|
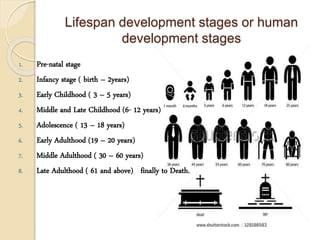
Development refers to the progressive, orderly changes observed from conception to death, including physical changes and alterations in thinking, language use, and social relationships.  |
Card: 2 / 50 |
|
True or False: Development is a linear process that only involves growth until adulthood. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
False. Development is not linear; it involves both growth and decline throughout the life-span.
|
Card: 4 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Life-Span Perspective on Development emphasizes that development occurs ___ and involves both gains and losses. |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
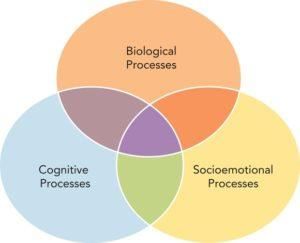
What are the three interconnected processes of development as described in the Life-Span Perspective? |
Card: 7 / 50 |
|
Multi-directional development refers to the idea that as individuals age, some abilities may improve, such as wisdom, while others may decline, such as speed-related tasks.  |
Card: 10 / 50 |
|
True or False: Individual development is solely determined by inherited traits. |
Card: 11 / 50 |
|
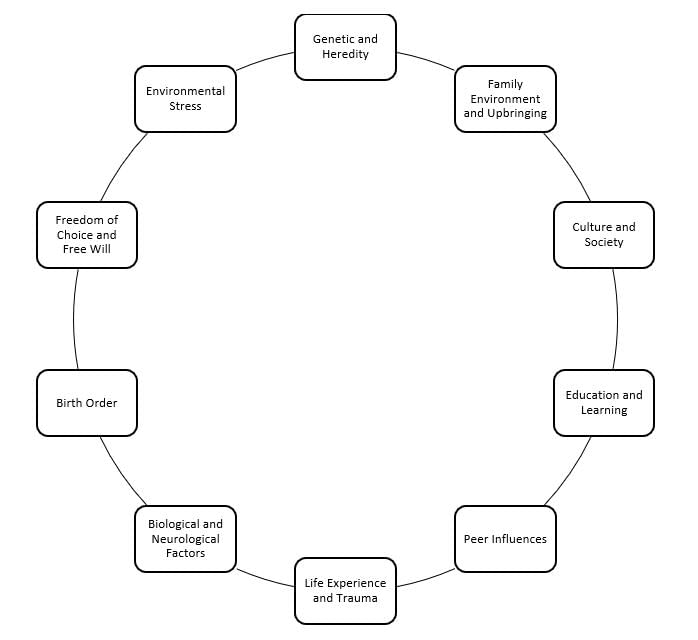
False. Individual development is influenced by a combination of inherited traits, physical surroundings, social settings, and cultural influences. 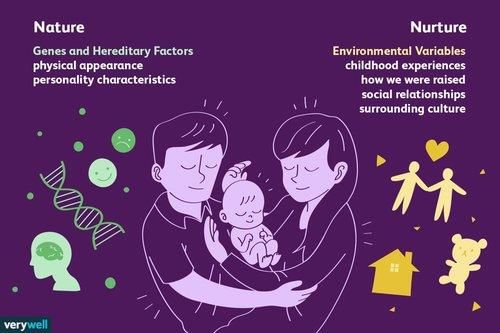 |
Card: 12 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Development is highly ___, meaning that skills and abilities can be enhanced at any stage of life. |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
Environmental factors interact with genetic predispositions to influence an individual's development within genetic limits, shaping unique characteristics from infancy to adolescence.  |
