / 96 |
During extreme weather, frogs undergo two different states of dormancy known as ___ in summer and ___ in winter. |
|
Card: 59 / 96 |
In male frogs, the presence of ___ and ___ are characteristics that distinguish them from females. |
|
Card: 61 / 96 |
What is the significance of the short length of the alimentary canal in frogs? |
|
Card: 62 / 96 |
The short length of the alimentary canal in frogs is significant because frogs are carnivores, which allows for quicker digestion and absorption of nutrients from their food. |
|
Card: 63 / 96 |
In which part of the frog's digestive system does the first stage of digestion occur, and what substances are involved? |
|
Card: 64 / 96 |
The first stage of digestion occurs in the stomach, where hydrochloric acid (HCl) and gastric juices break down food into a semi-liquid form called chyme. |
|
Card: 65 / 96 |
Frogs utilize ___ respiration in water and ___ respiration on land, highlighting their adaptability to different environments. |
|
Card: 67 / 96 |
What are the main components of the frog's circulatory system, and how do they function together? |
|
Card: 68 / 96 |
The main components of the frog's circulatory system include the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart, which has three chambers (two atria and one ventricle), pumps blood through arteries to various body parts and receives it back through veins. Blood carries nutrients, gases, and water, with circulation enabled by the heart's muscular pumping action. |
|
Card: 70 / 96 |
Frog kidneys are compact, dark red, bean-like structures located posteriorly along the vertebral column. Each kidney consists of nephrons, which are responsible for filtering blood and excreting nitrogenous wastes. In male frogs, the ureters function as urinogenital ducts, while in females, they open separately into the cloaca. |
|
Card: 71 / 96 |
Frogs excrete urea and are classified as ___ animals; describe the process of waste elimination in their excretory system. |
|
Card: 72 / 96 |
Frogs are classified as ureotelic animals, as they excrete urea. The excretory system includes kidneys that filter blood to separate wastes, ureters that transport these wastes to the cloaca, and a urinary bladder for storage. Wastes are eliminated from the body through the cloaca. |
|
Card: 73 / 96 |
What are the primary components of the nervous system in frogs, and how are they organized? |
|
Card: 74 / 96 |
The nervous system in frogs is organized into three main components: the central nervous system (including the brain and spinal cord), the peripheral nervous system (comprising cranial and spinal nerves), and the autonomic nervous system (divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems). |
|
Card: 75 / 96 |
The endocrine system in frogs includes several glands; name at least four of these glands and their role. |
|
Card: 76 / 96 |
The prominent endocrine glands in frogs include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and gonads. These glands secrete hormones that are responsible for the chemical coordination of various bodily functions. |
|
Card: 78 / 96 |
Frog eyes are described as simple eyes and are located in the orbit of the skull. |
|
Card: 79 / 96 |
What are the primary male reproductive organs in frogs and where are they located? |
|
Card: 80 / 96 |
The primary male reproductive organs in frogs are a pair of testes, which are yellowish ovoid structures located near the kidneys, connected to the urinogenital duct via vasa efferentia. |
|
Card: 81 / 96 |
Describe the female reproductive system of frogs, including the role of the oviducts. |
|
Card: 82 / 96 |
The female reproductive system in frogs consists of a pair of ovaries located near the kidneys, with oviducts that open separately into the cloaca, allowing for the passage of eggs. |
|
Card: 84 / 96 |
Fertilization in frogs is external and occurs in water. The development includes a larval stage called a tadpole, which undergoes metamorphosis to become an adult frog. |
|
Card: 86 / 96 |
Organ systems allow for the efficient and coordinated activities of cells by organizing various organs that perform specific functions together. |
|
Card: 88 / 96 |
A frog's body has a smooth, slippery, and moist skin due to mucus, with a dorsal side typically olive green and speckled, while the ventral side is pale yellow. The body is divided into a head and trunk, lacking a neck or tail. |
|
Card: 89 / 96 |
Male frogs exhibit sexual dimorphism characterized by the presence of ___ and ___ which are absent in females. |
|
Card: 94 / 96 |
The frog's heart is a muscular structure with three chambers: two atria and one ventricle, covered by a pericardium. It receives blood through the sinus venosus and pumps it into the conus arteriosus, distributing it to the body. |
|
Card: 95 / 96 |
The vascular system of a frog includes the heart, blood vessels, and ___ system. |