|
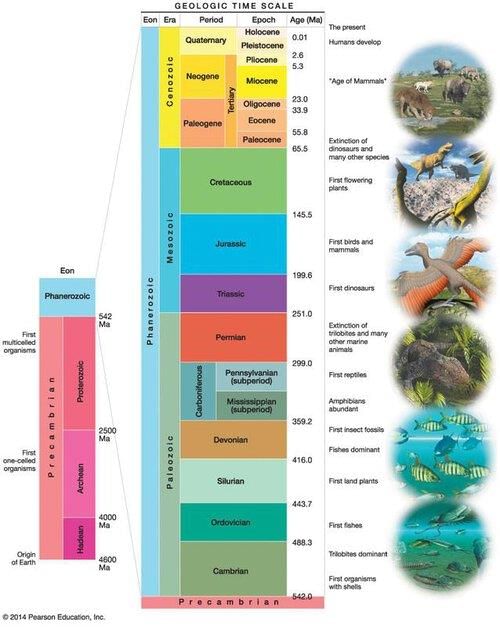
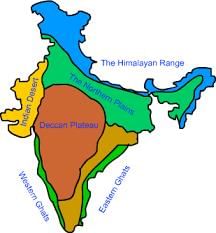
The Peninsular Block consists mainly of very old gneisses and granites, has remained mostly unchanged since the Cambrian period, and includes features like rift valleys.  |
Card: 6 / 40 |
|
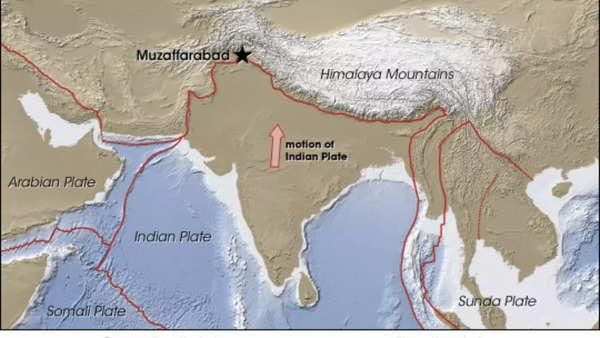
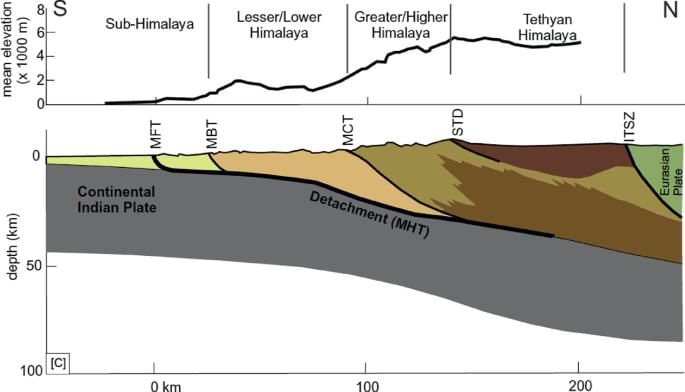
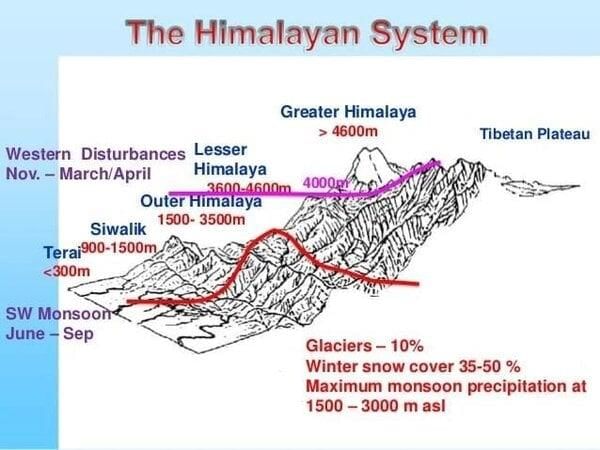
False. The Himalayas are young, weak, and flexible in their geological structure. 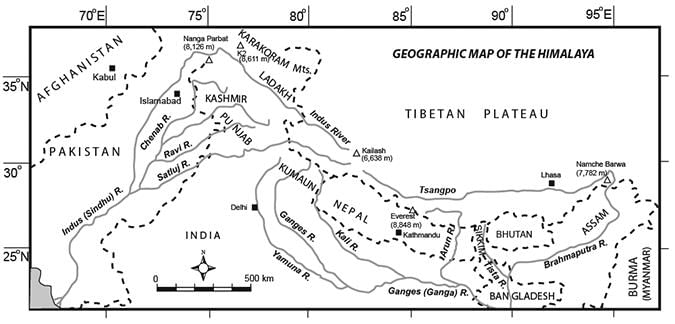 |
Card: 8 / 40 |
|
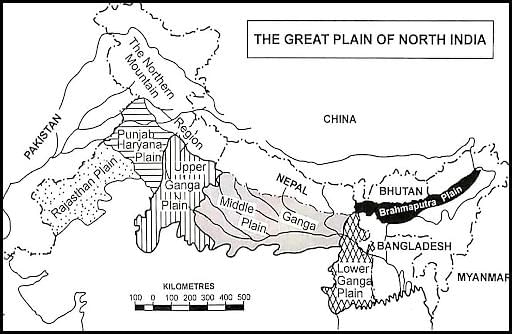
Fill in the blank: The average depth of alluvial deposits in the Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra plains ranges from ___ to ___ meters. |
Card: 9 / 40 |
|
What geological features result from the interaction of endogenic and exogenic forces in the Himalayas? |
Card: 11 / 40 |
|
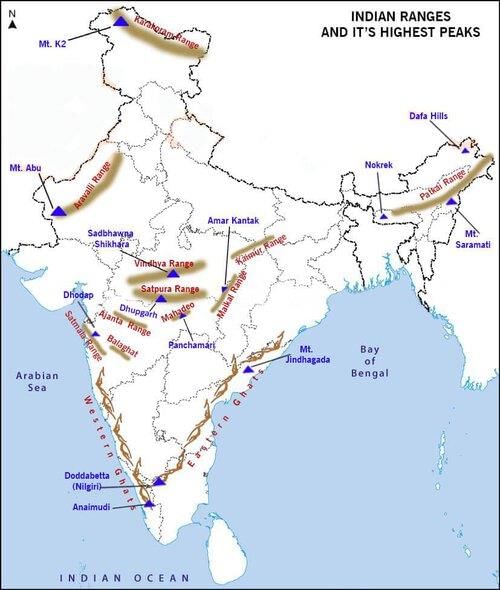
Fill in the blank: The northern boundary of the Peninsular Block is an uneven line starting from Kachchh, going along the ___ Range near Delhi. |
Card: 13 / 40 |
|
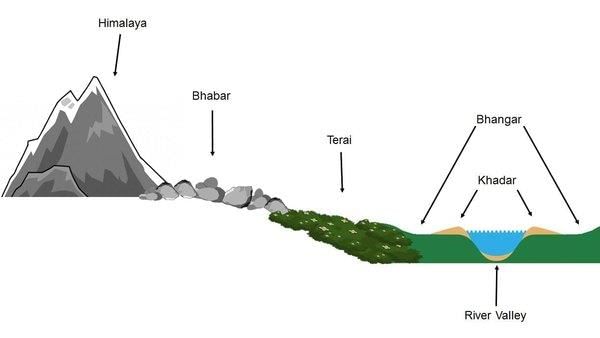
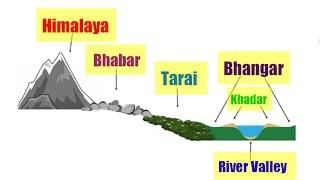
The Northern Plains of India are primarily formed by ___ deposits from the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers. |
Card: 15 / 40 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