Card: 16 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blanks: Genetic transmission involves combinations of numerous genes, forming an individual's ___, with not all genetic material visibly expressed in ___ . |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
True or False: The phenotype is solely determined by environmental influences. |
Card: 19 / 50 |
|
False. The phenotype is influenced by both genetic factors and environmental conditions.  |
Card: 20 / 50 |
|
How do parents influence their children's development beyond genetic material? |
Card: 21 / 50 |
|
Parents create environments that may align with their genetic predispositions, thereby influencing their children's development through both genetics and the environment.  |
Card: 22 / 50 |
|
What is the significance of understanding the interplay between genes and environment in relation to academic success? |
Card: 23 / 50 |
|
Understanding this interplay helps explain individual outcomes like academic success and job attainment, highlighting how both inherited traits and external circumstances shape opportunities. 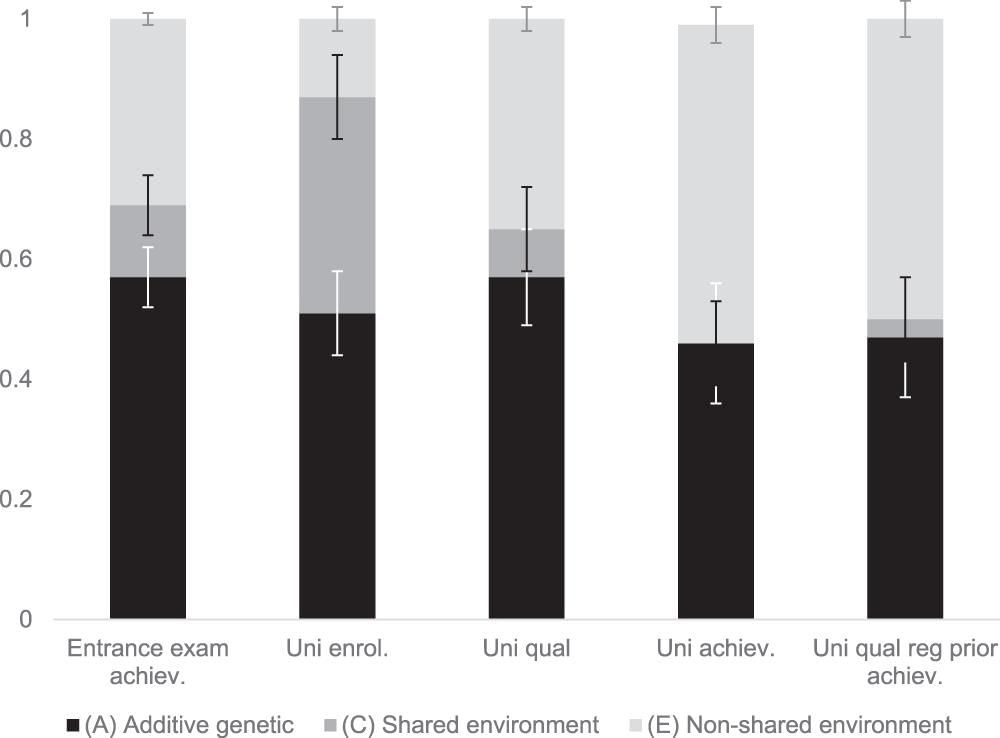 |
Card: 24 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Genes provide a blueprint for development, but ___ factors play a crucial role in shaping an individual's unique characteristics. |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
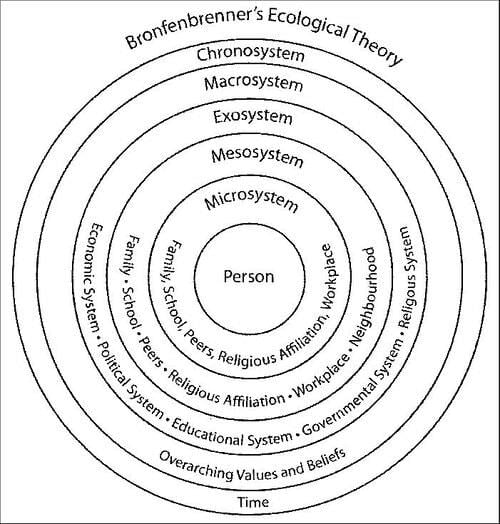
What are the main components of Urie Bronfenbrenner's Ecological Systems Theory? |
Card: 27 / 50 |
|
The main components are the microsystem, mesosystem, exosystem, macrosystem, and chronosystem. 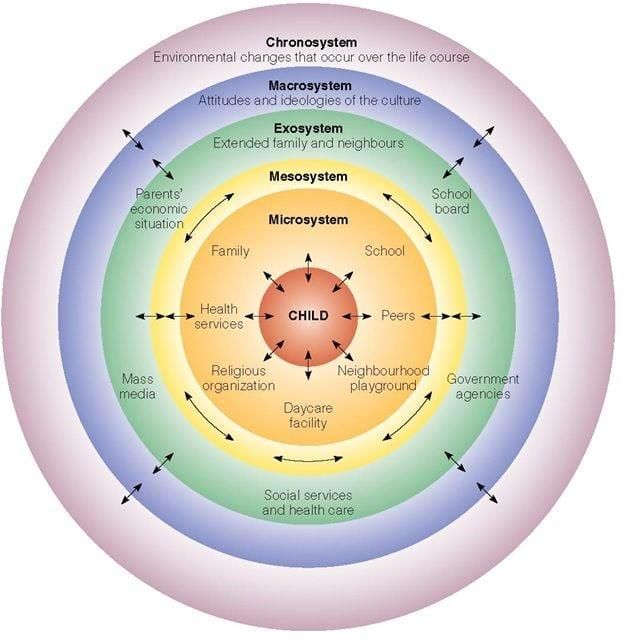 |
Card: 28 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The ___ includes the immediate environment where interactions with family, peers, teachers, and neighbors occur. |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
True or False: The exosystem includes social settings that directly involve the individual. |
Card: 31 / 50 |
|
