|
Card: 3 / 42 |
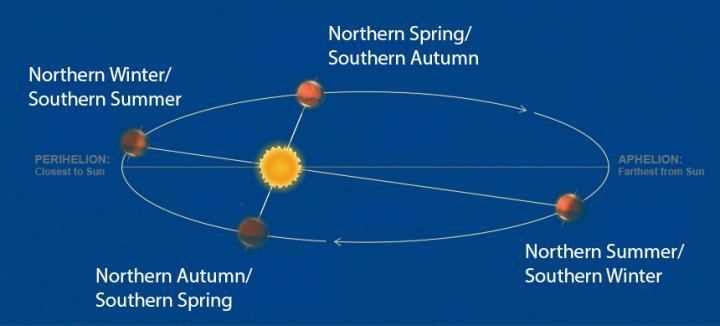
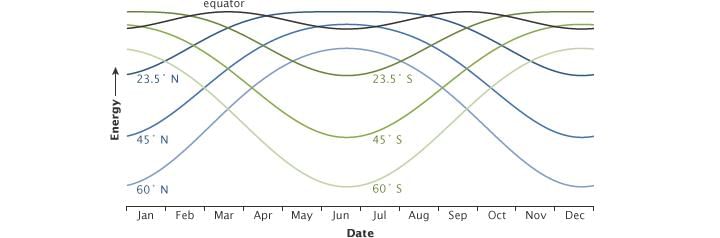
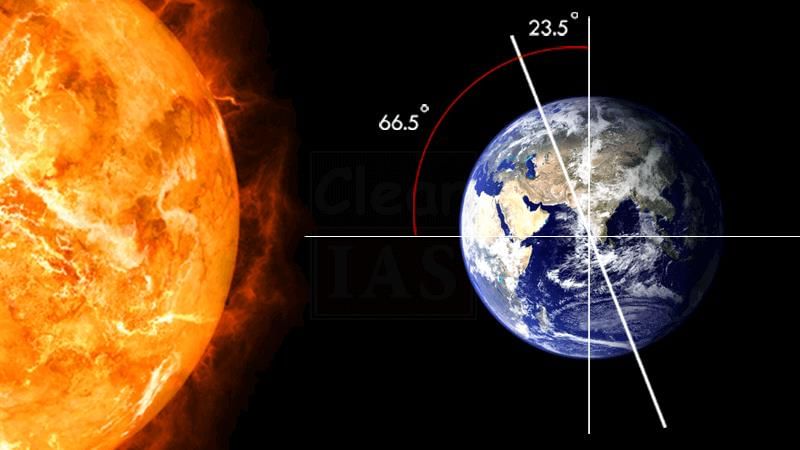
Fill in the blank: The insolation received at the surface varies from about ___ Watt/m² in the tropics to about ___ Watt/m² in the poles. |
|
Card: 5 / 42 |
True or False: The angle of inclination of the sun’s rays has no effect on the amount of insolation received at different latitudes. |
|
Card: 6 / 42 |
False. The angle of inclination of the sun's rays significantly affects the amount of insolation received at different latitudes. 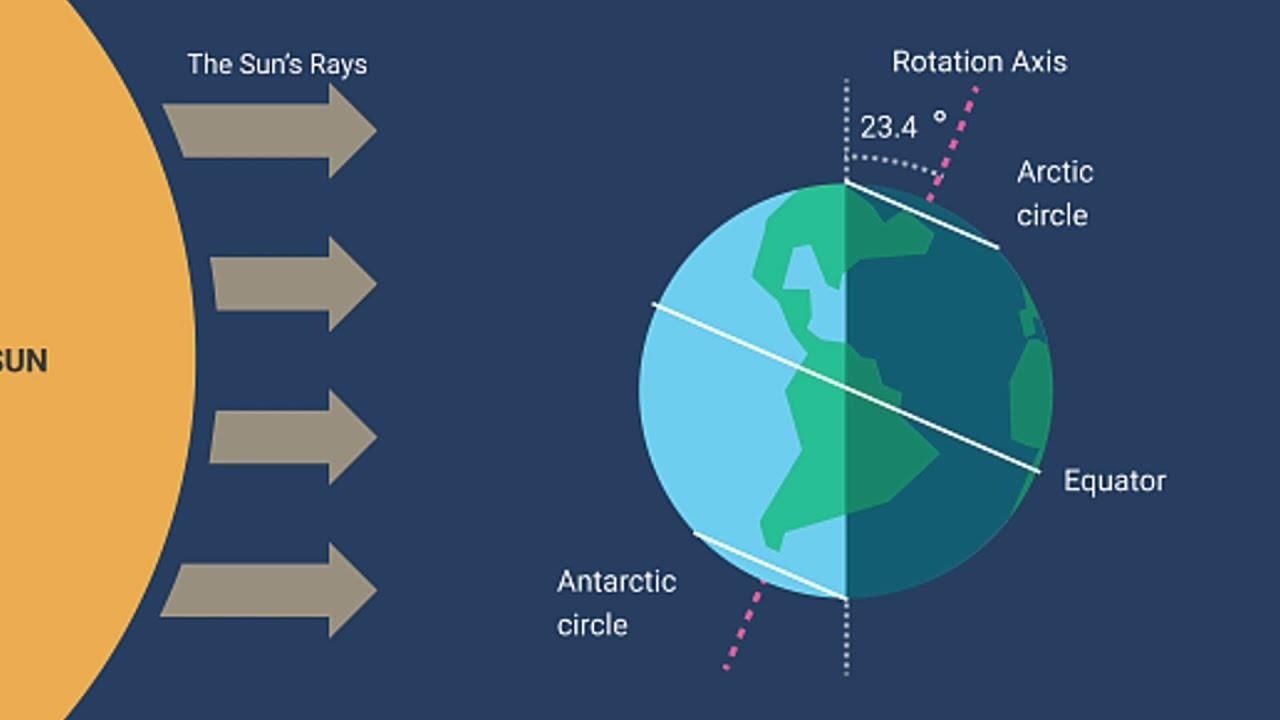 |
|
Card: 7 / 42 |
What is the primary reason for the color of the sky and the red color of the setting sun? |
|
Card: 8 / 42 |
