|
Thinking is exclusively a cognitive function of ___ and involves processes such as reasoning and problem-solving. |
Card: 1 / 50 |
|
Identify two key processes involved in thinking that enable us to manipulate and analyze information. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
Thinking often includes the ability to ___, which allows individuals to create scenarios that are not present. |
Card: 7 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The nature of thinking involves examining and processing information obtained from the ___. |
Card: 9 / 50 |
|
What distinguishes thinking from mere observation, such as when viewing a painting? |
Card: 11 / 50 |
|
Thinking involves interpreting deeper meanings and relating them to existing knowledge.  |
Card: 12 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Organized and goal-directed thinking is essential for completing tasks like cooking a meal or solving a ___. |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
Mental images are internal representations of sensory experiences within the mind. They allow individuals to visualize places, events, and other sensory information, facilitating thought processes. |
Card: 16 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blanks: A memory image closely resembles the object being represented, while an ___ image is a vivid and detailed visual representation of something seen before. |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
Natural concepts lack a clearly defined set of features and are often based on prototypes, while logical concepts are clearly defined by a specific set of rules or features.  |
Card: 20 / 50 |
|
False. Concept formation helps organize knowledge, making it easily accessible and streamlining thought processes. |
Card: 22 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Concepts help us to ___ our knowledge and make it easily accessible. |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Forming concepts saves time and effort by streamlining thought processes, allowing for quicker and more efficient cognitive functioning.  |
Card: 28 / 50 |
|
The primary function of concepts is to categorize and organize knowledge based on shared properties and features of ideas and objects.  |
Card: 30 / 50 |
|
A mental set is the tendency to approach problems in a specific way that has previously been successful. This can lead to inflexibility, making it difficult to consider alternative solutions and potentially hindering effective problem-solving. |
Card: 32 / 50 |
|
Lack of motivation can hinder problem-solving. Explain how motivation influences this process. |
Card: 33 / 50 |
|
Motivation plays a critical role in problem-solving because even intelligent individuals may struggle to engage with problems without the desire or interest to solve them. A lack of motivation can lead to disengagement and ineffective problem-solving strategies.  |
Card: 34 / 50 |
|
Inductive reasoning is commonly used in problem-solving. Explain what inductive reasoning involves. |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
Inductive reasoning involves collecting specific observations or evidence and drawing general conclusions from them. It is often employed in scientific inquiry and everyday decision-making to form hypotheses or theories based on patterns observed in data. 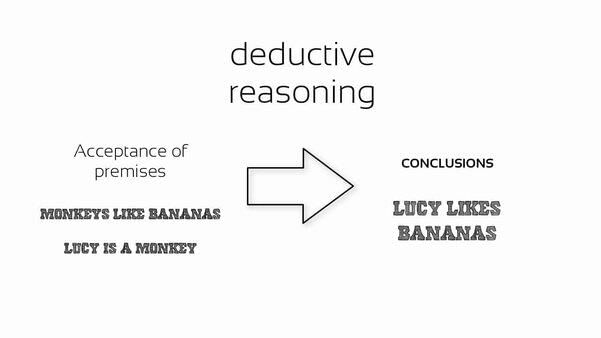 |
Card: 36 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Deductive reasoning uses ___ to arrive at a conclusion, while inductive reasoning uses ___ to infer general principles. |
Card: 37 / 50 |
|
True or False: Analogy is a form of reasoning that only involves comparing two similar objects. |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
False. Analogy involves comparing relationships between two different sets of things, highlighting similarities in their relationships rather than merely in their characteristics. |
Card: 40 / 50 |
|
Reasoning is a cognitive process that involves the analysis of information to draw conclusions, enabling individuals to make informed decisions and solve problems effectively. |
Card: 42 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The ability to solve problems can be significantly impaired by a lack of ___. |
Card: 43 / 50 |
|
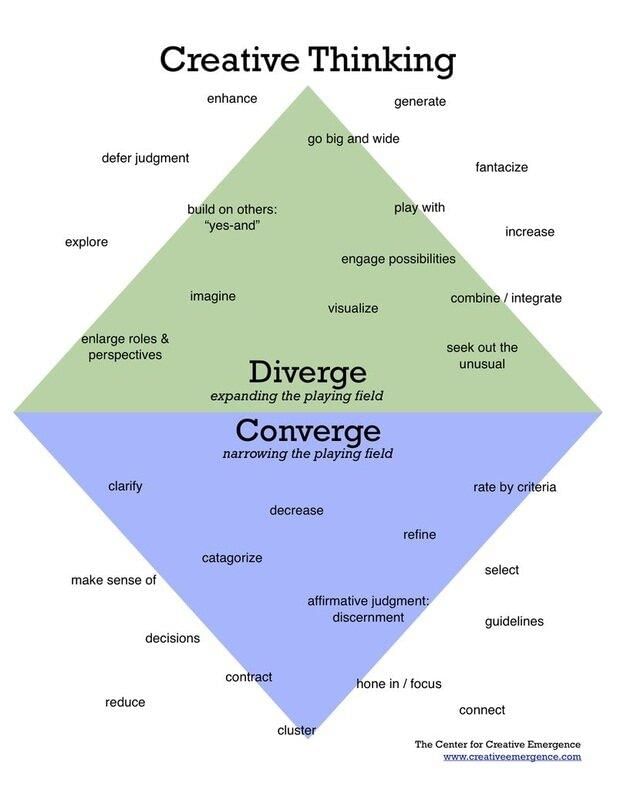
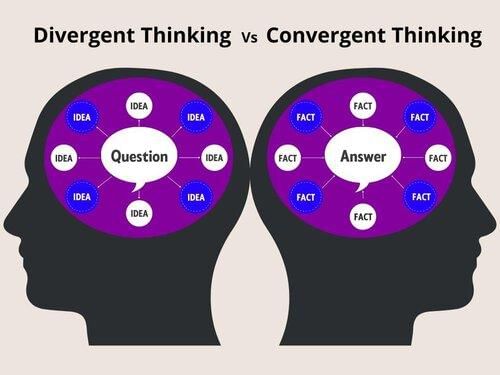
What are the two main types of thinking identified by J.P. Guilford related to creativity? |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
In the context of creative thinking, the stage where the problem is clearly defined and information is collected is known as ___? |
Card: 47 / 50 |
|
True or False: Divergent thinking is characterized by seeking a single correct answer to a problem. |
Card: 49 / 50 |