|
A market is defined as an entire area where buyers and sellers of a commodity interact, allowing for sales and purchases, without the necessity of a physical location or face-to-face contact. |
Card: 2 / 46 |
|
True or False: In a perfect competition market, a single seller can influence the market price significantly. |
Card: 3 / 46 |
|
False. In perfect competition, a single seller cannot influence the market price due to the large number of buyers and sellers, making each participant a price-taker. |
Card: 4 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: Perfect competition is characterized by a large number of buyers and sellers selling ___ goods at a ___ uniform price. |
Card: 5 / 46 |
|
What is the implication of having a large number of buyers and sellers in perfect competition? |
Card: 7 / 46 |
|
The implication is that no individual buyer or seller has enough market power to influence the price, leading to uniform prices set by the forces of demand and supply. |
Card: 8 / 46 |
|
Riddle: I exist where many compete, selling the same treat. No one controls the price, and everyone pays the same slice. What am I? |
Card: 9 / 46 |
|
What type of products are sold in a market characterized by perfect competition? |
Card: 11 / 46 |
|
Homogeneous products, meaning the goods are identical in nature and can be substituted for one another. |
Card: 12 / 46 |
|
True or False: Perfect knowledge in a market leads to firms having cost advantages. |
Card: 17 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: A seller cannot charge high prices for homogenous goods because buyers can ___ the product from another seller. |
Card: 19 / 46 |
|
Riddle: I am a market condition where firms can enter or exit freely without barriers. What am I? |
Card: 21 / 46 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
It allows resources to move freely to where they are most needed, ensuring efficiency.  |
Card: 24 / 46 |
|
What is the result of buyers having perfect knowledge about the product market? |
Card: 25 / 46 |
|
What is the implication of free entry and exit in a perfectly competitive market regarding the supply of commodities? |
Card: 27 / 46 |
|
