|
Card: 2 / 44 |
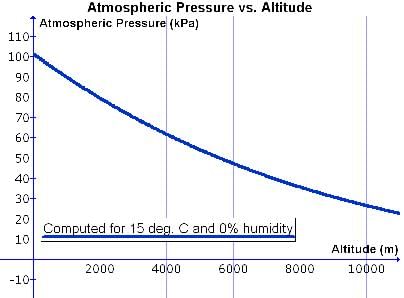
Atmospheric pressure is the weight of a column of air contained in a unit area from mean sea level to the top of the atmosphere, expressed in units of millibar. It is measured using a mercury barometer or an aneroid barometer. 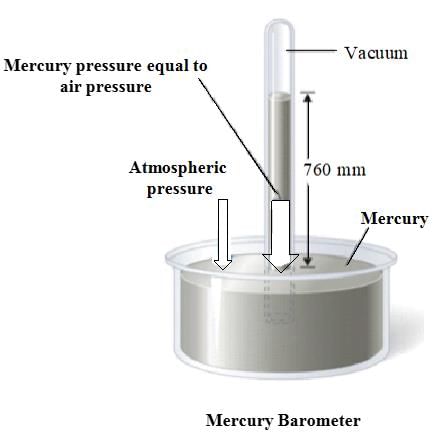 |
|
Card: 3 / 44 |
Fill in the blank: The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is ___ milibar. |
|
Card: 8 / 44 |
The primary cause of air motion is the variation in atmospheric pressure, where air moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas. 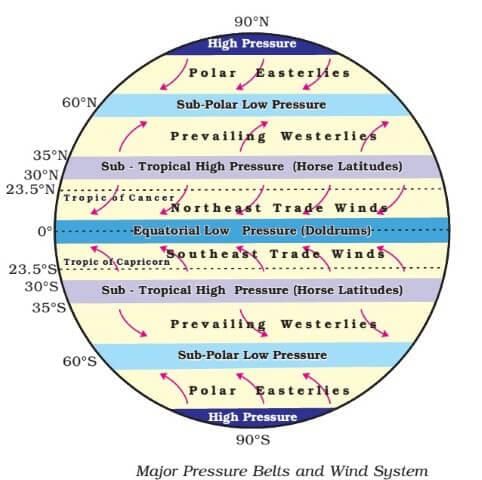 |
|
Card: 9 / 44 |
The vertical pressure gradient force is generally balanced by which other force? |
|
Card: 10 / 44 |
The vertical pressure gradient force is generally balanced by a nearly equal but opposite gravitational force. 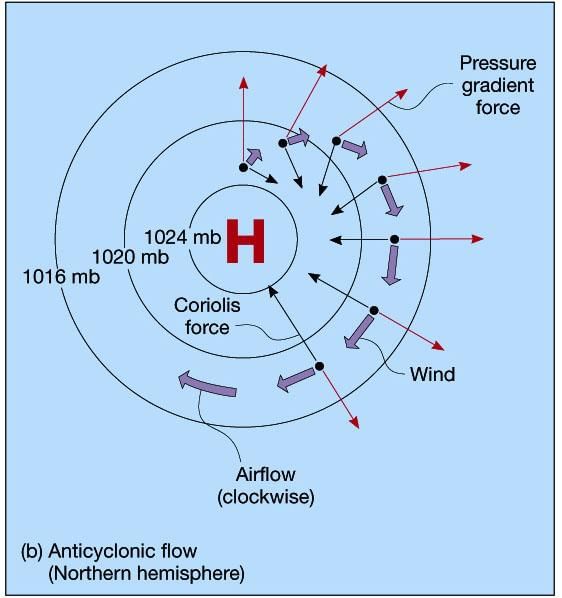 |
|
Card: 11 / 44 |
Fill in the blanks: In the lower atmosphere, the pressure decreases rapidly with height, approximately ___ mb for each ___ m increase in elevation. |
|
Card: 13 / 44 |
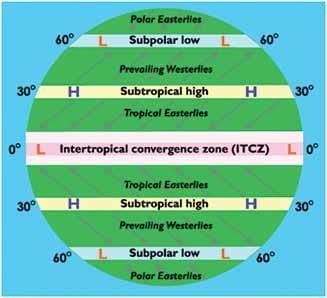
What are isobars and what do they represent in the study of atmospheric pressure? |
|
Card: 14 / 44 |
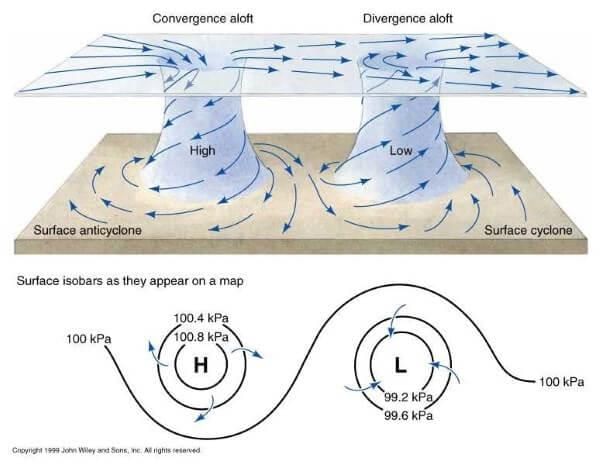
