|
Learning is a long-lasting modification in behavior or potential behavior that is the result of an individual's experiences.
|
Card: 2 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Learning is demonstrated by changes in behavior that are relatively permanent and due to ___ and ___. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
True or False: Changes in behavior caused by fatigue or drugs are considered learning. |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The conditioned stimulus (CS) is a stimulus that has been learned through prior experience and is paired with an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) to elicit an ___ response. |
Card: 9 / 50 |
|
Observational learning involves learning by observing and imitating the actions and behaviors of others. |
Card: 12 / 50 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which of the following is NOT a method of learning? A) Classical Conditioning B) Observational Learning C) Reflexive Response D) Cognitive Learning |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Learning can be the result of a single experience, such as a child burning their fingers, which teaches them to be cautious with ___. |
Card: 15 / 50 |
|
What is the primary difference between learning and performance in psychology? |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
Learning refers to the acquisition of new knowledge or skills, while performance is the execution of those skills or knowledge, which may not always reflect true learning. |
Card: 18 / 50 |
|
Simultaneous Conditioning, Delayed Conditioning, Trace Conditioning, and Backward Conditioning. |
Card: 20 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blanks: Aversive conditioning is generally ___ than appetitive conditioning. |
Card: 21 / 50 |
|
What is the primary function of the Skinner Box in operant conditioning experiments? |
Card: 23 / 50 |
|
To allow researchers to observe the effects of reinforcement on behavior as animals learn to press a lever to receive food. |
Card: 24 / 50 |
|
True or False: Delayed conditioning is the least effective method for acquiring a conditioned response (CR). |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
False. Delayed conditioning is the most effective for acquiring a conditioned response. |
Card: 26 / 50 |
|
The lever represents an operant response that the animal must perform to receive a reward. |
Card: 28 / 50 |
|
What impact does the intensity of a conditioned stimulus (CS) have on the acquisition of a conditioned response? |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
A more intense conditioned stimulus accelerates the acquisition of the conditioned response. |
Card: 30 / 50 |
|
The rat learns to press the lever more quickly and efficiently to obtain food through repeated trials. |
Card: 34 / 50 |
|
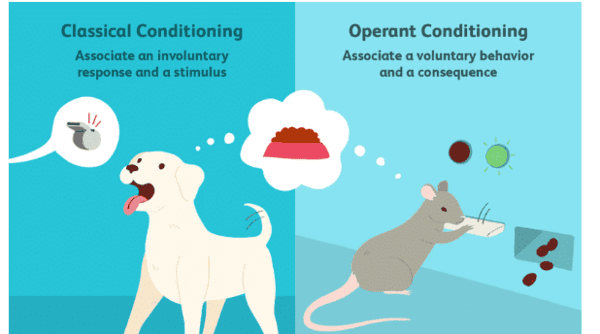
What is operant conditioning and how does it differ from classical conditioning? |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
Operant conditioning is a type of learning where behavior is influenced by its consequences, specifically through reinforcers that increase the likelihood of a response. Unlike classical conditioning, where responses are controlled by stimuli, operant conditioning allows the organism to control its responses based on the consequences it experiences. |
Card: 36 / 50 |
|
False. Negative reinforcement involves stimuli that help organisms escape or avoid unpleasant situations, while punishment aims to decrease the likelihood of a behavior. |
Card: 40 / 50 |
|
Learned helplessness is a phenomenon where continuous failure leads to reduced persistence and performance. It often occurs in situations where individuals feel they have no control over their outcomes, such as in cases of depression. |
Card: 42 / 50 |
|
In reinforcement schedules, continuous reinforcement means ___ while partial reinforcement leads to ___ of learned behaviors. |
Card: 43 / 50 |
|
Delayed reinforcement negatively impacts the effectiveness of reinforcement, leading to lower performance levels. |
Card: 46 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Bobo doll experiment by Albert Bandura demonstrated that children learn behaviors through ___. |
Card: 47 / 50 |
|
Insight learning involves a sudden realization or understanding of a problem that leads to a solution without the need for trial-and-error, while trial-and-error learning requires repeated attempts to find a solution. |
Card: 50 / 50 |