|
Card: 1 / 50 |
What were the three parts into which India was divided at the time of independence? |
|
Card: 3 / 50 |
The challenge of establishing democracy in India involved ensuring that democratic practices matched ___ outlined in the Constitution. |
|
Card: 5 / 50 |
True or False: The Constitution of India prioritizes economic development only for the majority communities. |
|
Card: 6 / 50 |
False. The Constitution emphasizes equality and provides special protection for socially disadvantaged and minority communities. 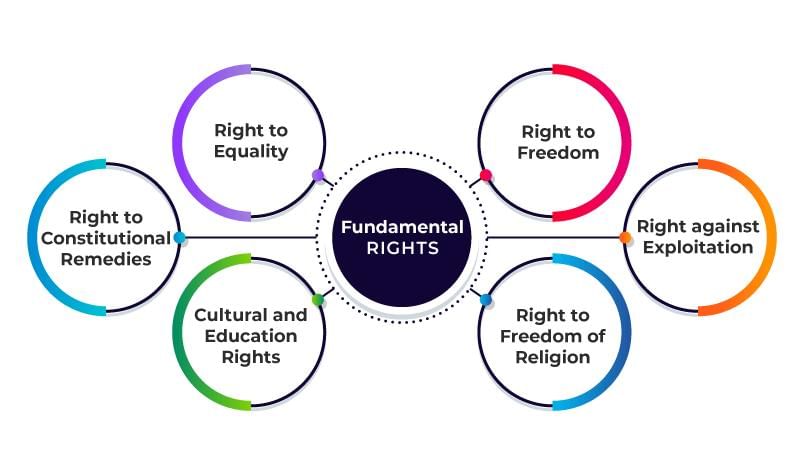 |
|
Card: 7 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: One of the major challenges of nation-building after independence was ___ a united India. |
|
Card: 9 / 50 |
Riddle: I was delivered at the stroke of midnight on August 15, 1947, and spoke of a new destiny for a nation. What am I? |
|
Card: 11 / 50 |
What was the primary goal of the Directive Principles of State Policy in the Indian Constitution? |
|
Card: 16 / 50 |
The primary ideological basis was the Muslim League's 'two-nation theory,' which argued that India consisted of two distinct peoples, Hindus and Muslims, necessitating a separate Muslim state.  |
|
Card: 17 / 50 |
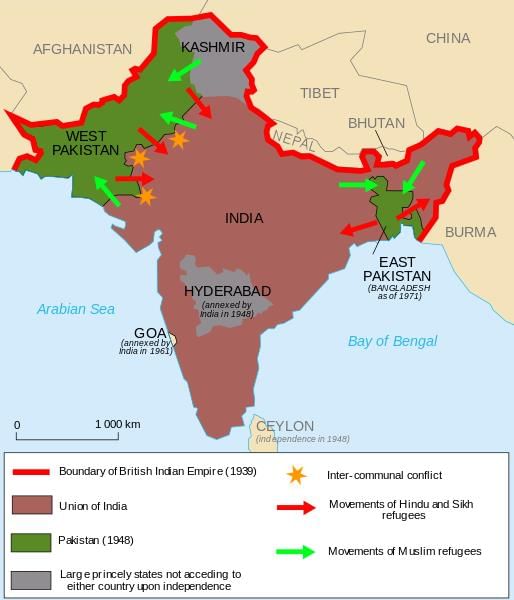
Fill in the blank: The partition of British India resulted in the formation of two independent nations, ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 19 / 50 |
True or False: The partition of Punjab and Bengal was based on cultural and linguistic boundaries rather than religious majorities. |
|
Card: 21 / 50 |
What were the significant geographical challenges faced during the partition of British India? |
|
Card: 22 / 50 |
There was no single Muslim-majority region, leading to the creation of Pakistan with two separate areas: West Pakistan and East Pakistan, which were separated by Indian territory. 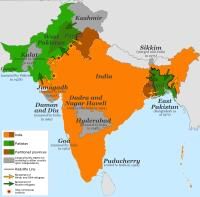 |
|
Card: 23 / 50 |
Riddle: I caused millions to flee and changed borders overnight, creating two nations where once there was one. What am I? |
|
Card: 25 / 50 |
What were the immediate consequences of the mass population transfer during the partition in 1947? |
|
Card: 26 / 50 |
The immediate consequences included widespread communal violence, displacement of millions, and the establishment of refugee camps where many minorities found temporary shelter.  |
|
Card: 27 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Many Hindus and Sikhs in Pakistan and Muslims in India found themselves ___ during the partition. |
|
Card: 29 / 50 |
What role did local opposition play in the partition process, particularly regarding the North-West Frontier Province? |
|
Card: 30 / 50 |
Local opposition, notably from Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan, highlighted that not all Muslim-majority areas wanted to join Pakistan; however, his opposition was ignored, and the province was included in Pakistan.  |
|
Card: 32 / 50 |
Women were often abducted, raped, attacked, and killed, and many were forcefully converted to other religions.  |
|
Card: 35 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The Instrument of Accession was a Memorandum of Understanding prepared for the ___ of the princely states into the Indian Union. |
|
Card: 37 / 50 |
True or False: The political and administrative machinery functioned effectively on both sides during the Partition. |
|
Card: 39 / 50 |
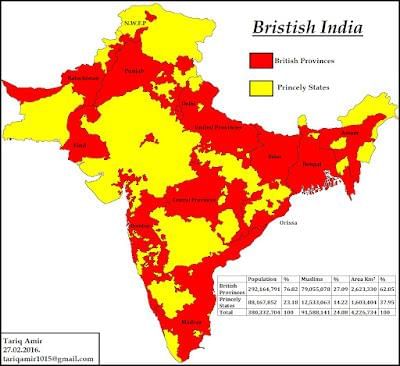
What was the primary concern of the Indian government regarding the princely states after independence? |
|
Card: 40 / 50 |
The consolidation of the territorial boundaries of the nation had assumed supreme importance.  |
|
Card: 41 / 50 |
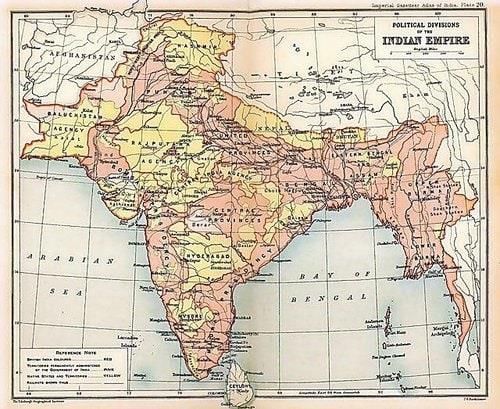
Riddle: I cover one-third of a land but govern myself under British rule; what am I? |
|
Card: 43 / 50 |
Short Answer: How many princely states were there immediately after independence? |
|
Card: 47 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: An estimated ___ to ___ people were killed during the violence of the Partition. |
|
Card: 49 / 50 |
Multiple Choice: What were the three considerations guiding the government's approach to the princely states? A) Economic stability, B) Public sentiment, C) Territorial consolidation, D) Military strength. |