Isobars are lines connecting places having equal atmospheric pressure, and they are used to study the horizontal distribution of pressure in the atmosphere. 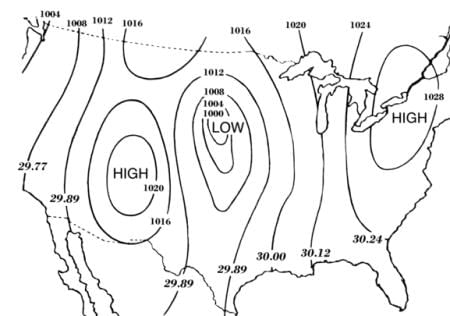 |
|
Card: 15 / 44 |
True or False: A low-pressure system is always enclosed by one or more isobars with the highest pressure in the center. |
|
Card: 16 / 44 |
False. A low-pressure system is enclosed by one or more isobars with the lowest pressure in the center. 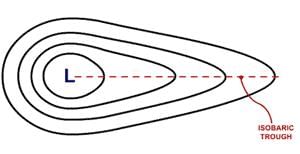 |
|
Card: 19 / 44 |
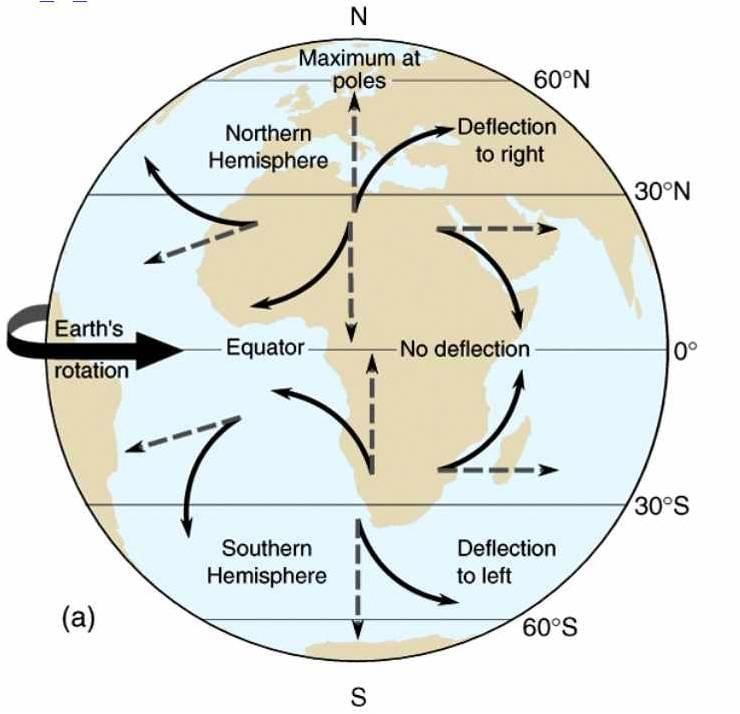
What is the primary force that causes wind to move from high pressure to low pressure? |
|
Card: 23 / 44 |
Fill in the blank: Winds at the surface diverge from high pressure areas and converge at ___ pressure areas. |
|
Card: 26 / 44 |
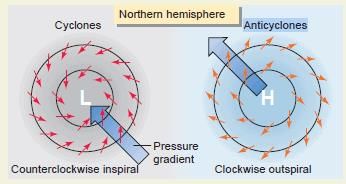
The wind blows perpendicular to the isobars, and the low pressure gets filled instead of intensified. 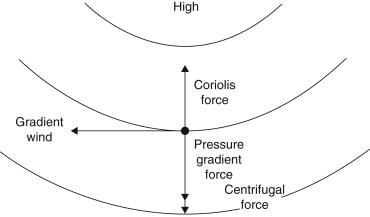 |
|
Card: 27 / 44 |
Fill in the blank: The wind circulation around a low pressure area is called ___ circulation. |
|
Card: 29 / 44 |
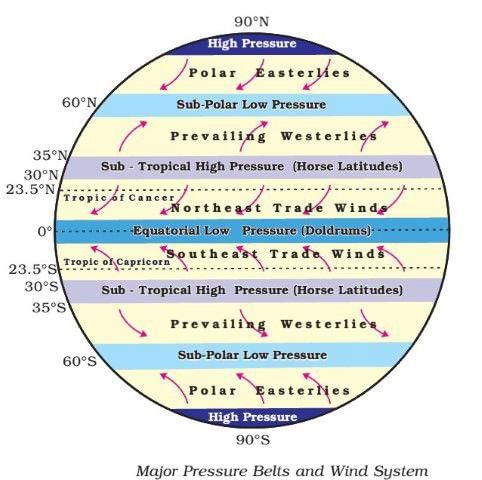
The pattern of planetary winds is primarily influenced by the ___ and ___ of atmospheric heating. |
|
Card: 31 / 44 |
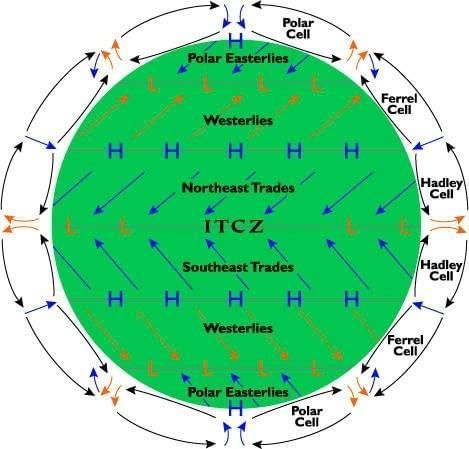
