|
Card: 2 / 50 |
Social stratification refers to the structured inequalities between different groups in society regarding their access to material or symbolic rewards, highlighting differences in power and advantage among various groups.  |
|
Card: 3 / 50 |
Social stratification affects an individual's health, longevity, and educational success. True or False? |
|
Card: 4 / 50 |
True. Stratification impacts every aspect of an individual's life, including opportunities for health, longevity, security, educational success, job satisfaction, and political influence.  |
|
Card: 5 / 50 |
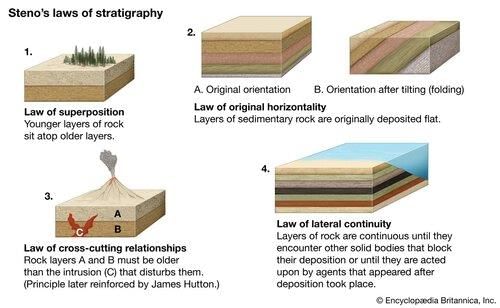
Fill in the blanks: Social stratification can be compared to geological layers of rock, where society has different levels or ___ of people, with those at the top having more advantages than those at the ___ . |
|
Card: 8 / 50 |
Social stratification organizes society by creating a hierarchy where different groups have unequal access to resources and opportunities, leading to systematic differences in power and privilege.  |
|
Card: 9 / 50 |
Which aspect of life is NOT directly affected by social stratification? a) Job satisfaction b) Political influence c) Weather patterns d) Educational success |
|
Card: 10 / 50 |
C) Weather patterns. Social stratification affects job satisfaction, political influence, and educational success, but it does not directly impact weather patterns.  |
|
Card: 12 / 50 |
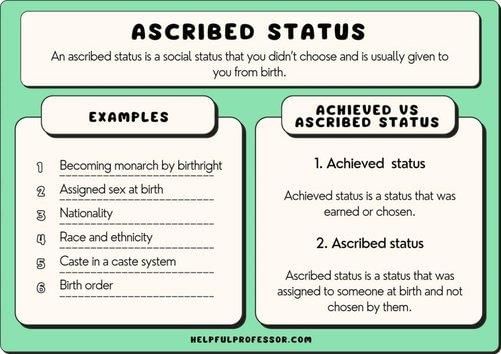
A person's position is determined by status attributes ascribed by birth, rather than by achievements throughout life. 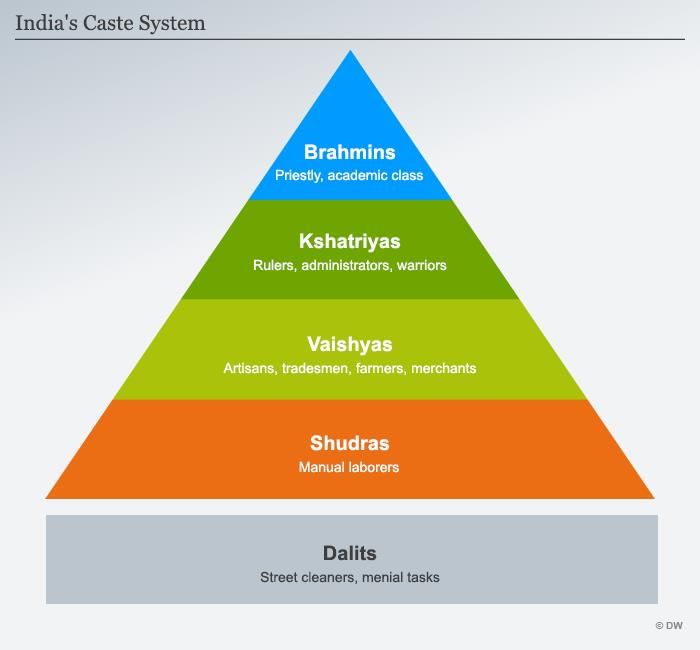 |
|
Card: 15 / 50 |
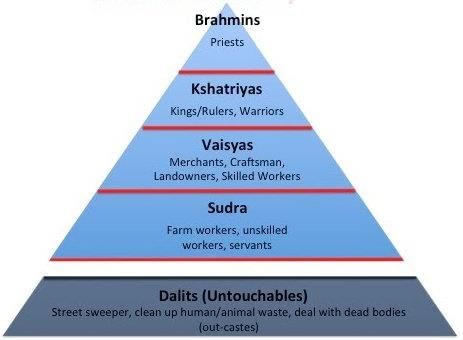
True or False: In traditional Indian caste hierarchy, the Brahmins are considered the least pure. |
