|
Card: 3 / 62 |
True or False: The Harappan Civilization was primarily located in the northeastern part of the Indian subcontinent. |
|
Card: 4 / 62 |
False. The Harappan Civilization was primarily located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent. |
|
Card: 5 / 62 |
The Harappan Civilization is notable for its urban planning, which included features such as ___, ___, and ___ in its cities. |
|
Card: 7 / 62 |
True or False: The geographical extent of the Harappan Civilization was smaller than that of ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia. |
|
Card: 11 / 62 |
True or False: The drainage system of the Harappan cities was less advanced than that of contemporary Mesopotamia. |
|
Card: 12 / 62 |
False. The drainage system of the Harappan cities was highly impressive, with attention to health and cleanliness. |
|
Card: 13 / 62 |
The Indus Valley Civilization was known for being among the earliest producers of ___, which the Greeks referred to as sindon. |
|
Card: 15 / 62 |
True or False: The granaries in Mohenjo-daro and Harappa were likely used exclusively for storing rice. |
|
Card: 16 / 62 |
False. The granaries were used to store a variety of food grains including wheat, barley, and possibly rice. |
|
Card: 18 / 62 |
The Harappans primarily domesticated oxen, buffaloes, goats, sheep, pigs, dogs, cats, asses, and camels.  |
|
Card: 20 / 62 |
False. The Harappan culture was not horse-centered, as evidenced by the lack of horse bones and representations in their archaeological sites. |
|
Card: 21 / 62 |
Bronze tools and weapons recovered from Harappan sites indicate that ___ constituted an important group of artisans in Harappan society. |
|
Card: 23 / 62 |
Trade in the Indus Valley Civilization primarily relied on ___ rather than metal money. |
|
Card: 25 / 62 |
The Harappan culture is characterized by a political organization that likely required ___ to maintain cultural homogeneity. |
|
Card: 27 / 62 |
True or False: The Harappan civilization is characterized by the worship of trees and animals, but lacks evidence of gods worshipped in temples. |
|
Card: 29 / 62 |
The pipal tree is significant in the worship practices of the Indus region, serving as a symbol of ___ and ___ in various religious beliefs. |
