|
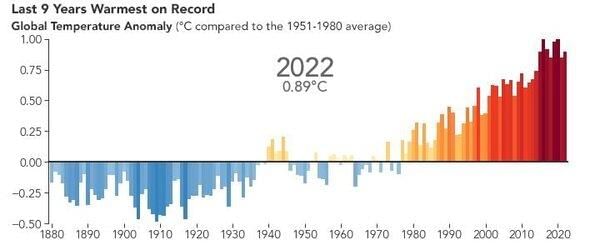
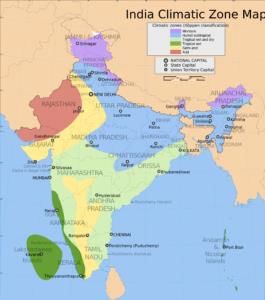
Climate refers to the average of weather conditions over a period of time of ___ or more. |
Card: 1 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: The monsoonal climate is associated with seasonal reversal in the direction of ___ in India. |
Card: 5 / 42 |
|
Temperature, pressure, wind direction and velocity, humidity, and precipitation.  |
Card: 8 / 42 |
|
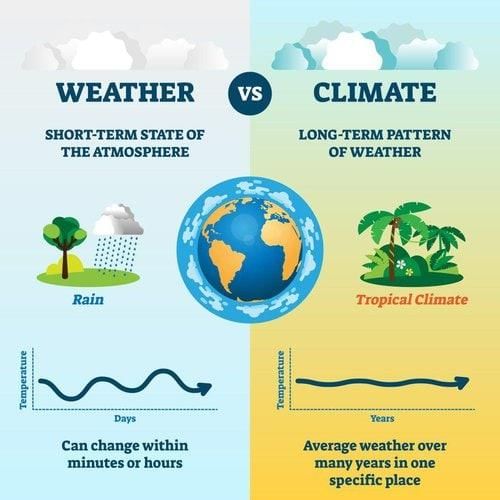
Weather is the short-term state of the atmosphere, while climate is the long-term average of weather conditions. 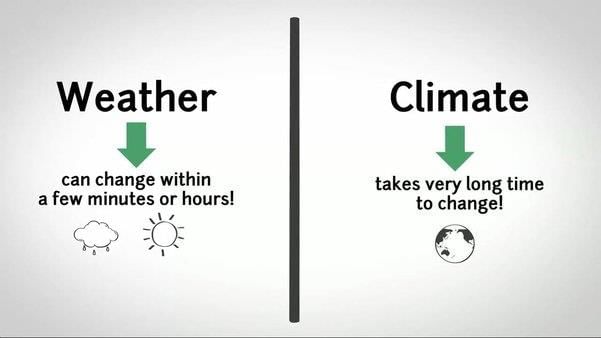 |
Card: 10 / 42 |
|
The monsoon climate of India exhibits both unity and diversity. True or False? |
Card: 11 / 42 |
|
True. The monsoon climate shows broad unity across the Southeast Asian region but also significant regional variations.  |
Card: 12 / 42 |
|
55°C. In contrast, temperatures can drop to as low as -45°C in winter around Leh.  |
Card: 14 / 42 |
|
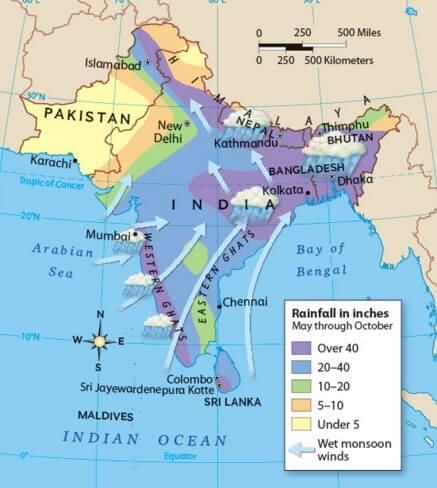
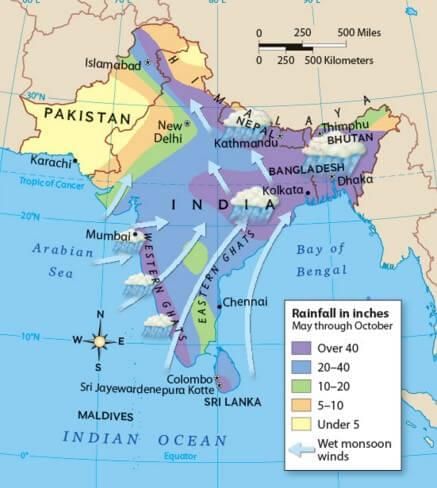
In terms of precipitation, Cherrapunji receives over ___ cm of rainfall annually, while Jaisalmer receives less than ___ cm. |
Card: 15 / 42 |
|
1,080 cm; 10 cm. This highlights the regional variation in rainfall across India. 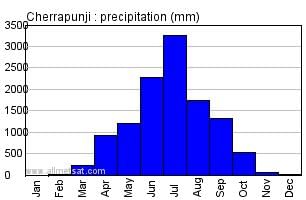 |
Card: 16 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: The climate of Kerala and Tamil Nadu is vastly different from that of ___ and ___ despite all having a monsoon type of climate. |
Card: 17 / 42 |
|
Uttar Pradesh; Bihar. This demonstrates the regional diversity within the monsoon framework. 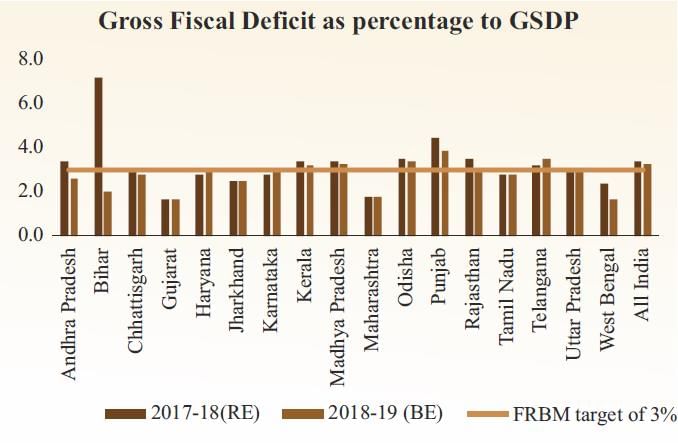 |
Card: 18 / 42 |
|
Most areas receive rainfall during the months of June to September, with some regions like Tamil Nadu experiencing rain in the winter months. 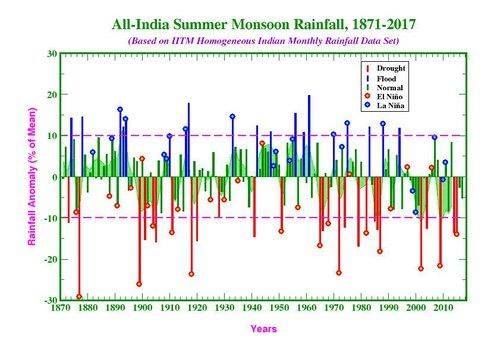 |
