|
What are the two main categories of security concepts discussed in contemporary security frameworks? |
Card: 1 / 50 |
|
Traditional security, which includes military and national defense, and non-traditional security, which encompasses economic, environmental, and social issues. 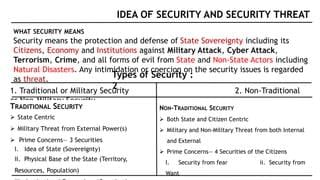 |
Card: 2 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blanks: Security is freedom from serious threats, focusing on threats to ___ values that may vary across ___ and communities. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
True or False: The concept of security remains static and does not evolve over time. |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
Riddle: I can be a threat that is not a soldier, but can cause fear and chaos. What am I? |
Card: 7 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Economic stability, environmental sustainability, and social justice are aspects of ___ security. |
Card: 11 / 50 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which of the following is NOT considered a non-traditional threat in security? A) Climate Change B) Military Invasion C) Cyber-Attacks D) Economic Crisis |
Card: 15 / 50 |
|
What are the three basic responses of governments to military threats from other nations? |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The concept of ___ is crucial for assessing potential threats between countries. |
Card: 19 / 50 |
|
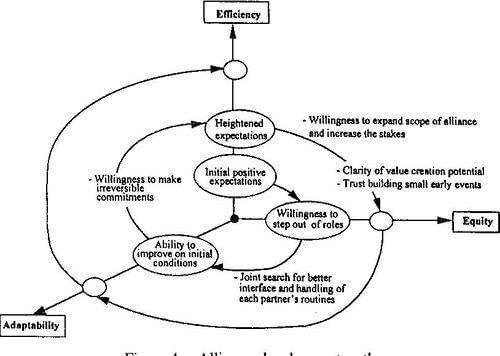
True or False: Alliance building is irrelevant in the context of national security. |
Card: 21 / 50 |
|
False. Alliance building is important for enhancing collective security against military threats. |
Card: 22 / 50 |
|
Riddle: I can be a friend or a foe, depending on how power flows. What am I in terms of national security? |
Card: 23 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Deterrence aims to make the cost of war unacceptable to potential aggressors to prevent attacks.  |
Card: 26 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: A powerful neighbor may pose a future threat, making it essential to maintain a favorable ___ of ___ between nations. |
Card: 27 / 50 |
|
Multiple Choice: What is a primary focus of traditional national security? A) Environmental threats B) Military threats from other countries C) Economic stability D) Cybersecurity |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
Major powers, feeling secure internally, shifted their focus from internal security to external threats.  |
Card: 34 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Internal conflicts now constitute over ___% of armed conflicts worldwide. |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
True or False: The United Nations acts as a central authority with full power over member states. |
Card: 37 / 50 |
|
What were the two primary types of threats faced by newly independent nations in the post-WWII context? |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
Riddle: I thrive in the absence of order and can lead to great strife; nations fear my presence more than external life. What am I? |
Card: 41 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Cold War created intense rivalry between the ___ and ___ blocs. |
Card: 43 / 50 |
|
What security challenges did colonial powers face during the post-WWII period? |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
Multiple Choice: What was a major consequence of the Cold War for Third World countries? A) Economic prosperity B) Increased civil wars C) Global disarmament D) Cultural exchange |
Card: 47 / 50 |
|
What are the primary justifiable reasons for countries to go to war according to traditional security views? |
Card: 49 / 50 |
|
Countries should only go to war for justifiable reasons such as self-defense or protecting others from genocide.  |
Card: 50 / 50 |