The color of the sky and the red color of the setting sun are primarily due to the scattering of light by small suspended particles in the troposphere. 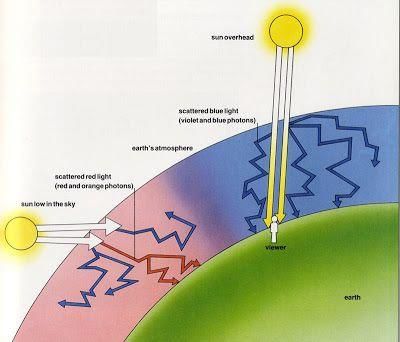 |
|
Card: 9 / 42 |
Fill in the blank: Maximum insolation is received over the ___, where cloudiness is the least. |
|
Card: 11 / 42 |
How does the amount of insolation received differ between continents and oceans at the same latitude? |
|
Card: 12 / 42 |
Generally, at the same latitude, the insolation is more over the continents than over the oceans. 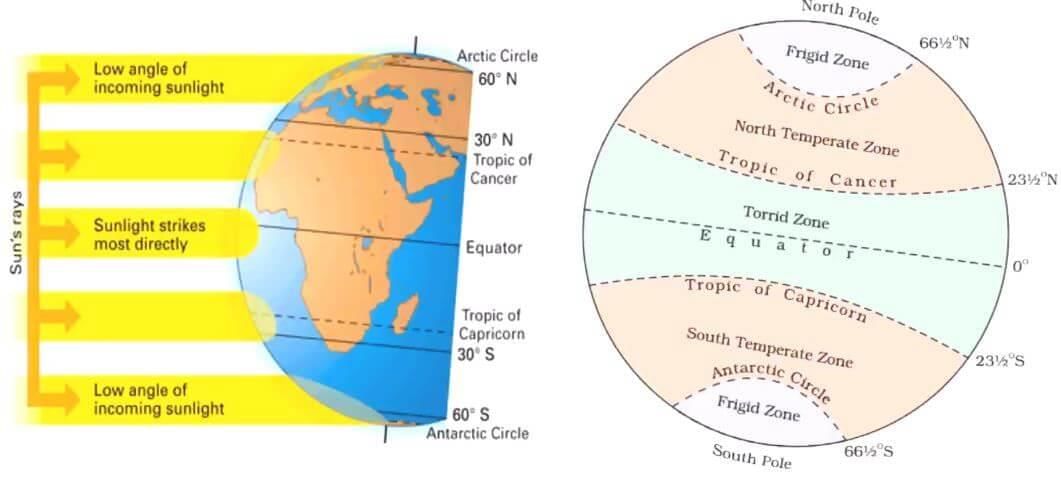 |
|
Card: 13 / 42 |
The process by which heat is transferred from one body to another when they are in contact is called ___. |
|
Card: 14 / 42 |