Card: 20 / 42 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
True or False: The Himalayan Mountains contribute to the extreme climate experienced in northern India. |
Card: 23 / 42 |
|
False. The Himalayan Mountains act as a climatic divide and protect the subcontinent from cold northern winds. 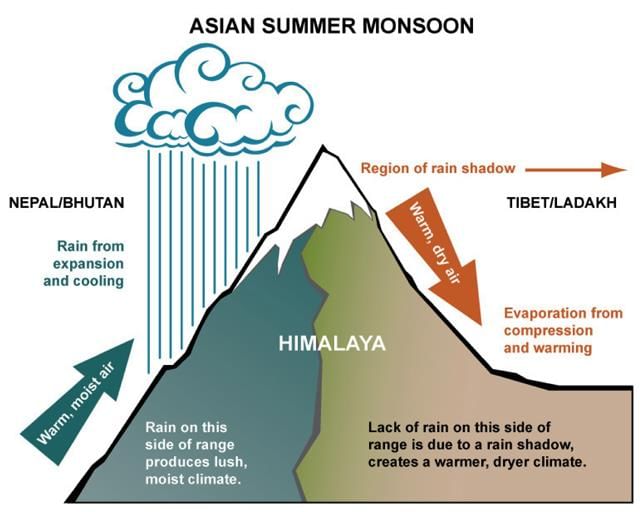 |
Card: 24 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: Areas in the interior of India experience extremes of climate due to their distance from the ___ influence of the sea. |
Card: 25 / 42 |
|
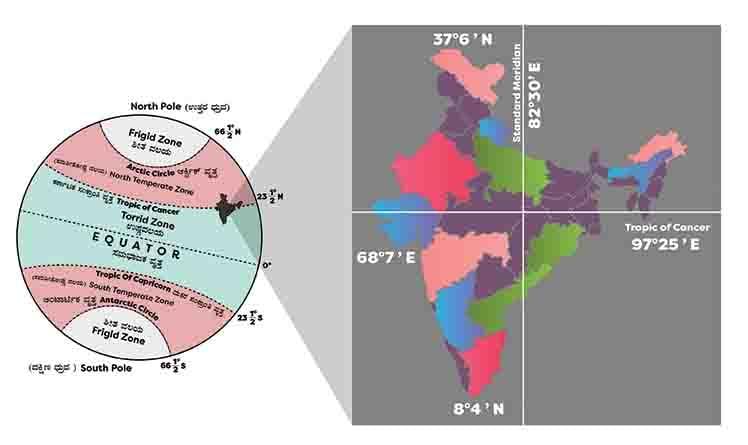
Latitude affects temperature ranges, with northern parts in the temperate zone experiencing greater extremes compared to the southern tropical zone, which has higher and more consistent temperatures.  |
Card: 28 / 42 |
|
True or False: The distribution of land and water around India does not significantly impact its climate. |
Card: 29 / 42 |
|
False. The differential heating of land and sea creates varying air pressure zones that affect India's climate.  |
Card: 30 / 42 |
|
Temperature decreases with height; therefore, places in the mountains are generally ___ than those on the plains. |
Card: 31 / 42 |
|
The physiography or relief of India influences temperature, air pressure, wind direction, and ___ distribution. |
Card: 33 / 42 |
|
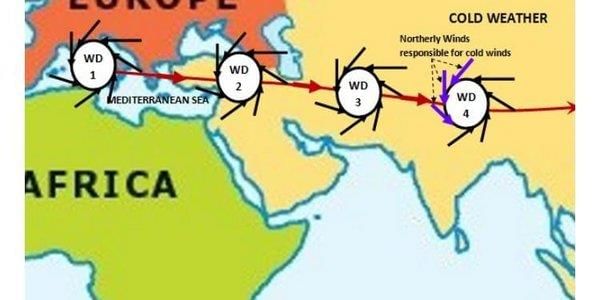
Fill in the blank: The inflow of western cyclones in India is generally known as ___ during the winter season. |
Card: 35 / 42 |
|
What effect does the leeward situation of the southern plateau have on its climate compared to the windward sides of the Western Ghats? |
Card: 37 / 42 |
|
The leeward situation of the southern plateau results in it remaining dry during the monsoon season, while the windward sides receive abundant rainfall.  |
Card: 38 / 42 |
|
True or False: Tropical depressions occur in India only during the winter season. |
Card: 39 / 42 |