|
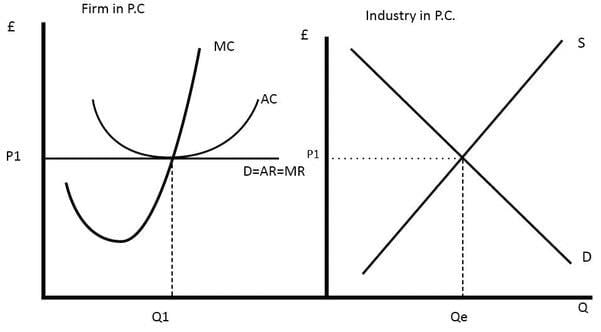
A large number of buyers and sellers compete for the same products at the same price, with firms having no ability to influence market prices. 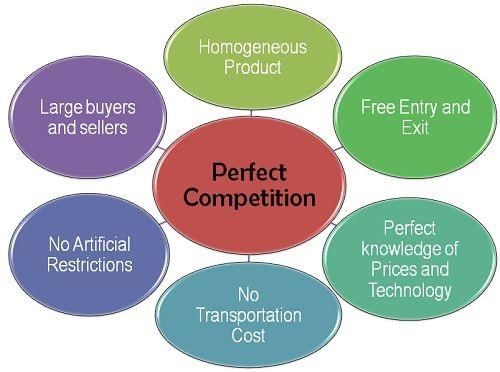 |
Card: 2 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: In perfect competition, firms are considered ___ because they cannot influence the market price. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
True or False: In a perfectly competitive market, individual firms can set their own prices for the products they sell. |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
False. Individual firms cannot set their own prices; they must accept the market price. 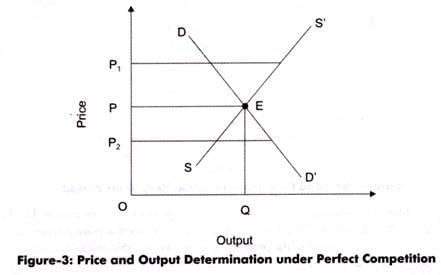 |
Card: 6 / 50 |
|
What does 'perfect knowledge about the markets' imply for consumers and producers? |
Card: 7 / 50 |
|
It implies that both consumers and producers have all the relevant information about prices and products, preventing price discrepancies and aiding in achieving market equilibrium. 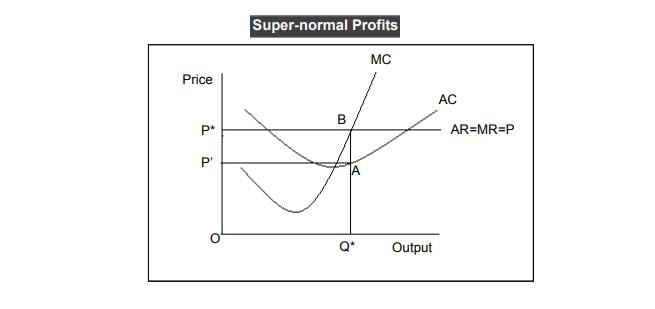 |
Card: 8 / 50 |
|
Riddle: I am a market where many sellers sell the same product, and no seller can change my price. What am I? |
Card: 9 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The factors of production in a perfectly competitive market are ___ and can be easily transferred from one firm to another. |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
What happens to market supply and price when new firms enter a perfectly competitive market earning abnormal profits? |
Card: 15 / 50 |
|
Market supply increases, leading to a decrease in market price and a reduction in profits. |
Card: 16 / 50 |
|
True or False: In a perfectly competitive market, firms can earn long-term abnormal profits. |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
False. Firms can only earn normal profits in the long run due to free entry and exit. |
Card: 18 / 50 |
|
Firms will exit the market, which decreases market supply, causing the market price to rise until losses are eliminated. |
Card: 20 / 50 |
|
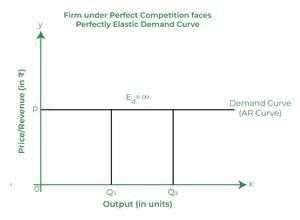