Conduction. Conduction occurs between two bodies at different temperatures, allowing energy to flow from the warmer to the cooler body. 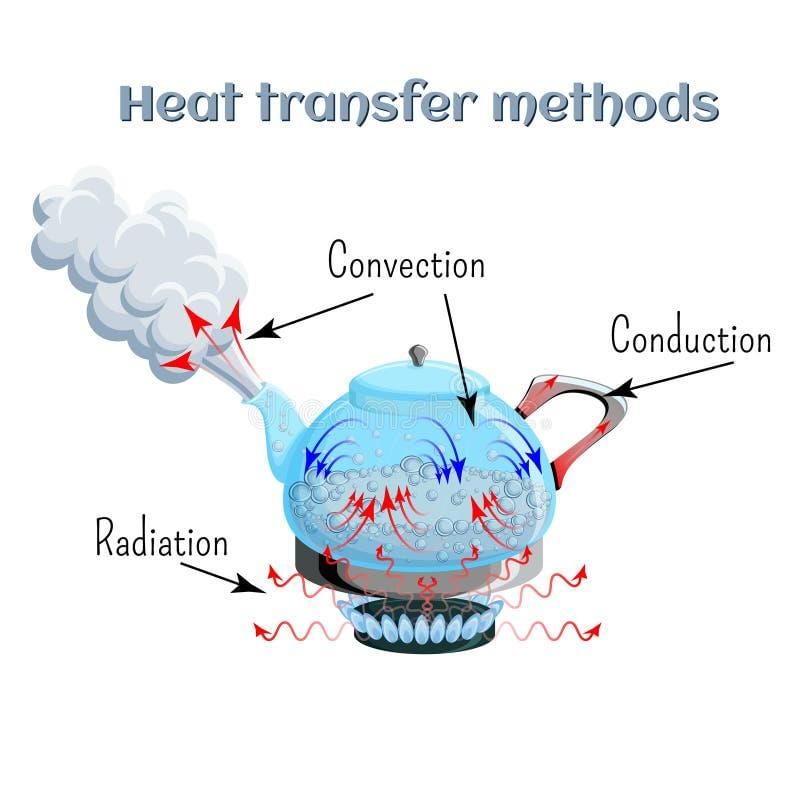 |
|
Card: 15 / 42 |
True or False: Convection is the horizontal movement of air that is less significant than vertical movement in the atmosphere. |
|
Card: 16 / 42 |
False. While horizontal movement is important, convection refers specifically to the vertical movement of air caused by heating. 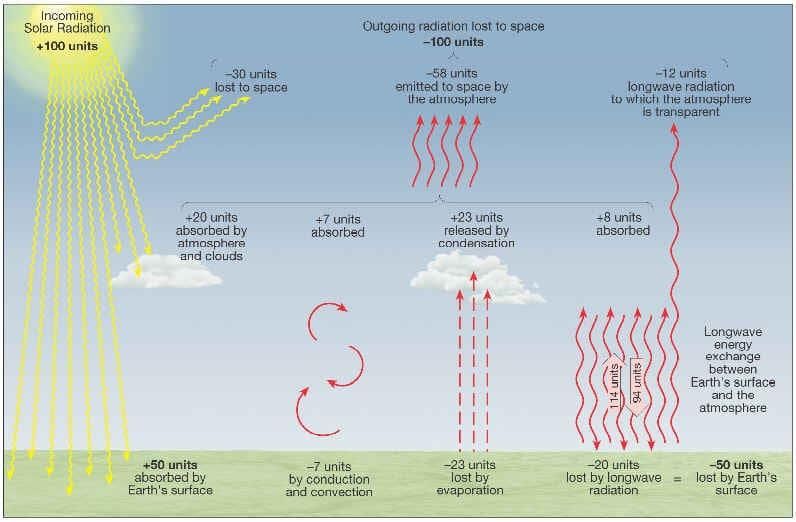 |
|
Card: 17 / 42 |
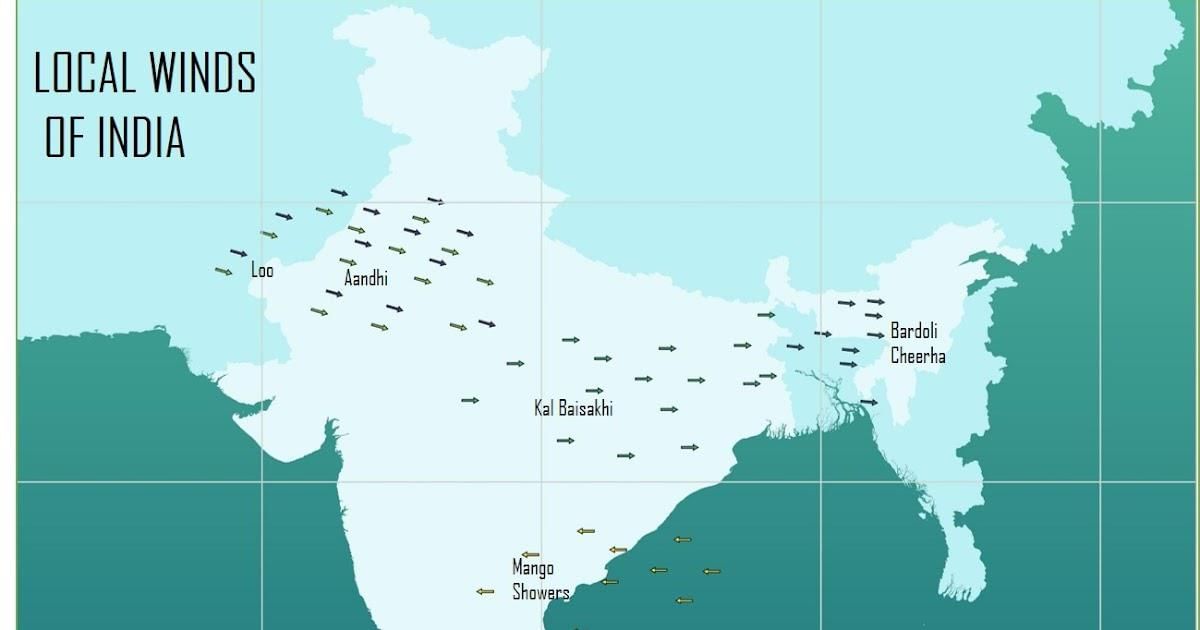
In which regions are local winds called 'loo' typically observed as a result of the advection process? |
|
Card: 19 / 42 |
The process by which the earth radiates energy to the atmosphere in long wave form is known as ___. |
|
Card: 20 / 42 |