The market supply of the commodity and factors of production are equal in all parts of the market, preventing shortages in some areas and excesses in others. |
Card: 28 / 46 |
|
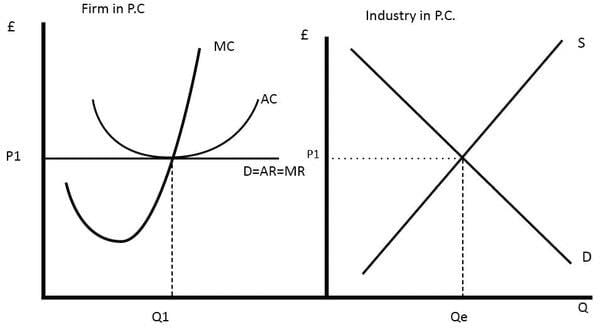
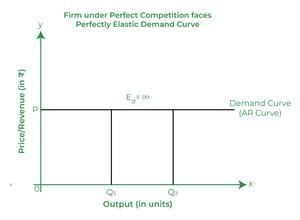
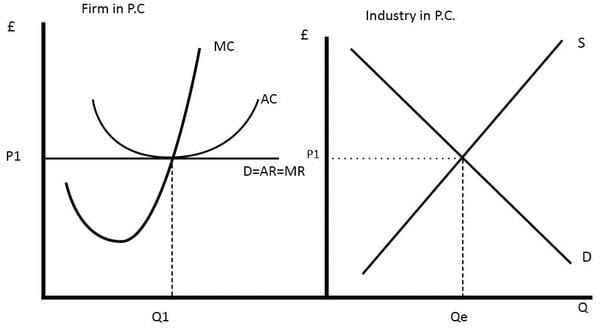
Fill in the blank: The demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is parallel to the ___-axis. |
Card: 29 / 46 |
|
True or False: In a perfectly competitive market, firms are price makers who can set the price for their products. |
Card: 31 / 46 |
|
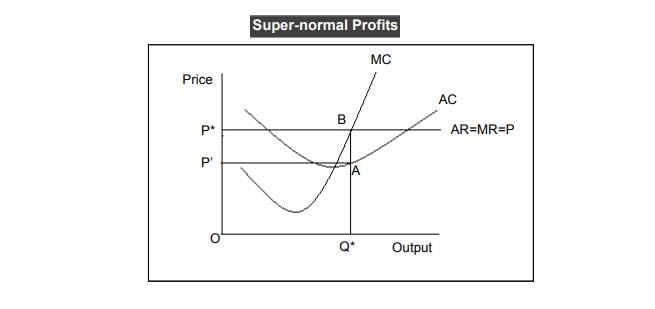
What happens to firms in a perfectly competitive market when they earn abnormal profits in the short run? |
Card: 33 / 46 |
|
New firms are attracted to enter the industry due to the high market price and potential for profit. |
Card: 34 / 46 |
|
Riddle: I have no walls, I allow resources to flow freely, and I ensure no transportation costs burden my firms. What am I? |
Card: 35 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: In a perfectly competitive market, every additional unit is sold at the prevailing price, which means ___ = ___ = ___ for the firm. |
Card: 37 / 46 |
|
Explain why there cannot be a shortage of commodities in a perfectly competitive market. |
Card: 39 / 46 |
|
Due to free entry and exit, resources move to where they are most rewarded, ensuring that supply meets demand across the market.  |
Card: 40 / 46 |
|
How does the assumption of no extra transportation costs affect the production process in a perfectly competitive market? |
Card: 41 / 46 |
|
It allows firms to operate without the burden of additional costs, thereby enhancing efficiency and potentially lowering prices for consumers. 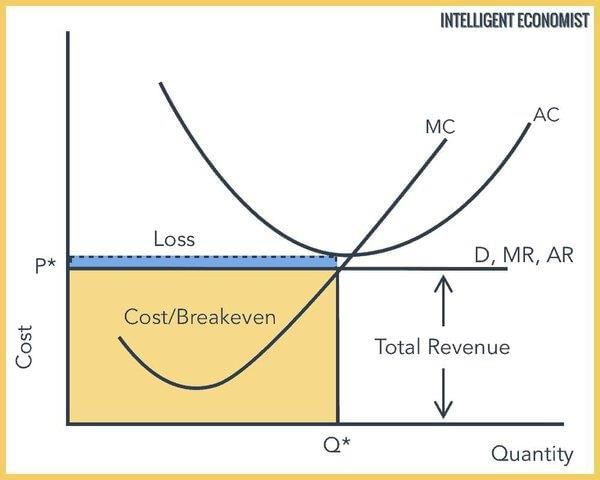 |
Card: 42 / 46 |
|
In a competitive market, the entry of more firms generally leads to ___ in product prices and ___ in factor prices such as rent and wages. |
Card: 43 / 46 |
|
What happens to abnormal profits in the long run when firms can freely enter and exit a market? |
Card: 45 / 46 |
|
Abnormal profits will be driven to zero as firms enter the market, increasing supply and lowering prices until only normal profits are earned. 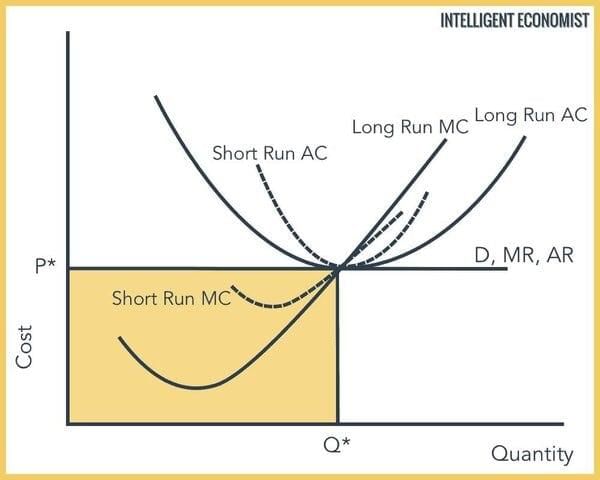 |
Card: 46 / 46 |