|
Card: 17 / 50 |
What significant effect did urbanization have on the traditional caste system in India? |
|
Card: 18 / 50 |
Urbanization challenged traditional practices like endogamy and ritual avoidance of contact with lower castes.  |
|
Card: 19 / 50 |
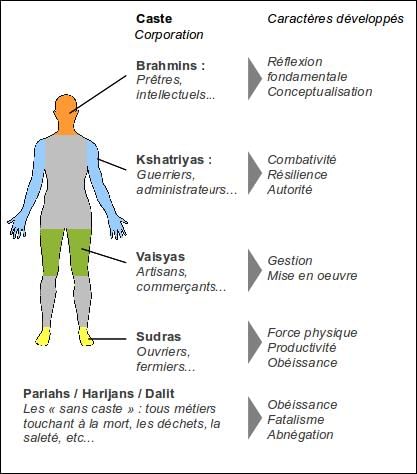
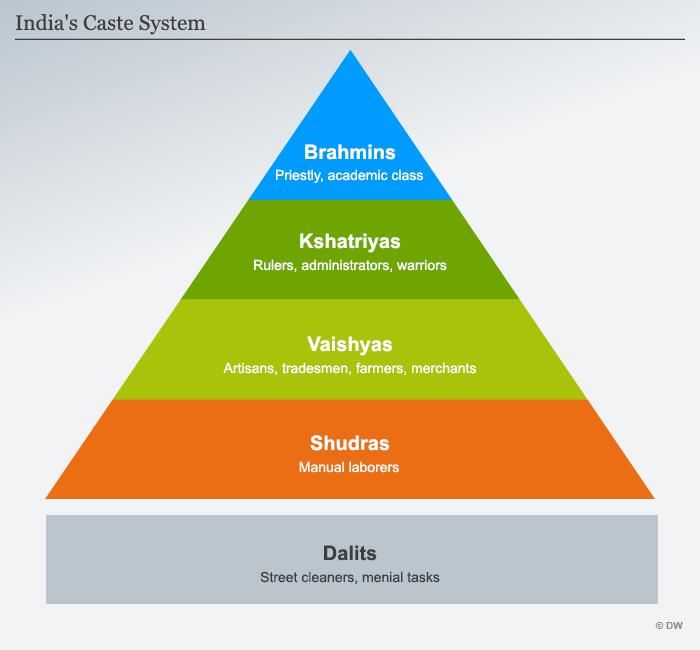
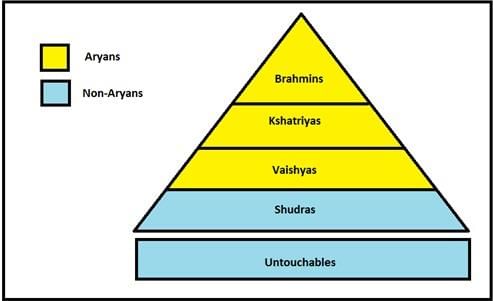
Fill in the blank: The caste system in India is often described in terms of the four-fold varna: Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and ___. |
|
Card: 21 / 50 |
What did A.R. Desai observe about the impact of urbanization on caste interactions? |
|
Card: 22 / 50 |
Desai noted that urban spaces led to interactions among different caste members, including those from depressed classes, despite caste not disappearing.  |
|
Card: 23 / 50 |
Multiple Choice: Which group is considered to be at the bottom of the traditional caste hierarchy? A) Brahmins B) Kshatriyas C) Vaishyas D) Panchamas |
|
Card: 25 / 50 |
What are the two primary perspectives on social class discussed in the content? |
|
Card: 26 / 50 |
The two primary perspectives are Marx's theory, which focuses on the relationship to the means of production, and Weber's concept of life chances, which considers economic relations as well as prestige and political power. 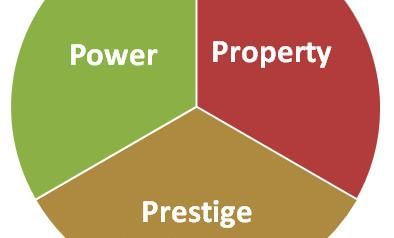 |
|
Card: 27 / 50 |
Caste discrimination persists in private interactions despite changes in ___ settings. |
|
Card: 29 / 50 |
True or False: The traditional caste system is characterized by a flexible structure that allows for social mobility. |
|
Card: 30 / 50 |
False. The traditional caste system is characterized by a fixed and rigid hierarchy that is transmitted across generations. 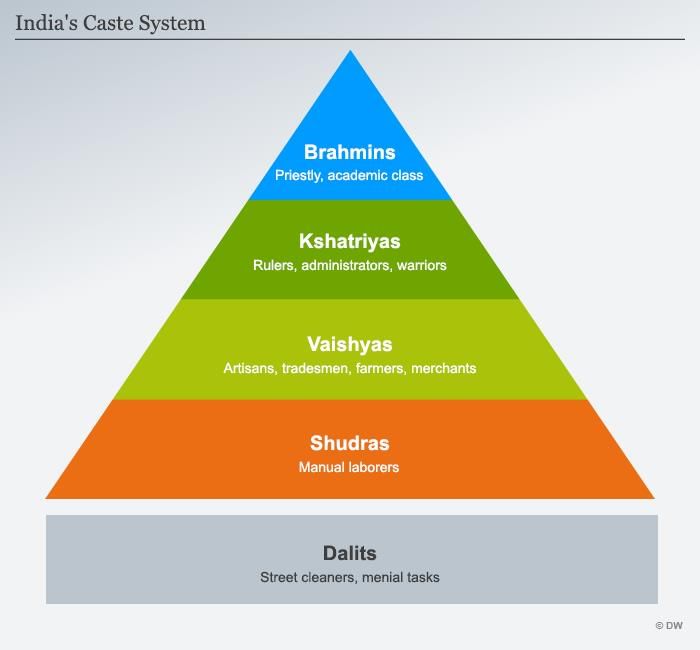 |