The physiographic divisions of India include all of the following except ___: (i) Northern and North-eastern Mountains, (ii) Indian Desert, (iii) Great Plains of India. |
Card: 21 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Himalayas serve only as a physical barrier and do not influence climate. |
Card: 23 / 40 |
|
The Deccan Plateau is characterized by significant erosion and discontinuous formations, making it a classic example of ___ mountains. |
Card: 27 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The elevation of the Central Highlands ranges between ___ and ___ meters above sea level. |
Card: 29 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Great Indian Desert experiences heavy annual rainfall, exceeding 150 mm. |
Card: 31 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Meghalaya Plateau is subdivided into four regions: Garo Hills, Khasi Hills, Jaintia Hills, and Karbi Hills. |
Card: 35 / 40 |
|
False. The Meghalaya Plateau is subdivided into three regions: Garo Hills, Khasi Hills, and Jaintia Hills. 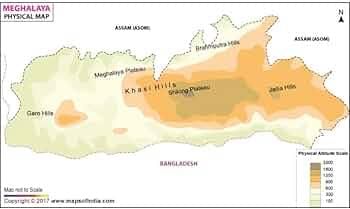 |
Card: 36 / 40 |
|
The desert regions of India are characterized by features such as ___ rocks, shifting dunes, and oases. |
Card: 37 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Luni River is significant in the ___ desert region of India. |
Card: 39 / 40 |