|
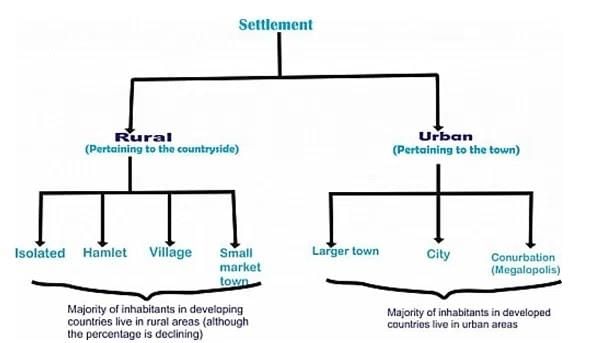
Human settlements can be categorized into ___ and ___ types based on their economic activities and geographical characteristics. |
Card: 1 / 50 |
|
True or False: Urban settlements primarily engage in primary economic activities such as agriculture. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
Rural settlements are mainly based on ___ and typically engage in ___ economic activities. |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
Urban areas serve as nodes of economic growth, linking rural hinterlands through goods, services, and resources. |
Card: 8 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The formation of settlements involves both the grouping of people and the allocation of ___ as a resource base. |
Card: 9 / 50 |
|
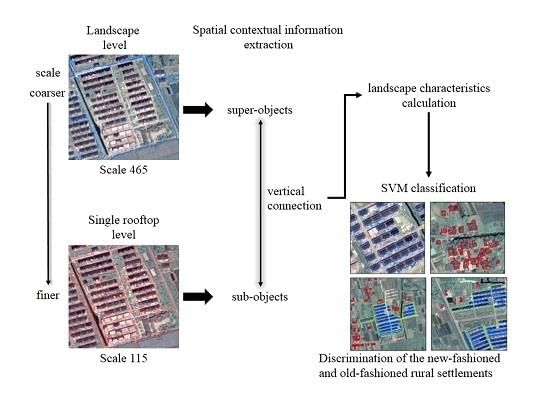
Which type of settlement is characterized by larger, compact areas focused on manufacturing and services? |
Card: 11 / 50 |
|
Clustered settlements are typically characterized by ___ layout and are commonly found in regions requiring ___ for efficient resource use. |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
True or False: Semi-clustered settlements reflect complete social equality among community members. |
Card: 15 / 50 |
|
False; Semi-clustered settlements often exhibit social hierarchies, with dominant communities occupying central positions. 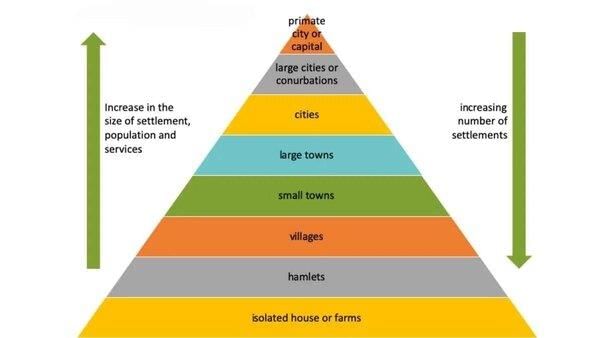 |
Card: 16 / 50 |
|
Hamleted settlements are fragmented into smaller units known locally as ___, and they often arise due to ___ within the village. |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
Dispersed settlements are typically found in areas with ___ terrain and result from ___ land fragmentation. |
Card: 19 / 50 |
|
Which type of rural settlement features a core cluster surrounded by more isolated homes, often influenced by social hierarchies? |
Card: 21 / 50 |
|
True or False: In hamleted settlements, the smaller units share a common identity but are physically separated. |
