|
Card: 2 / 50 |
The two main sociological perspectives are the functionalist perspective, which views social institutions as complex systems that meet societal needs, and the conflict perspective, which argues that institutions serve the interests of dominant groups. 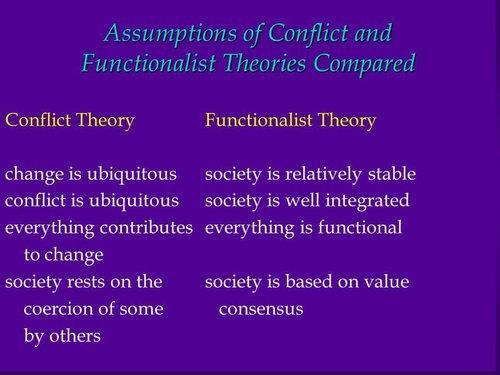 |
|
Card: 3 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Social institutions such as family and religion are considered ___ institutions, while law and education are considered ___ institutions. |
|
Card: 5 / 50 |
True or False: According to the conflict perspective, all individuals are treated equally by social institutions. |
|
Card: 6 / 50 |
False. The conflict perspective argues that social institutions serve the interests of dominant groups, leading to inequality. 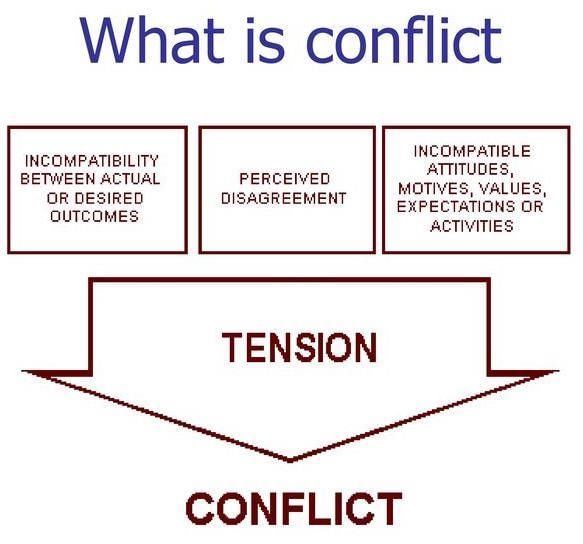 |
|
Card: 7 / 50 |
What role do social institutions play in society according to the functionalist perspective? |
|
Card: 8 / 50 |
Social institutions are seen as essential systems of social norms, beliefs, values, and role relationships that emerge to fulfill societal needs. 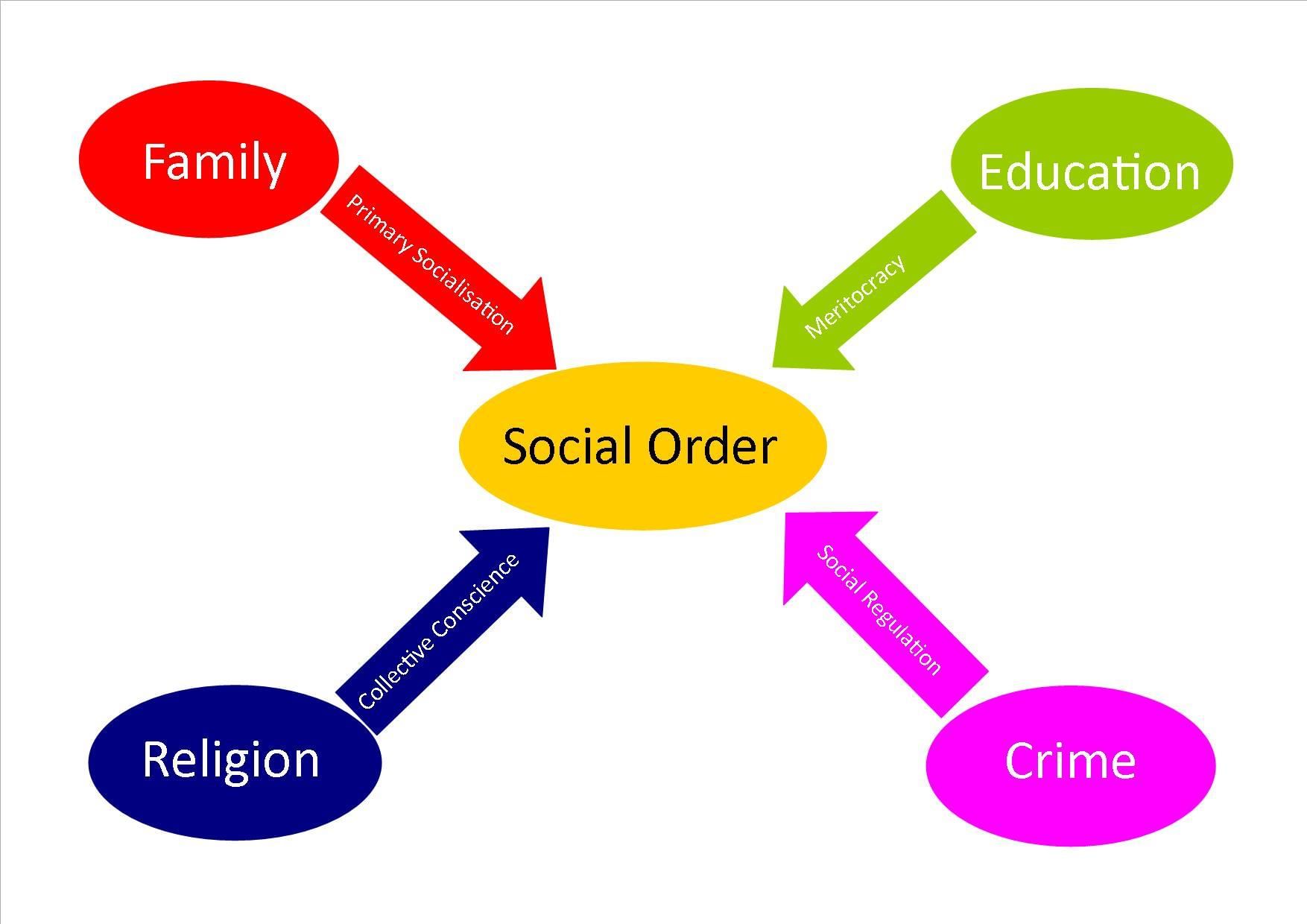 |
|
Card: 9 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: An institution operates based on established ___ which can be set by law or custom. |
|
Card: 12 / 50 |
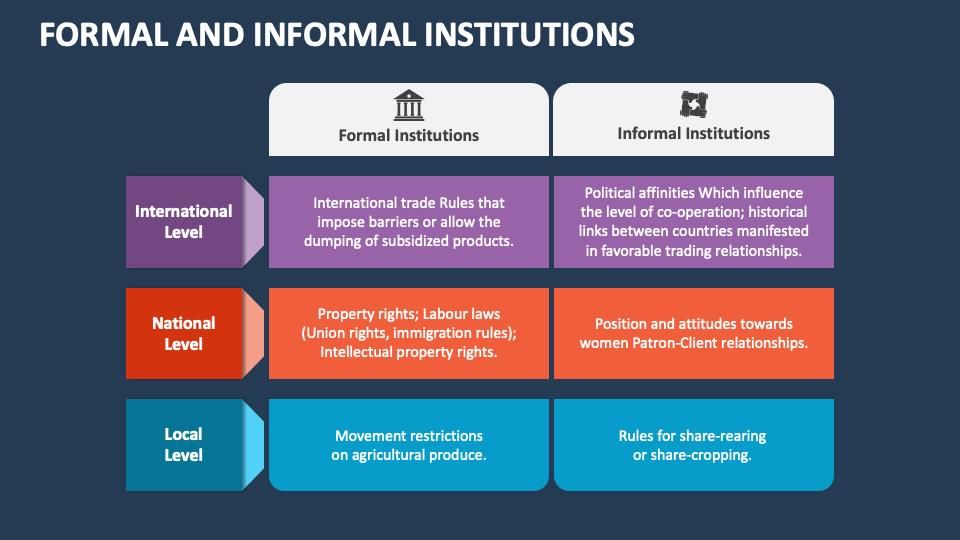
Informal institutions include family and religion, while formal institutions include law and education. 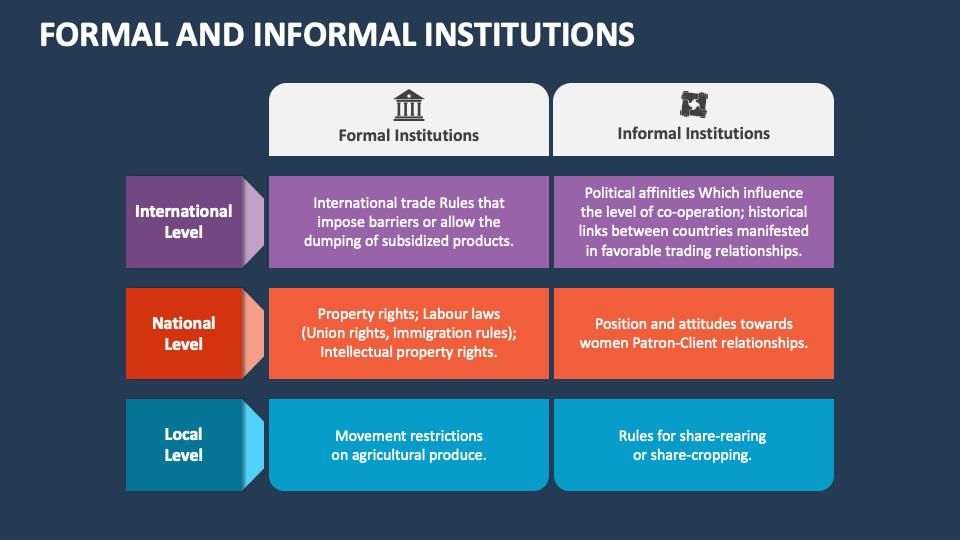 |
|
Card: 14 / 50 |
