|
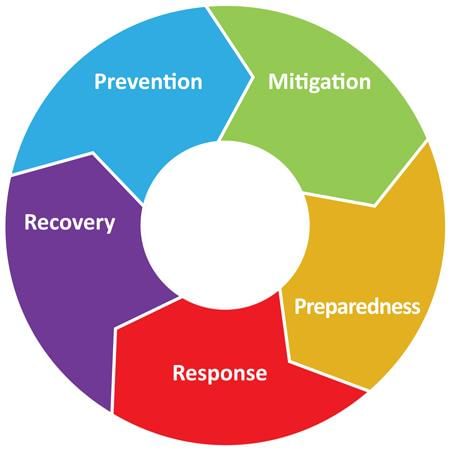
The key components of effective disaster management include preparedness, early warning systems, and ___ resilience. |
Card: 3 / 40 |
|
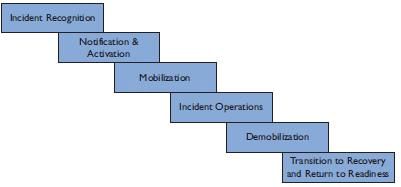
Fill in the blank: A disaster requires mobilization of efforts that exceed those normally provided by ___ emergency services. |
Card: 5 / 40 |
|
Early warning systems provide timely information that can help communities prepare for and respond to potential disasters, reducing their impact.  |
Card: 12 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The occurrence of a disaster can lead to serious disruption of life and ___ including death and injury to a large number of people. |
Card: 13 / 40 |
|
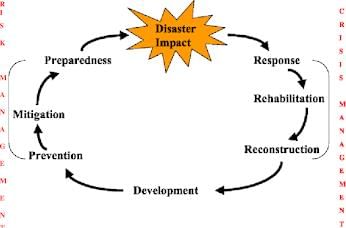
Natural hazards can disrupt social systems by causing damage to infrastructure, displacing communities, and leading to loss of life and resources, thereby threatening societal stability.  |
Card: 16 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Yokohama Strategy prioritizes attention to developing countries, particularly the least developed, land-locked countries, and ___ developing states. |
Card: 17 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Yokohama Strategy promotes sub-regional, regional, and international cooperation with an emphasis on human and institutional capacity-building and ___ sharing. |
Card: 19 / 40 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
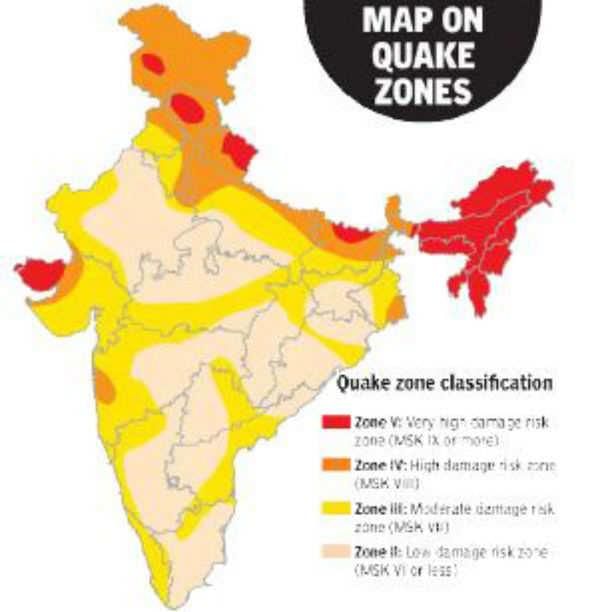
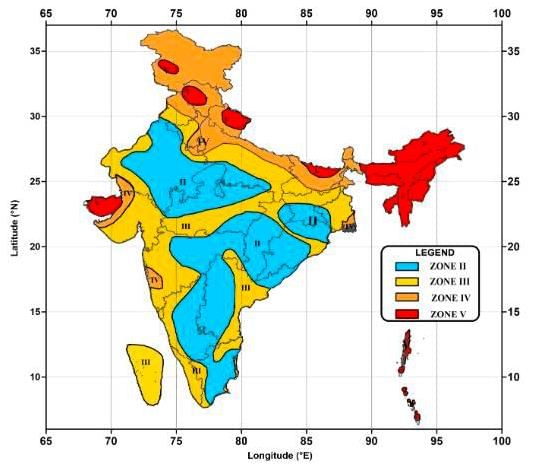
The most vulnerable states in India to earthquakes include Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and ___ . |
