|
Card: 2 / 50 |
A constitution restricts government power and guarantees a democratic system where individuals have certain rights.  |
|
Card: 3 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Legal intervention is crucial in rectifying violations of rights as demonstrated by key cases in ___'s history. |
|
Card: 5 / 50 |
True or False: The right against exploitation is not considered a fundamental right in most democratic nations. |
|
Card: 6 / 50 |
False. The right against exploitation is a fundamental right in many democratic nations.  |
|
Card: 7 / 50 |
Riddle: I can be violated but I am essential for justice, I protect you from unfair treatment. What am I? |
|
Card: 9 / 50 |
What was the outcome of the Asian Games Construction case regarding workers' rights? |
|
Card: 10 / 50 |
The Supreme Court ruled in favor of the workers, directing the government to pay them the prescribed minimum wages. |
|
Card: 11 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The case of Machal Lalung highlighted the right to '___ and ___'. |
|
Card: 14 / 50 |
A Bill of Rights ensures that individual rights are recognized and protected by the government, providing remedies when those rights are violated.  |
|
Card: 15 / 50 |
Multiple Choice: Which of the following rights is emphasized in the Indian Constitution? A) Right to Privacy B) Right against Exploitation C) Right to Bear Arms D) Right to Vote |
|
Card: 18 / 50 |
The government must ensure that individual rights are not violated by any of its organs or by other persons or organizations. |
|
Card: 19 / 50 |
What is the significance of the Motilal Nehru Committee's demand for a bill of rights in 1928 in the context of Indian democracy? |
|
Card: 20 / 50 |
The Motilal Nehru Committee's demand highlighted the importance of protecting individual rights, which laid the groundwork for the inclusion of fundamental rights in the Indian Constitution after independence.  |
|
Card: 21 / 50 |
Fundamental rights in the Indian Constitution differ from ordinary legal rights in that they are ___ and can only be changed by ___ . |
|
Card: 23 / 50 |
True or False: Fundamental rights in India are absolute and cannot be restricted by the government. |
|
Card: 24 / 50 |
False; Fundamental rights are not absolute and the government can impose reasonable restrictions on their exercise. 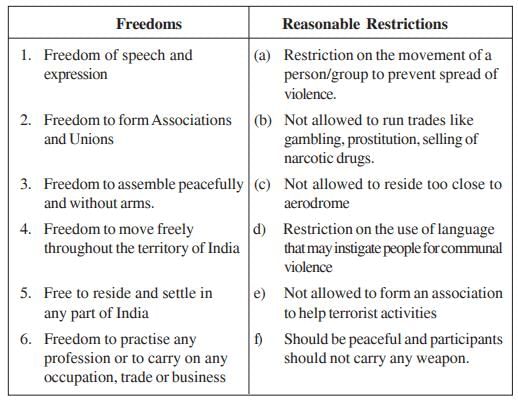 |
|
Card: 25 / 50 |
What role does the judiciary play in the protection of fundamental rights in India? |
|
Card: 26 / 50 |
The judiciary has the power to protect fundamental rights and can declare government actions illegal if they violate or unreasonably restrict these rights. 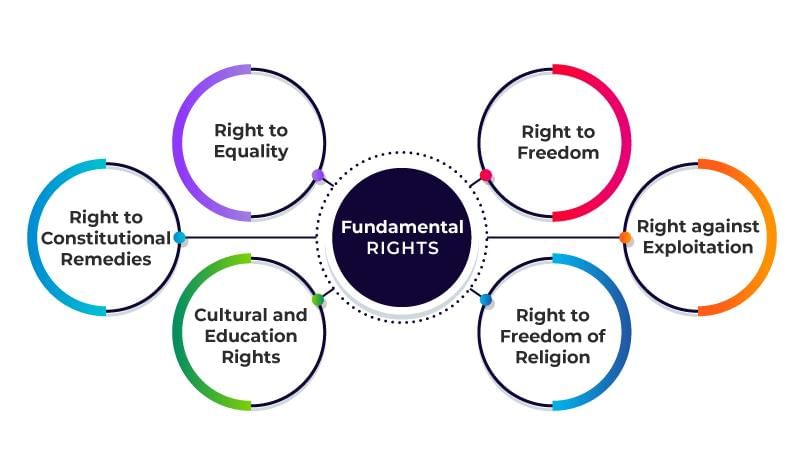 |
|
Card: 27 / 50 |
Riddle: I am a cornerstone of democracy, protecting individuals from discrimination based on many factors. What am I? |
|
Card: 33 / 50 |
Multiple Choice: Which of the following is NOT a right protected by the South African Constitution? A) Right to adequate housing B) Right to travel freely C) Right to health care D) Right to fair labor practices |
|
Card: 36 / 50 |
The Constitutional Court is responsible for enforcing the rights enshrined in the South African Constitution.  |
|
Card: 37 / 50 |
True or False: The Bill of Rights in South Africa provides rights only to adults. |
|
Card: 40 / 50 |
It prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.  |
|
Card: 41 / 50 |
The abolition of untouchability in India means ___ and forbids its practice in any form. |
|
Card: 43 / 50 |
True or False: The Right to Equality guarantees equal access to public places regardless of socio-economic status. |
|
Card: 44 / 50 |
False. It ensures equal access without discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.  |
|
Card: 45 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Article 16 (4) allows for the reservation of appointments for any ___ class of citizens. |
|
Card: 47 / 50 |
Riddle: I protect life and personal liberty, but can only be taken away by a legal process. What am I? |
|
Card: 50 / 50 |
It empowers the judiciary to declare government actions illegal if they violate fundamental rights. 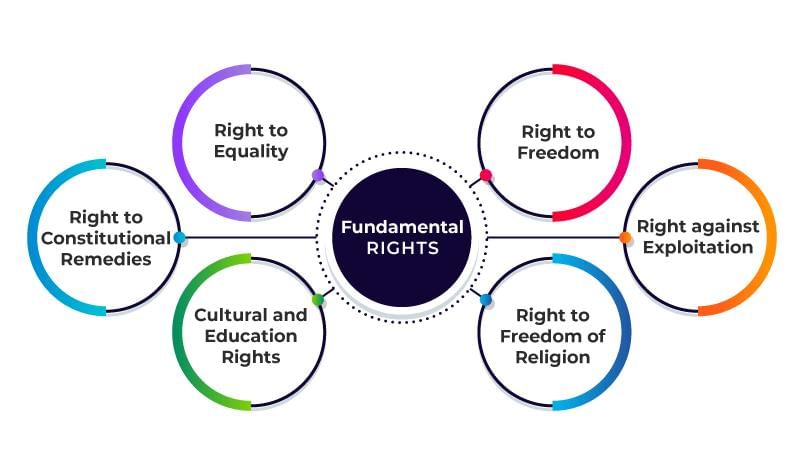 |




























