|
The primary functions of money in an economy are as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value. |
Card: 2 / 50 |
|
Money simplifies exchanges by eliminating the need for ___, which is a requirement in barter systems. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
True or False: Money must be easily convertible and universally accepted to serve as a store of value. |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Money provides a standard measure for valuing goods and services, known as a ___ of account. |
Card: 7 / 50 |
|
Inflation can erode money's purchasing power, making it less effective as a store of value. |
Card: 10 / 50 |
|
I am a concept that allows you to trade goods without needing to find someone who wants what you have. What am I? |
Card: 11 / 50 |
|
Which function of money allows individuals to express the relative value of different goods, such as valuing a wristwatch at Rs 500? |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
What makes money more convenient than other assets like gold or property for storing value? |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
A cashless economy relies on digital transactions, using digital money transfers instead of physical currency. |
Card: 22 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Indian government's financial reforms aim for greater inclusion through ___ accounts, ___ enabled payment systems, and e-wallets. |
Card: 23 / 50 |
|
True or False: The central bank is not essential for the supply of money in a modern economy. |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
False: The central bank is crucial for the supply of money in a modern economy. |
Card: 26 / 50 |
|
As income increases, people engage in more transactions, thus increasing their demand for money. |
Card: 28 / 50 |
|
Riddle: I am needed for transactions, but my value can change with interest rates. What am I? |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
When interest rates rise, people prefer to earn interest rather than hold cash, leading to a decrease in their demand for money. 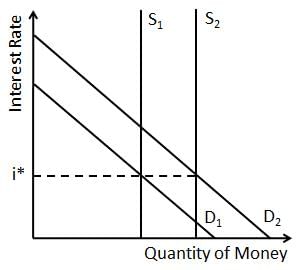 |
Card: 32 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), established in 1935, is India's ___ bank. |
Card: 33 / 50 |
|
What are the two types of institutions that create the supply of money in an economy? |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
To issue currency and control the money supply through methods like adjusting the bank rate and reserve ratios. |
Card: 38 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Commercial banks earn profit by charging borrowers a higher interest rate than they pay to ___ on deposits. |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
True or False: Banks can lend out all the money they receive in deposits without any restrictions. |
Card: 41 / 50 |
|
False. Banks must keep a portion of deposits to ensure they can meet withdrawal demands. |
Card: 42 / 50 |
|
Riddle: I hold your money safe and sound, but I do not spend a dime. I help you make transactions with ease, what am I? |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The difference between the interest rate charged to borrowers and the interest rate paid to depositors is known as the ___. |
Card: 47 / 50 |
|
The availability of funds for withdrawals and the safety of storing money in banks. |
Card: 50 / 50 |





