|
Card: 31 / 62 |
What role did amulets play in the religious practices of the Harappan civilization? |
|
Card: 32 / 62 |
Amulets were believed to provide protection against ghosts, diseases, and evil forces. |
|
Card: 33 / 62 |
Fill in the blank: The absence of evidence of ___ in temples distinguishes the Harappan civilization from ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia. |
|
Card: 35 / 62 |
True or False: Evidence suggests that the Harappans had a clear understanding of their gods and religious practices. |
|
Card: 36 / 62 |
False - The religious beliefs of the Harappans remain unclear due to the undeciphered script. |
|
Card: 39 / 62 |
The Harappans primarily used weights that were multiples of ___ for their weighing systems. |
|
Card: 41 / 62 |
True or False: The tradition of using 16 annas to make one rupee has been completely abandoned in modern Indian currency. |
|
Card: 43 / 62 |
The Harappans were skilled in pottery and utilized ___ for creating various designs. |
|
Card: 45 / 62 |
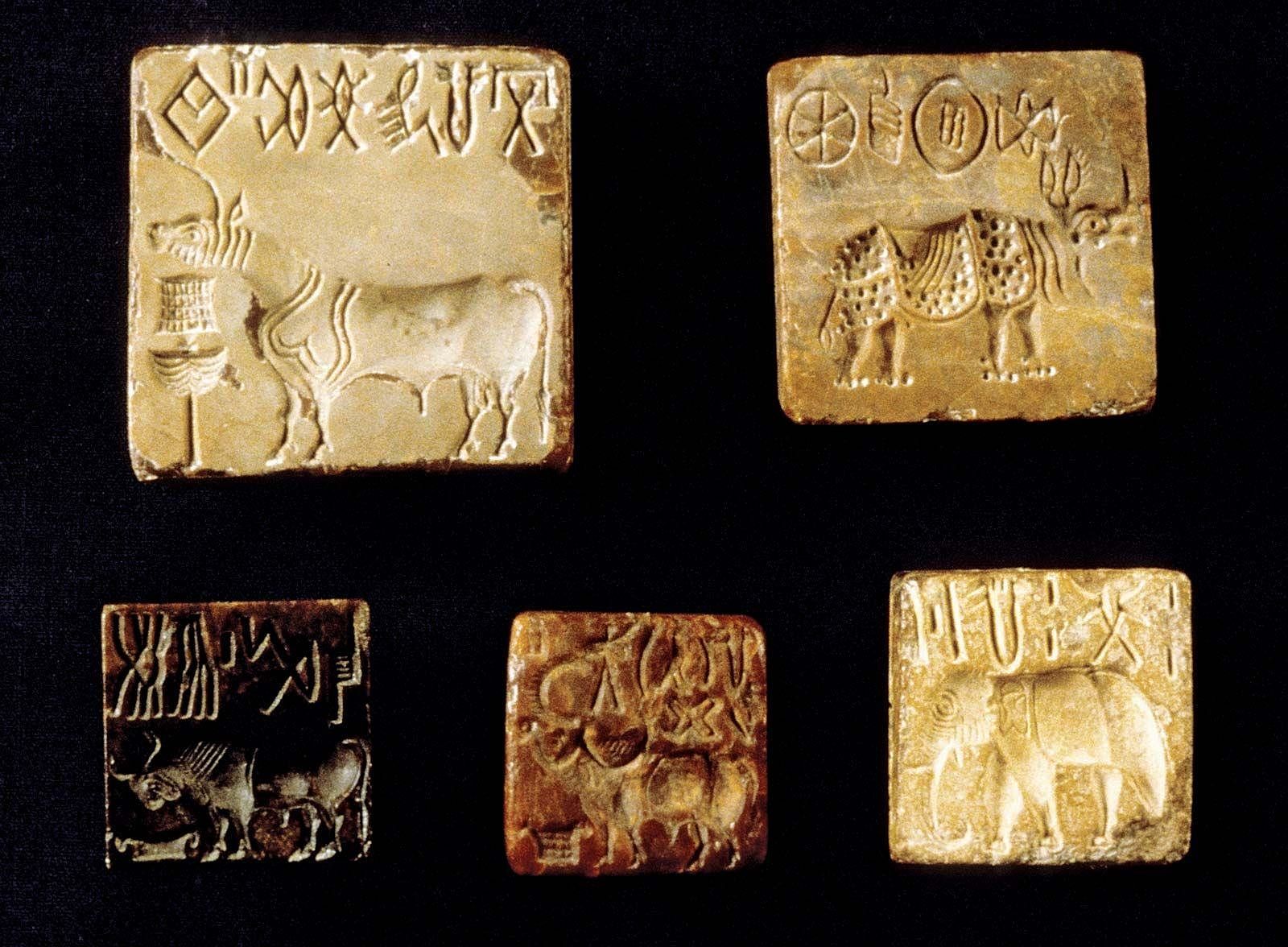