Terrestrial radiation. This process involves the earth absorbing solar energy and then emitting it as long wave radiation, which heats the atmosphere. 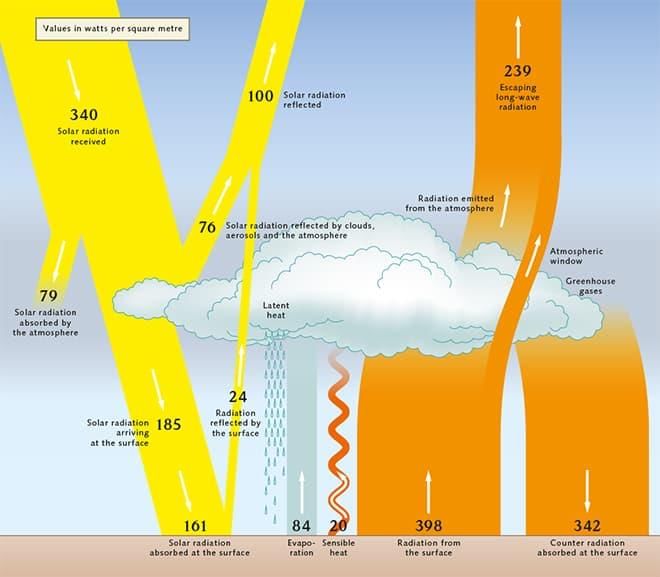 |
|
Card: 21 / 42 |
True or False: Long wave radiation emitted by the earth is not absorbed by atmospheric gases. |
|
Card: 22 / 42 |
False. Long wave radiation is absorbed by atmospheric gases, particularly carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, contributing to the heating of the atmosphere. 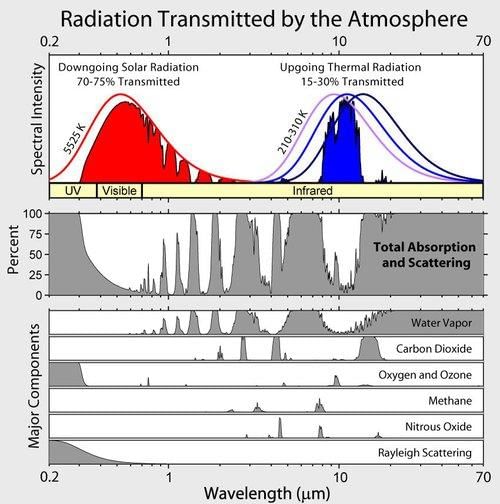 |
|
Card: 23 / 42 |
The amount of heat received from the sun that is eventually returned to space is essential for maintaining ___. |
|
Card: 25 / 42 |
Fill in the blank: The primary mechanism for the vertical movement of air in the atmosphere is called ___. |
