|
Fill in the blanks: Secondary economic activities involve transforming raw materials into ___ products, enhancing their ___ value. |
Card: 1 / 50 |
|
True or False: Secondary activities are primarily focused on the extraction of natural resources. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
False; secondary activities focus on manufacturing and processing raw materials, not on extraction.  |
Card: 4 / 50 |
|
The primary role of secondary activities is to add value to natural resources by transforming them into manufactured goods and products. |
Card: 6 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: An example of a secondary activity includes processing ___ into yarn for clothing production. |
Card: 7 / 50 |
|
Iron ore needs to be processed into steel to be useful for manufacturing machinery and tools. 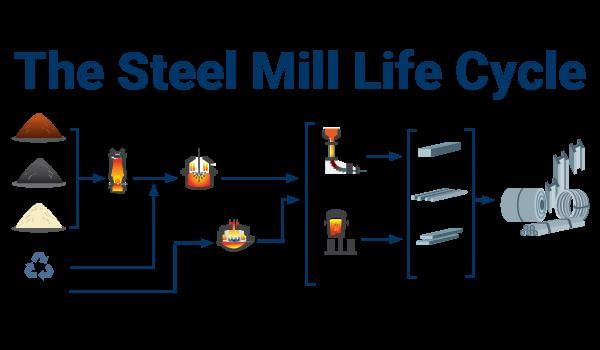 |
Card: 10 / 50 |
|
True or False: The quaternary sector is involved in manufacturing and processing activities. |
Card: 11 / 50 |
|
False; the quaternary sector focuses on knowledge-based activities like research and development, not directly on manufacturing.  |
Card: 12 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Secondary activities mainly involve the ___, processing, and construction industries. |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
Manufacturing processes typically involve the application of ___ for production. |
Card: 15 / 50 |
|
True or False: Specialized labor in manufacturing is primarily utilized in home-based production settings. |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Modern manufacturing techniques often utilize ___ and ___ for efficient production. |
Card: 19 / 50 |
|
Mass production focuses on producing identical products and typically involves specialized labor. |
Card: 22 / 50 |
|
True or False: Traditional manufacturing techniques are predominantly used in developed countries. |
Card: 23 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Manufacturing encompasses production activities such as ___, molding iron and steel, and ___ components. |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Modern large-scale manufacturing emphasizes the specialization of skills and production methods. True or False? |
Card: 27 / 50 |
|
True. Specialization allows workers to focus on specific tasks, increasing efficiency and lowering production costs.  |
Card: 28 / 50 |
|
Mass production is characterized by ___ quantities of standardized parts and ___ focus on individual tasks by workers. |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
Mechanization involves using machines to perform tasks, with automation being a more advanced form where machines operate without human intervention.  |
Card: 32 / 50 |
|
Technological innovation in manufacturing aims to improve ___, reduce ___, and address ___ issues. |
Card: 33 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blanks: Modern manufacturing features high levels of specialization and division of labor, allowing for increased production with lower ___ and ___ costs. |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
False. Modern manufacturing is concentrated in specific regions, often covering less than 10% of the world's land area. |
Card: 38 / 50 |
|
What is one reason why manufacturing sites are less visible compared to agricultural sites? |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
Manufacturing sites cover smaller areas due to the intensity of production, allowing many factories to operate within a compact region. |
Card: 40 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Significant ___ investment is required for modern manufacturing to support complex machinery and large organizational structures. |
Card: 41 / 50 |
|
The availability of a market for manufactured goods is crucial for industrial location because it refers to consumers who not only demand products but also have the ___ to buy them. |
Card: 43 / 50 |
|
True or False: Regions with sparse populations are more attractive for industry due to their limited markets. |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
False. Regions with sparse populations are less attractive for industry due to limited markets. |
Card: 46 / 50 |
|
Industries that rely on heavy, bulky, or perishable materials, such as ___ and ___, are usually located near their sources. |
Card: 47 / 50 |
|
Access to a skilled labor supply is crucial because some manufacturing sectors require ___ workers, while increased mechanization has reduced the overall need for ___ . |
Card: 49 / 50 |