|
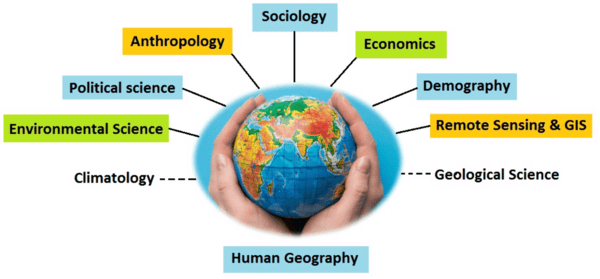
True or False: Human geography only focuses on the physical environment without considering human societies. |
Card: 1 / 42 |
|
False; Human geography studies the interaction between human societies and the physical environment.
|
Card: 2 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: The two major components that make up the Earth are ___ and ___. |
Card: 3 / 42 |
|
True or False: There is a widely accepted division between physical geography and human geography. |
Card: 7 / 42 |
|
False; The divisions are not very valid as nature and human activities are closely interconnected.  |
Card: 8 / 42 |
|
Organizing geographic studies by themes or systems, such as climate or population. |
Card: 10 / 42 |
|
True or False: According to Ellen C, human geography focuses solely on the physical environment without considering human actions. |
Card: 11 / 42 |
|
False. Human geography considers the changing relationship between humans and the unstable earth. |
Card: 12 / 42 |
|
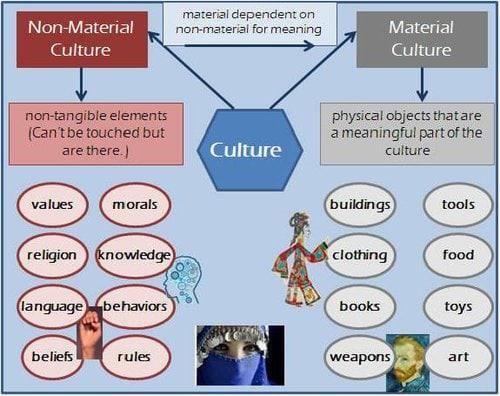
The term ‘material culture’ in the context of human geography refers to ___ created by human beings. |
Card: 13 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: Paul Vidal de la Blache emphasizes a synthetic knowledge of the physical laws governing our earth and the relationships between living beings which inhabit it, describing human geography as a ___ study. |
Card: 15 / 42 |
|
Short Answer: What is the significance of the interaction between the physical environment and human societies in human geography? |
Card: 17 / 42 |
|
The interaction signifies how humans modify their physical environment while being influenced by it, impacting both cultural and environmental changes. 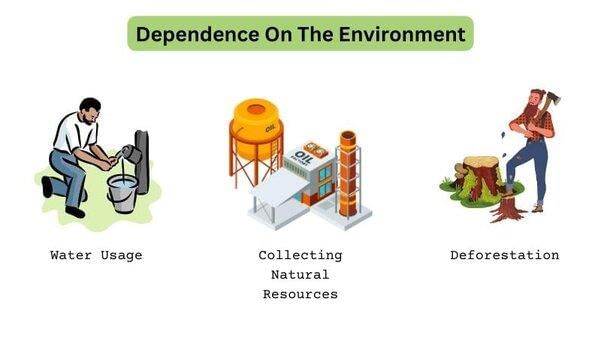 |
Card: 18 / 42 |
|
True or False: The physical environment has remained unchanged despite human activities. |
Card: 19 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: The elements created by human beings using resources from the physical environment include ___ and ___ . |
Card: 21 / 42 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
What does the concept of human geography suggest about the nature of human activities? |
Card: 23 / 42 |
|
It suggests that human activities are interdependent with the physical environment, showcasing a dynamic relationship that evolves over time. |
Card: 24 / 42 |
|
Human beings create technology primarily after gaining a deeper understanding of ___ and ___. |
Card: 25 / 42 |
|
True or False: Environmental determinism suggests that human societies have complete control over their environment. |
Card: 27 / 42 |
|
False. Environmental determinism posits that human societies are significantly shaped by their natural environment. |
Card: 28 / 42 |
|
The transition from a state of necessity to a state of freedom in human development is associated with the concept of ___. |
Card: 29 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: Human activities create ___ on nature, which include urban sprawls, health resorts, and agricultural fields. |
Card: 31 / 42 |
|
Neodeterminism refers to the idea that while humans can shape their environment through technology, they are still influenced by environmental constraints. |
Card: 34 / 42 |
|
True or False: The humanisation of nature involves adapting to environmental constraints without altering them. |
Card: 35 / 42 |
|
False. The humanisation of nature involves overcoming environmental constraints through technology. |
Card: 36 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: The early human connection to nature was characterized by fear and ___ of its power. |
Card: 37 / 42 |
|
True or False: Neodeterminism advocates for absolute freedom in human development without considering environmental limits. |
Card: 39 / 42 |
|
False. Neodeterminism emphasizes balancing human development with environmental constraints. |
Card: 40 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: Neodeterminism aims to harmonize human progress with ___ to prevent irreversible damage to the natural world. |
Card: 41 / 42 |