|
Card: 26 / 42 |
Convection. This process involves warm air rising and cool air sinking, creating currents that distribute heat. 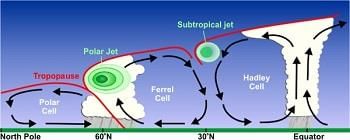 |
|
Card: 27 / 42 |
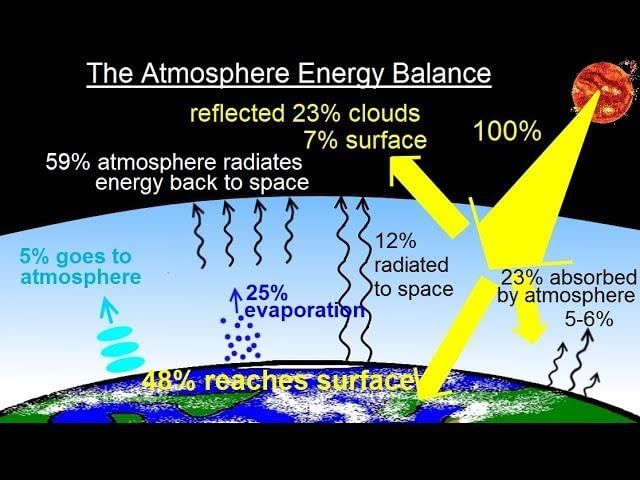
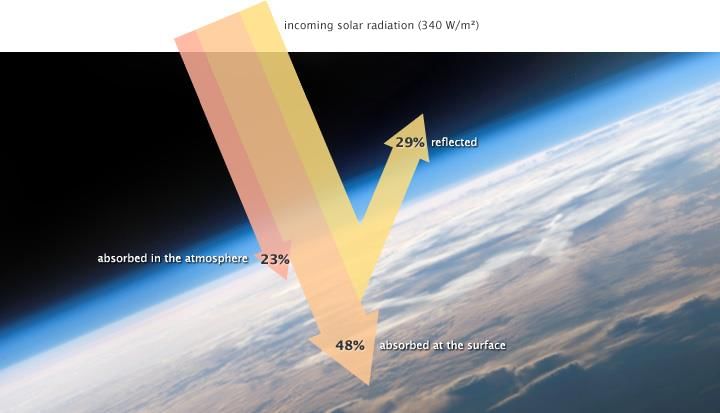
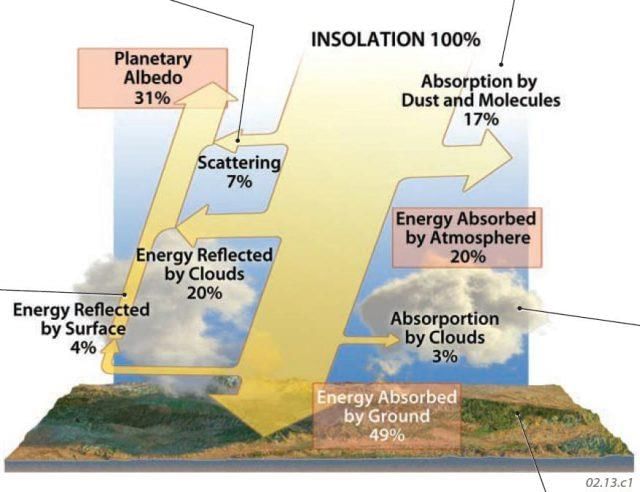
___ units of energy are reflected back to space before reaching the Earth's surface. |
|
Card: 29 / 42 |
What are the two main factors that influence the temperature of air at any location? |
|
Card: 30 / 42 |
The interaction of insolation with the atmosphere and the characteristics of the Earth's surface. 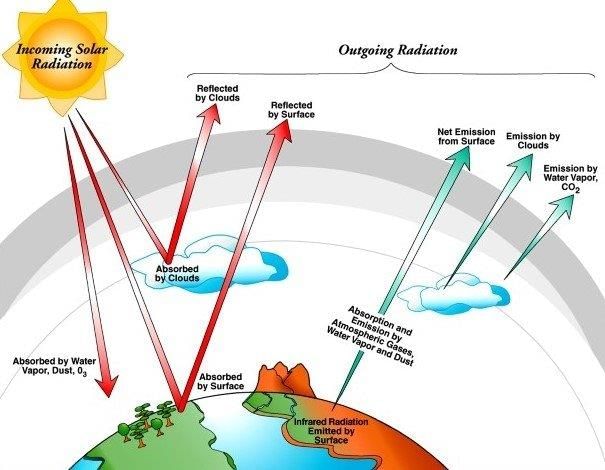 |
|
Card: 31 / 42 |
True or False: The tropics accumulate excess heat, leading to progressively higher temperatures. |