False. Institutions can be viewed as both means to an end and ends in themselves. |
|
Card: 15 / 50 |
What role does the functionalist perspective attribute to the family in society? |
|
Card: 16 / 50 |
The functionalist perspective argues that the family is crucial for fulfilling society's basic needs and maintaining social order.  |
|
Card: 17 / 50 |
The shift from nuclear families to joint families in India is primarily attributed to an increase in ___ and ___ in life expectancy. |
|
Card: 19 / 50 |
True or False: Matrilocal family structures involve living with the husband's parents. |
|
Card: 21 / 50 |
What is the primary reason for greater investment in male children according to societal beliefs? |
|
Card: 22 / 50 |
The belief that a male child will support parents in old age, while a female child will leave upon marriage.  |
|
Card: 23 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The division of labor within the nuclear family typically involves the husband taking on the '___' role and the wife assuming the '___' role. |
|
Card: 26 / 50 |
It led to a decline in marriage due to the withdrawal of welfare schemes and economic insecurity, influencing people to refuse marriage.  |
|
Card: 29 / 50 |
True or False: Functionalists believe that modern industrial societies function best when men handle family care and women earn the family's income. |
|
Card: 30 / 50 |
False. Functionalists believe that women should handle family care while men earn the family's income.  |
|
Card: 32 / 50 |