|
Card: 31 / 50 |
According to functionalist theory, social stratification is seen as a necessary mechanism for ___ individuals within the social structure. |
|
Card: 33 / 50 |
What does sociological research reveal about the ideal models of social mobility in society? |
|
Card: 34 / 50 |
Sociological research reveals that ideal models of perfect mobility are rarely achieved, highlighting ongoing challenges to both the caste system and social mobility. 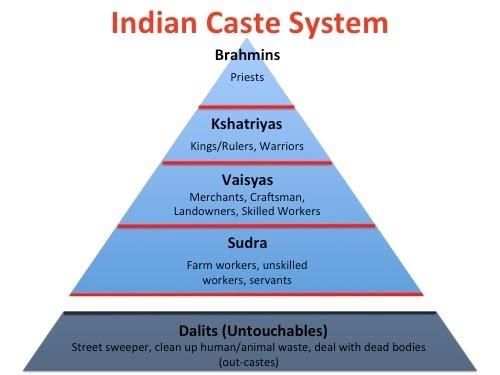 |
|
Card: 35 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Individuals at lower levels of the social system face significant ___ challenges along with social disadvantages. |
|
Card: 38 / 50 |
Democracy influences the caste system by allowing castes to act as interest groups and enabling discriminated castes to assert their democratic rights.  |
|
Card: 40 / 50 |
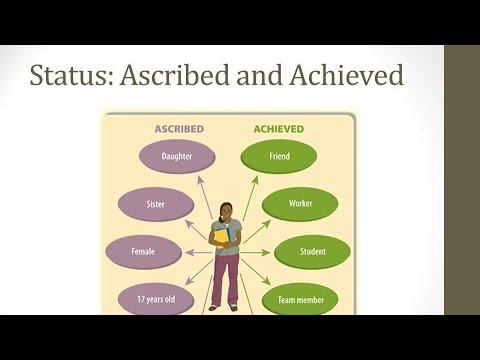
Status refers to a person's social position which comes with specific rights and responsibilities, while role is the active aspect of that status, representing how individuals behave in that position.  |
|
Card: 41 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Ascribed status is a position assigned at birth or involuntarily, often based on factors such as ___, ___, or ___ . |
|
Card: 43 / 50 |
True or False: Achieved status is a position that one is born into and cannot change. |
|
Card: 46 / 50 |
Status set refers to the collection of multiple statuses that an individual holds simultaneously. 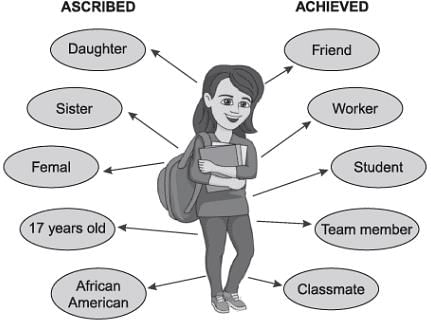 |
|
Card: 49 / 50 |
Which type of status is more emphasized in modern societies: ascribed status or achieved status? |