|
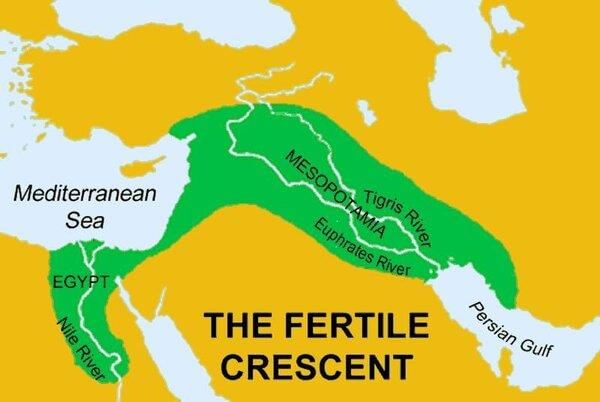
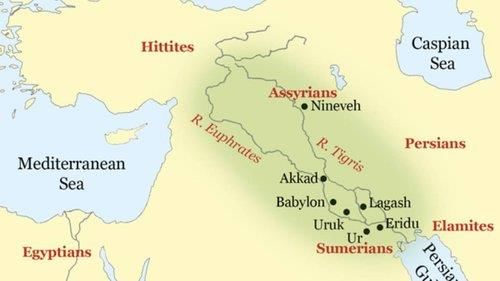
Fill in the blank: After 2000 BCE, the southern region of Mesopotamia became known as ___. |
Card: 5 / 48 |
|
What was the significance of Mesopotamia's writing system in relation to other kingdoms? |
Card: 11 / 48 |
|
It allowed communication between kingdoms in the region and with the Pharaoh of Egypt.  |
Card: 12 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The urbanized south of Mesopotamia was originally called ___ and ___. |
Card: 13 / 48 |
|
Short Answer: Describe the impact of Babylon's rise on the nomenclature of southern Mesopotamia. |
Card: 15 / 48 |
|
As Babylon rose in importance after 2000 BCE, the southern region was referred to as Babylonia. |
Card: 16 / 48 |
|
What geographical features contributed to agricultural development in Mesopotamia? |
Card: 19 / 48 |
|
The fertile silt deposited by the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, along with natural and man-made irrigation channels, supported agriculture despite low rainfall.  |
Card: 20 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The primary crops cultivated in southern Mesopotamia included ___, ___, ___, and ___. |
Card: 21 / 48 |
|
True or False: Mesopotamia's agriculture was mainly dependent on high rainfall. |
Card: 23 / 48 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Which livestock were primarily raised in the steppe region of northern Mesopotamia? |
Card: 25 / 48 |
|
The Tigris tributaries offered routes to the Iranian mountains, facilitating trade and movement.  |
Card: 28 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The desert region of Mesopotamia is where the first ___ and ___ emerged. |
Card: 29 / 48 |
|
What are the key features that contribute to the interdependence of urban residents? |
Card: 33 / 48 |
|
Urban residents rely on each other's products and services, with specialization and division of labour being essential. For example, a stone seal carver relies on a bronze tool maker for tools, while the tool maker depends on others for metals and charcoal. |
Card: 34 / 48 |
|
Trade in Mesopotamia was crucial for acquiring resources that were scarce locally. What were some of the goods Mesopotamians traded? |
Card: 35 / 48 |
|
Mesopotamians traded textiles and agricultural produce for wood, copper, tin, silver, gold, shell, and stones from regions like Turkey and Iran, where minerals were abundant but agricultural capacity was limited.  |
Card: 36 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: Efficient urban functioning relies on organized trade and storage systems, which transport resources like ___ and ___ from various locations. |
Card: 37 / 48 |
|
True or False: The movement of goods into cities was primarily facilitated by land transport, which was the cheapest and most efficient method. |
Card: 39 / 48 |
|
False. While land transport was used, the cheapest and most efficient method was transport over water using river boats or barges.  |
Card: 40 / 48 |
|
Canals and natural channels served as major routes for transporting goods, with the Euphrates River being a key world route for trade between settlements. |
Card: 42 / 48 |
|
Division of labour enhances efficiency in urban economies by allowing individuals to specialize in specific tasks, making them dependent on each other for various products and services. |
Card: 44 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: Cities and towns thrive when the economy diversifies beyond food production to include ___, ___, and ___. |
Card: 45 / 48 |
|
The earliest Mesopotamian writings were primarily used to keep records of transactions, such as lists of goods in temples.  |
Card: 48 / 48 |