In a perfectly competitive market, the price line is represented as ___ because firms cannot influence the market price. |
Card: 21 / 50 |
|
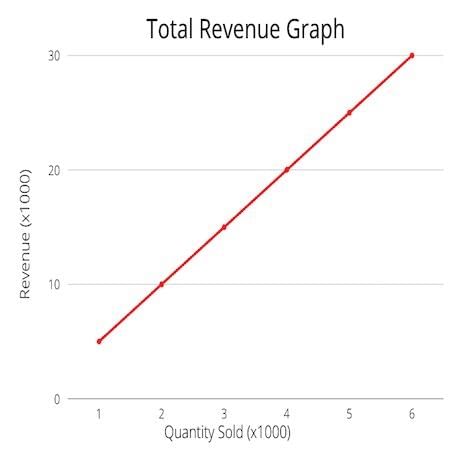
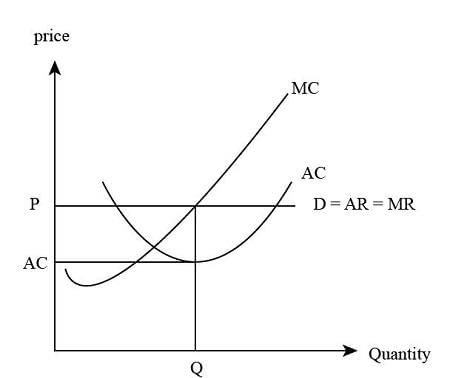
Total Revenue (TR) is calculated using the formula ___ where p represents price and q represents quantity. |
Card: 23 / 50 |
|
True or False: In a perfectly competitive market, marginal revenue (MR) is always less than the price. |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
False. In a perfectly competitive market, marginal revenue is equal to the price. 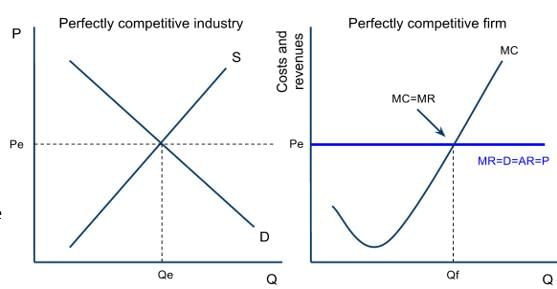 |
Card: 26 / 50 |
|
What is the significance of the total revenue curve in relation to a firm's total cost curve? |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
It helps determine economic profit and the profit-maximizing level of production. 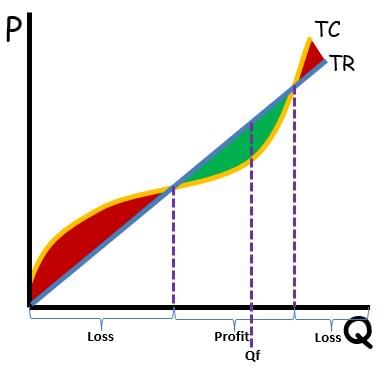 |
Card: 30 / 50 |
|
What happens to the overall demand for a firm's product if it attempts to raise its price above the market level in a perfectly competitive market? |
Card: 33 / 50 |
|
In a perfectly competitive market, the relationship between price and marginal revenue can be expressed as MR = ___ . |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
True or False: A break-even point occurs when total revenue is greater than total cost. |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
Marginal revenue (MR) must equal marginal cost (MC), and MC must be rising or cut MR from below. |
Card: 42 / 50 |
|
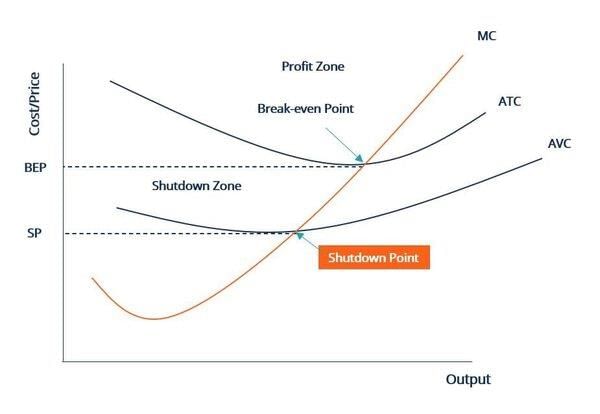
Fill in the blank: The shutdown point is defined as when ___ equals ___ or average revenue equals average variable cost. |
Card: 43 / 50 |
|
Riddle: I define a condition where a company has no profit and no loss. What am I? |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
A supply schedule is a table that shows the quantities of a commodity that a firm is willing to sell at different prices, assuming constant technology and factor prices. 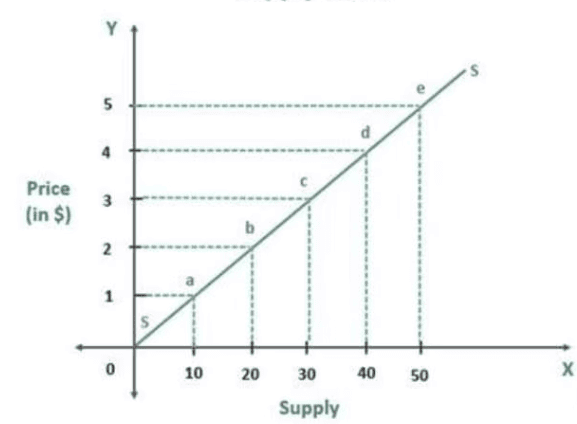 |
Card: 48 / 50 |
|
The supply curve depicts the quantities of output a firm chooses to produce in response to varying market prices. |
Card: 50 / 50 |