False. The exosystem includes events in social settings that do not directly involve the individual but affect their immediate context. 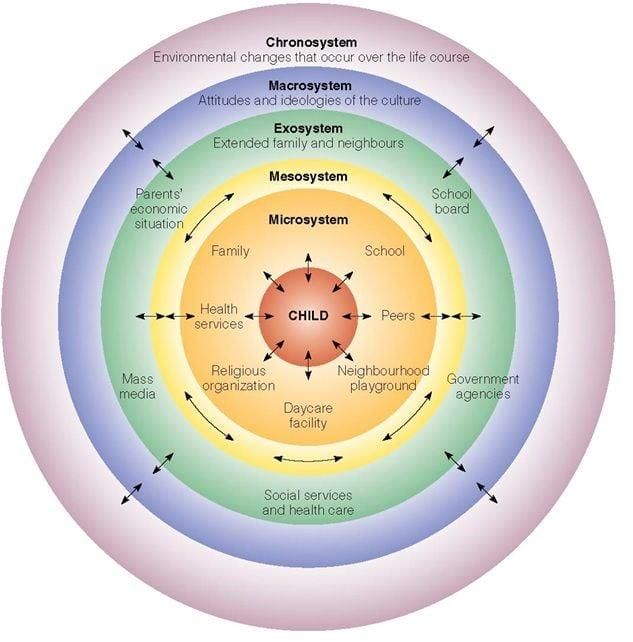 |
Card: 32 / 50 |
|
The macrosystem encompasses the cultural environment in which an individual resides. |
Card: 34 / 50 |
|
In Durganand Sinha's ecological model, what layers significantly influence a child's development? |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
The upper layers such as home, school, and peer groups significantly influence a child's development. |
Card: 36 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blanks: Transitions in life, such as ___, ___, and ___, result from a combination of biological changes and environmental influences. |
Card: 37 / 50 |
|
What role does the chronosystem play in individual development according to Bronfenbrenner? |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
The chronosystem encompasses life events and historical circumstances that impact the individual. 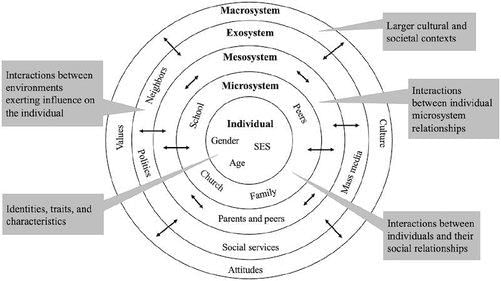 |
Card: 40 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Maternal characteristics such as the mother's age, nutrition, and emotional well-being influence ___ development. |
Card: 43 / 50 |
|
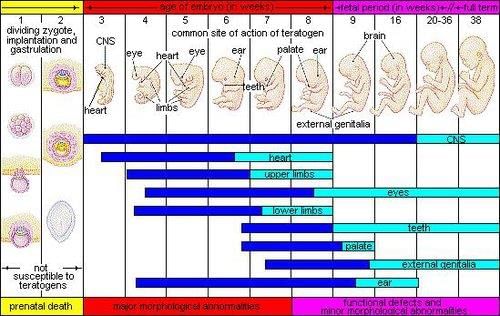
True or False: Environmental pollutants pose no threat to the unborn child during prenatal development. |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
False. Environmental pollutants like carbon monoxide, mercury, and lead endanger the unborn child. 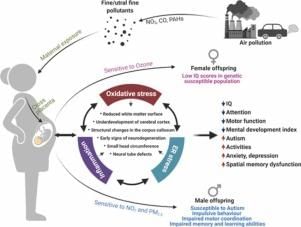 |
Card: 46 / 50 |
|
Teratogens are environmental factors that disrupt normal development and can cause severe abnormalities or even death, affecting the fetus during prenatal development. 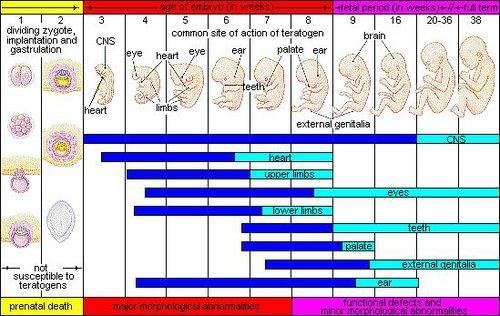 |
Card: 48 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Diseases such as ___ and ___ can impact prenatal development. |
Card: 49 / 50 |