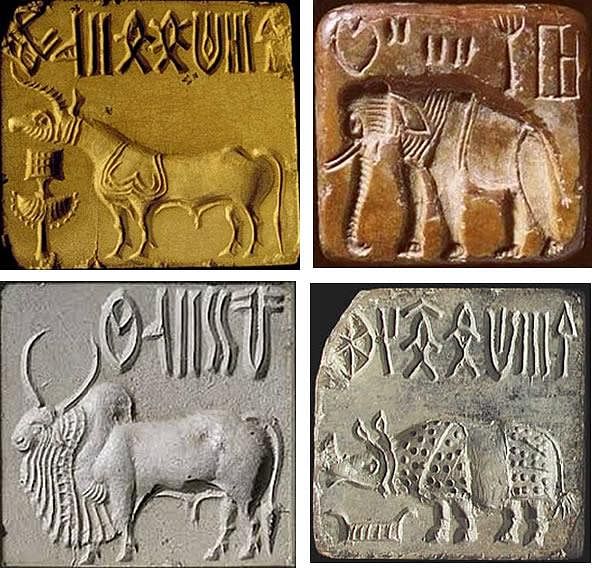
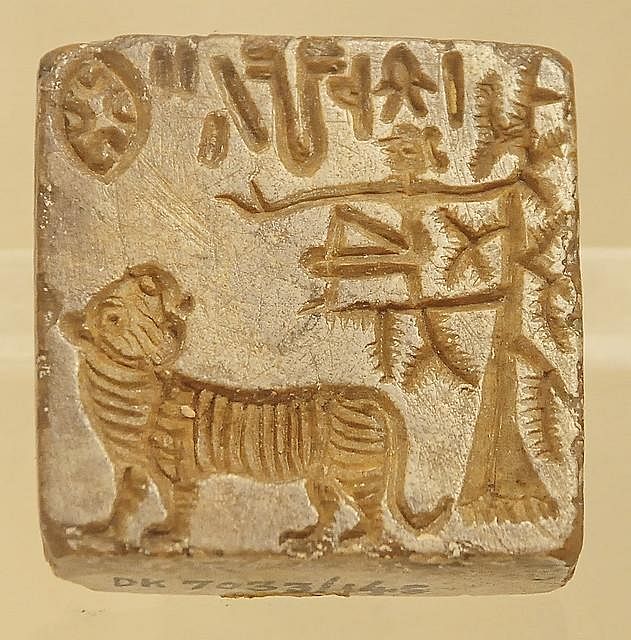
Fill in the blank: Harappan seals often feature images of various animals including the one-horned bull, the buffalo, and the ___. |
|
Card: 48 / 62 |
They represent some of the greatest artistic creations of the Harappan culture, often featuring inscriptions and images of animals. |
|
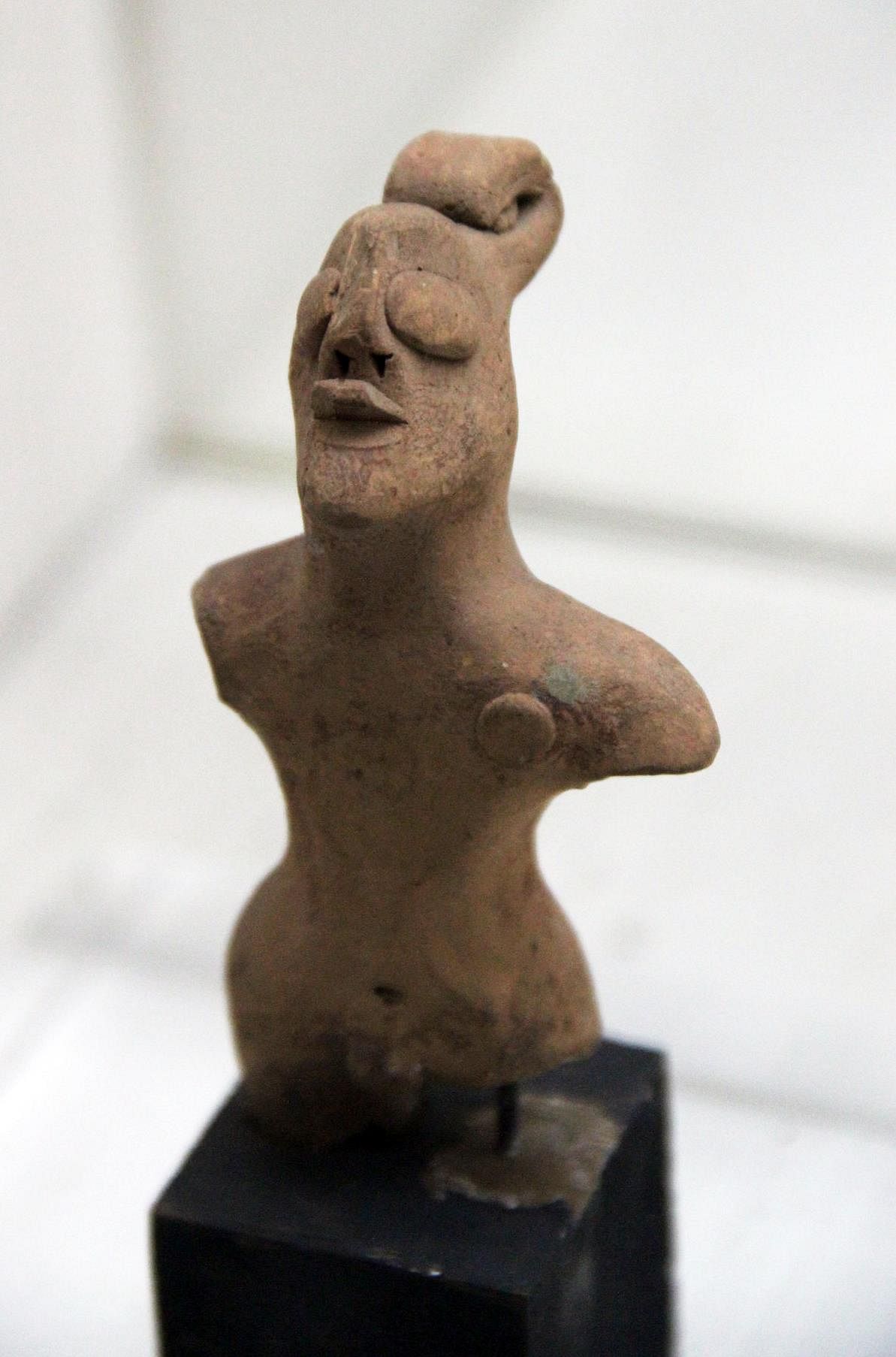
Card: 49 / 62 |
Terracotta figurines in the Harappan culture served as both ___ and ___ objects. |
|
Card: 53 / 62 |
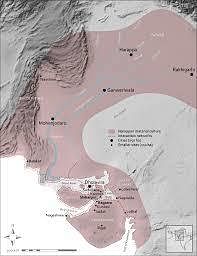
The area described extends from Jammu in the north to the Narmada estuary in the south, covering approximately ___ square kilometers. |
|
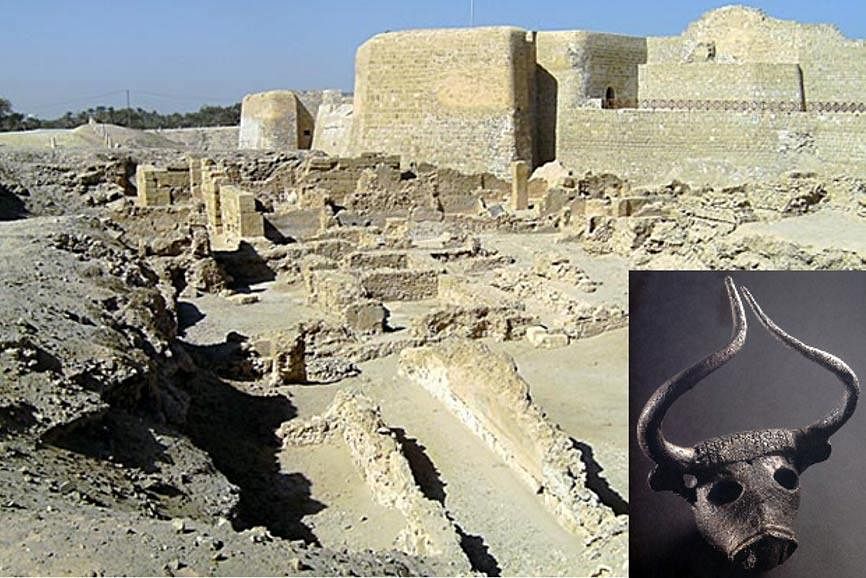
Card: 57 / 62 |
The Mesopotamian texts refer to two intermediate trading stations called ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 59 / 62 |
About how many seals have been found that carry short inscriptions with pictographs? |
|
Card: 61 / 62 |
The Indus Valley Civilization is also known as the ___ civilization because the first archaeological site was found at Harappa. |