|
What is inter-religious domination, and provide an example of its impact in India? |
Card: 1 / 28 |
|
It is the dominance of one religious group over others, which can lead to discrimination or social tension; for example, communal riots in India.  |
Card: 2 / 28 |
|
True or False: |
Card: 3 / 28 |
|
False. |
Card: 4 / 28 |
|
It enforces strict interpretations and hierarchies within a religion, marginalising certain groups or sects. |
Card: 6 / 28 |
|
What significant event took place during the post-Godhra riots in Gujarat in 2002, and what was its aftermath? |
Card: 7 / 28 |
 |
Card: 8 / 28 |
|
Dalits have faced discrimination, such as being barred from entering Hindu temples and being treated inhumanely by upper castes.  |
Card: 10 / 28 |
|
True or False: |
Card: 11 / 28 |
|
False. |
Card: 12 / 28 |
|
The state structure plays a crucial role in preventing inter-community conflicts and promoting harmony among different religious groups.  |
Card: 14 / 28 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Working together for mutual enlightenment through education to change people's mindsets. |
Card: 16 / 28 |
|
|
Card: 17 / 28 |
|
It implies that Religion and government operate independently; state decisions are not based solely on religious beliefs. |
Card: 18 / 28 |
|
|
Card: 21 / 28 |
|
To ensure that neither dictates or interferes with the decisions and authority of the other. |
Card: 22 / 28 |
|
A) Promote religion B) Fund religious schools C) Do not interfere unless the law is broken D) Decide who can practice a religion |
Card: 23 / 28 |
|
Indian secularism emphasises inter-religious equality and does not solely focus on the separation of church and state. 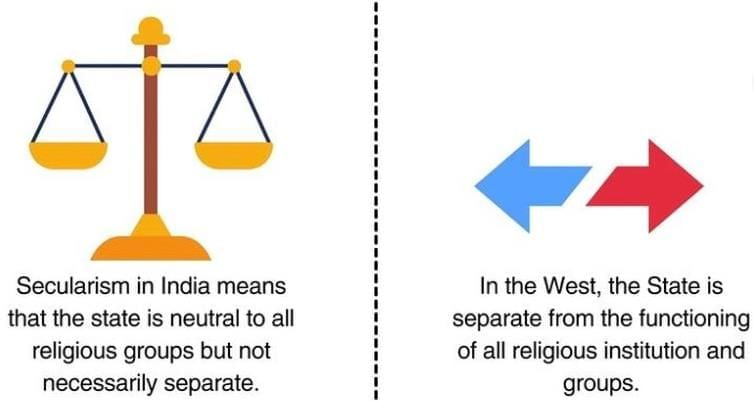 |
Card: 26 / 28 |
|
Indian secularism only protects the rights of individuals and not of minority communities. |
Card: 27 / 28 |