True or False: The Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is characterized by descending air and high pressure. |
|
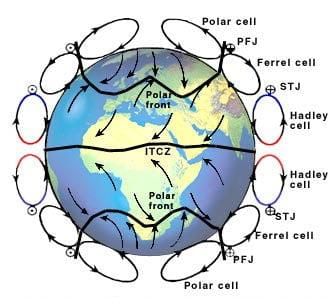
Card: 34 / 44 |
The Hadley Cell is a tropical atmospheric circulation cell where warm air rises at the ITCZ and sinks at about 30° N and S latitudes. 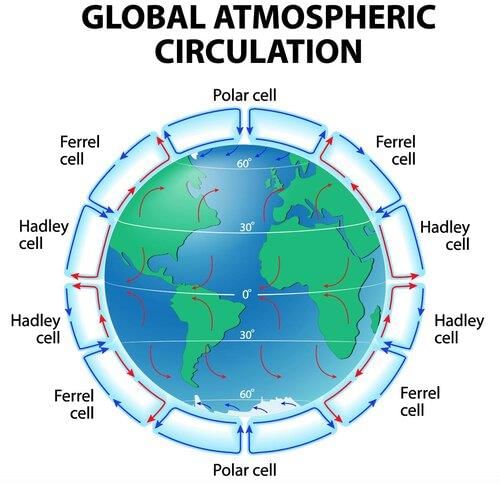 |
|
Card: 36 / 44 |
El Niño can cause heavy rainfall on the west coast of South America, droughts in Australia and India, and floods in China. 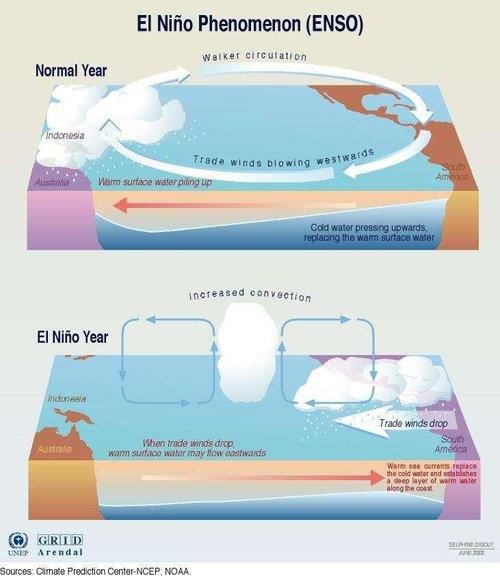 |
|
Card: 37 / 44 |
True or False: The Southern Oscillation is unrelated to the changes in atmospheric pressure associated with El Niño. |
|
Card: 38 / 44 |
False. The Southern Oscillation is closely related to the pressure changes associated with El Niño. 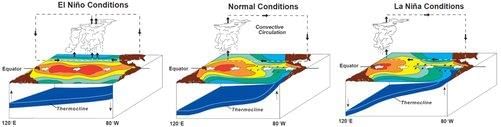 |
|
Card: 40 / 44 |
Ocean currents are initiated by atmospheric winds, and they provide energy and water vapor to the atmosphere, influencing climate patterns. 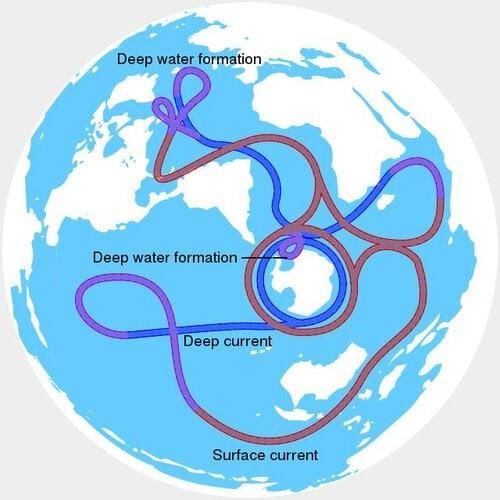 |
|
Card: 41 / 44 |
Fill in the blank: The circulation cell in the middle latitudes is known as the ___ cell. |
|
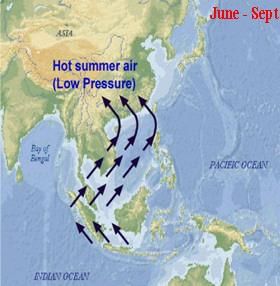
Card: 43 / 44 |
The seasonal wind patterns that change during monsoons in Southeast Asia are primarily influenced by ___ and ___. |