Card: 25 / 40 |
|
What are the five earthquake zones classified by the National Institute of Disaster Management? |
Card: 27 / 40 |
|
Very high damage risk zone, High damage risk zone, Moderate damage risk zone, Low damage risk zone, Very low damage risk zone. 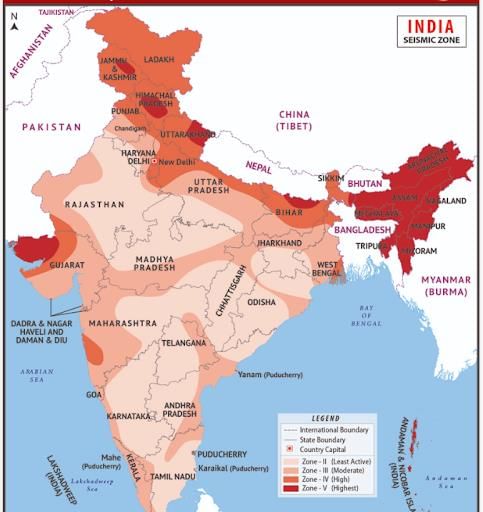 |
Card: 28 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: Earthquakes become particularly calamitous when they strike areas with ___ population density. |
Card: 29 / 40 |
|
True or False: Most of the areas considered safe from earthquakes are located on the Deccan plateau. |
Card: 31 / 40 |
|
Explain the socio-environmental consequences of earthquakes in high-density areas. |
Card: 33 / 40 |
|
They cause destruction of settlements, infrastructure, and developmental activities, leading to homelessness and additional economic pressure, especially in developing countries. 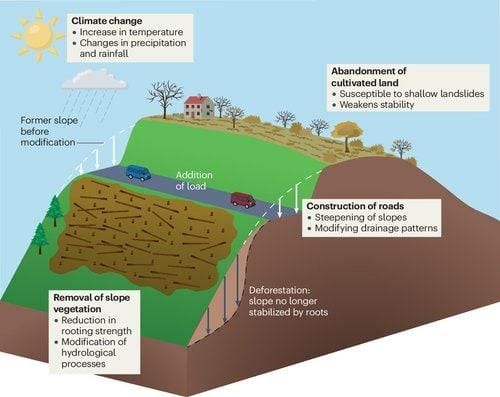 |
Card: 34 / 40 |
|
What is the next best option after recognizing that earthquakes cannot be prevented? |
Card: 35 / 40 |
|
Establishing monitoring centers, using GPS technology for tectonic plate movement, preparing vulnerability maps, educating the public on disaster risk, modifying building designs, and enforcing earthquake-resistant construction standards. 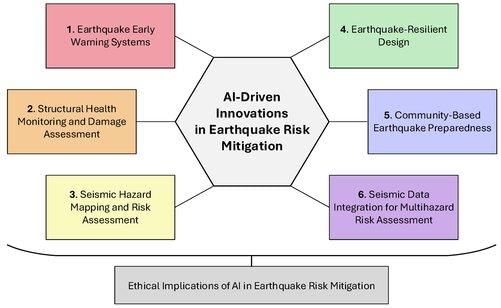 |
Card: 38 / 40 |
|
True or False: High-rise buildings are encouraged in vulnerable earthquake zones to promote urban development. |
Card: 39 / 40 |
|
False. High-rise buildings and large industrial establishments are discouraged in vulnerable areas to minimize risks. 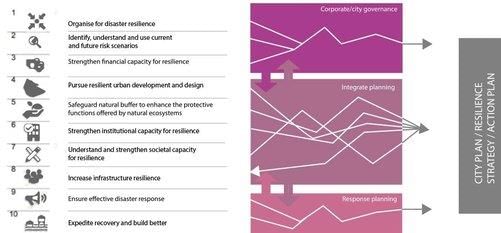 |
Card: 40 / 40 |