|
True or False: The population of India is less than the combined population of North America, South America, and Australia. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
False. The population of India exceeds the combined population of North America, South America, and Australia. |
Card: 4 / 50 |
|
The states of Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, and West Bengal together account for about ___% of India's total population. |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Areas near ___ and ___ tend to have higher population concentrations in India. |
Card: 7 / 50 |
|
What socio-economic factors contribute to the uneven distribution of population in India? |
Card: 9 / 50 |
|
Physical features, climate, water availability, urbanization, industrialization, and historical patterns of human settlement are significant socio-economic factors affecting population distribution. |
Card: 10 / 50 |
|
True or False: Jammu & Kashmir has a larger share of India's population compared to states like Maharashtra. |
Card: 11 / 50 |
|
False. Jammu & Kashmir has a very small share of the population (1.04%) compared to states like Maharashtra. |
Card: 12 / 50 |
|
Which Indian states have a very small population share despite their large geographical area? |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Urban areas like ___ and ___ have high population densities mainly due to industrial development. |
Card: 15 / 50 |
|
The population density of India in 2011 was ___ individuals per square kilometer. |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
True or False: The density of population is uniform across all states in India. |
Card: 19 / 50 |
|
False. The density varies widely across states, with some having as low as 17 individuals per square kilometer and others as high as 11,297 individuals per square kilometer. |
Card: 20 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Physiological density is calculated by dividing the total population by the ___ area. |
Card: 21 / 50 |
|
What is the significance of calculating agricultural density in understanding population pressure? |
Card: 23 / 50 |
|
Agricultural density helps to assess the pressure of the population engaged in agriculture on the available cultivable land, which is crucial for a country like India with a large agricultural population. |
Card: 24 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
False. Most Union Territories (excluding Andaman and Nicobar Islands) have very high population densities.  |
Card: 26 / 50 |
|
In which Indian states are high population densities observed? Name at least two. |
Card: 27 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Himalayan hill states and northeastern states generally exhibit ___ population densities. |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
Population growth is expressed as a change in the number of individuals living in a specific region between ___ points in time. |
Card: 31 / 50 |
|
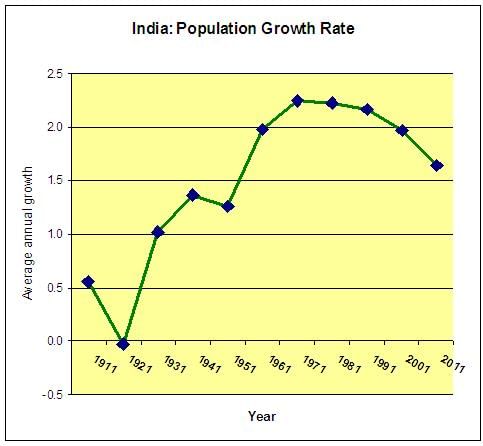
True or False: The annual population growth rate of India was 1.64 percent in 2011. |
Card: 33 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: States such as Kerala and Tamil Nadu have a growth rate below ___ percent over a decade. |
Card: 37 / 50 |
|
The four phases are: 1) Initial slow growth (1901-1921), 2) Rapid growth (1921-1951), 3) Steady growth (1951-1981), 4) Declining growth rate (1981-present). |
Card: 40 / 50 |
|
True or False: Kerala registered the highest growth rate in the country from 2001 to 2011. |
Card: 41 / 50 |
|
As of 2011, adolescents aged 10-19 comprise approximately ___ percent of India's population. |
Card: 43 / 50 |
|
What is the main goal of the National Youth Policy (NYP-2014) launched by the government of India? |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
To empower the youth of India to achieve their full potential and enable the country to find its rightful place in the global community. |
Card: 46 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The National Policy for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship provides a framework for all ___ activities in India. |
Card: 47 / 50 |