Card: 23 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Dispersed settlements consist of isolated dwellings scattered over a wide area, without a central ___ . |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Clustered settlements have close-knit communities with interconnected social and economic ties. |
Card: 28 / 50 |
|
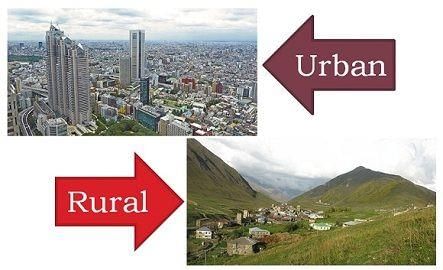
Urban areas are generally larger and more compact compared to ___ settlements. |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
True or False: Cities have no functional linkages with surrounding rural areas. |
Card: 31 / 50 |
|
False. Cities are intricately linked to surrounding rural areas, facilitating the exchange of goods and services. 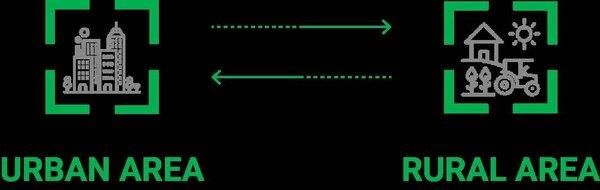 |
Card: 32 / 50 |
|
The origins of ancient towns can be traced back over ___ years, serving primarily as centers for religion, culture, and trade. |
Card: 33 / 50 |
|
Medieval towns emerged around fortifications and served as ___ and ___ bases during the era of kingdoms. |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Modern towns in India were influenced significantly by ___ expansion. |
Card: 37 / 50 |
|
True or False: The development of new administrative cities like Chandigarh occurred post-independence. |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
The first modern towns in India were initially established as coastal trading ___ such as Surat and Goa. |
Card: 41 / 50 |
|
They were characterized by fortifications and significant architectural developments like forts and palaces.  |
Card: 44 / 50 |
|
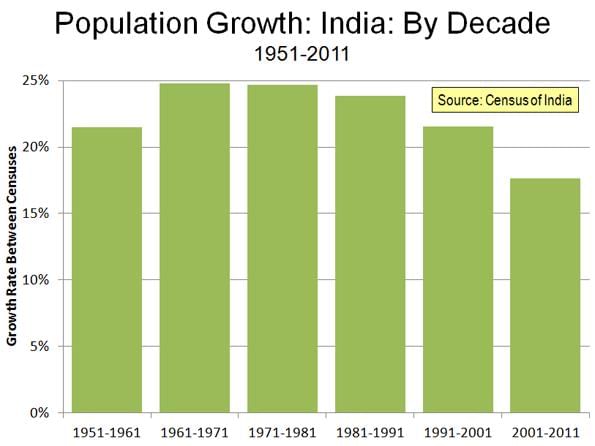
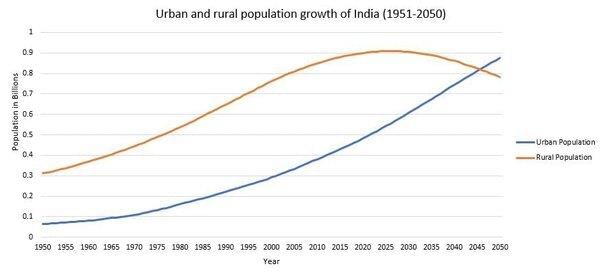
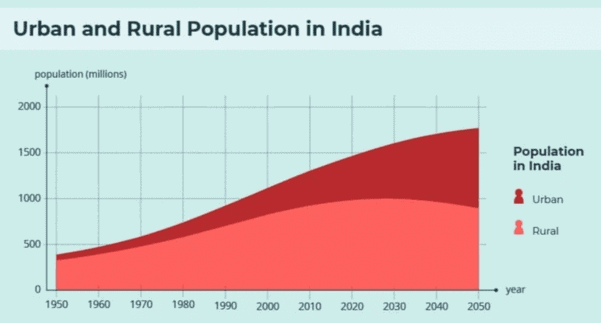
Urbanization in India was at ___% in 2011, which is low compared to developed countries. |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
True or False: The urban population in India increased eleven-fold during the 20th century. |
Card: 47 / 50 |