|
Card: 32 / 42 |
False. The surplus heat energy from the tropics is redistributed polewards to prevent excessive heating. 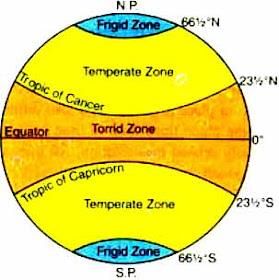 |
|
Card: 33 / 42 |
What is the primary reason that high latitudes do not become permanently frozen? |
|
Card: 34 / 42 |
The redistribution of surplus heat energy from the tropics prevents excessive cooling at high latitudes.  |
|
Card: 35 / 42 |
Fill in the blank: The amount of insolation received at the top of the atmosphere is ___ percent. |
|
Card: 39 / 42 |
True or False: Temperature generally increases with altitude in the atmosphere. |
|
Card: 40 / 42 |
False. Temperature generally decreases with increasing altitude, known as the normal lapse rate. 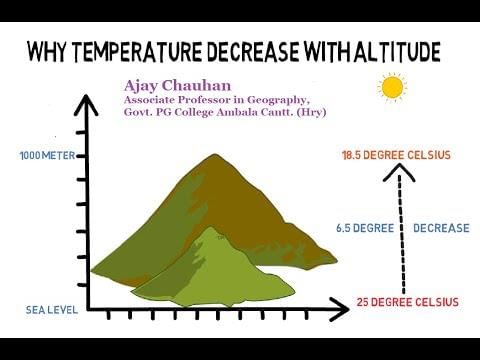 |