Matrilineal societies are characterized by tracing lineage through the mother. 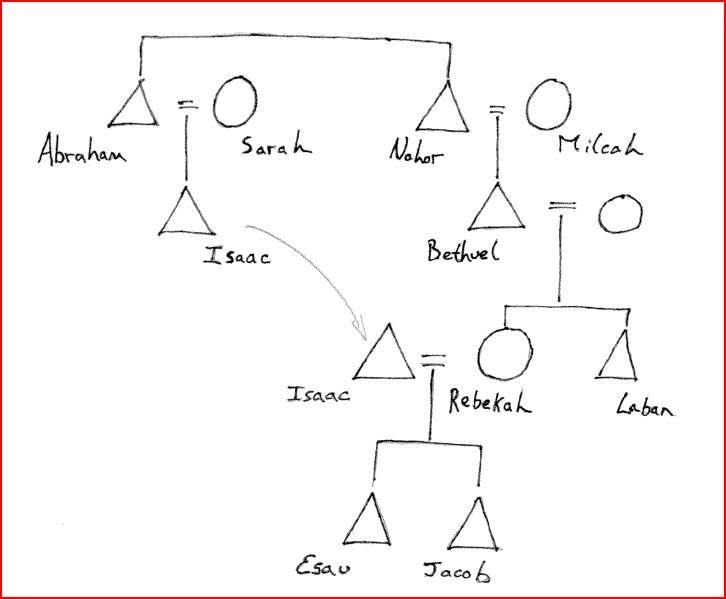 |
|
Card: 33 / 50 |
The institution of marriage has historically performed ___ functions in various contexts. |
|
Card: 36 / 50 |
Monogamy is a marital structure that restricts individuals to one spouse at a time, meaning that a man can have only one wife and a woman can have only one husband simultaneously.  |
|
Card: 37 / 50 |
In which economic conditions might polyandry arise, and what purpose can it serve? |
|
Card: 38 / 50 |
Polyandry may arise in harsh economic conditions where a single male cannot adequately support a wife and children. It can serve as a means of population limitation as well.  |
|
Card: 39 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Serial monogamy allows individuals to marry again after ___ or ___ but prohibits having more than one spouse at the same time. |
|
Card: 41 / 50 |
True or False: Exogamy requires individuals to marry within their own culturally defined group. |
|
Card: 44 / 50 |
Consanguineous kin are relatives related by blood, while affines are relatives related through marriage. 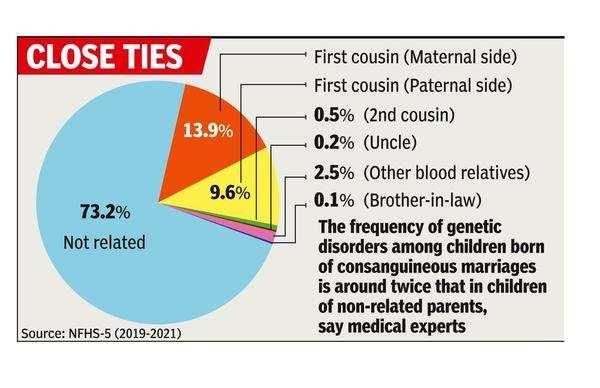 |
|
Card: 45 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: In India, village exogamy facilitates the bride's adjustment into the new family and minimizes interference from her ___ kin. |
|
Card: 48 / 50 |
The family of orientation is the family into which a person is born, providing early socialization and support.  |