|
What does the ability of the Jarawas, Great Andamanese, and Shompens to anticipate disasters illustrate about indigenous cultures? |
Card: 1 / 48 |
|
It illustrates that indigenous cultures can effectively cope with natural challenges, demonstrating that modern science and technology do not necessarily make contemporary cultures superior.  |
Card: 2 / 48 |
|
The diverse environments inhabited by humans include mountains, plains, deserts, and ___? |
Card: 3 / 48 |
|
True or False: Modern cultures are inherently superior to indigenous cultures due to their access to technology. |
Card: 5 / 48 |
|
False. Modern cultures should not be ranked as superior; effectiveness in dealing with challenges is more important.  |
Card: 6 / 48 |
|
Cultures should be evaluated based on their ability to ___ with natural challenges. |
Card: 7 / 48 |
|
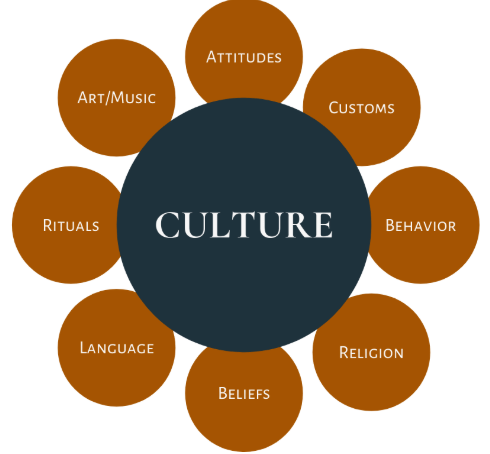
Edward Tylor defined culture as a complex whole that includes knowledge, beliefs, art, morals, laws, customs, and any other capabilities and habits acquired by individuals as members of society. 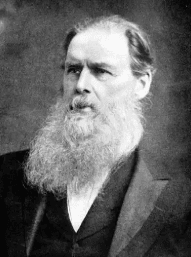 |
Card: 10 / 48 |
|
Culture was historically viewed as a means to separate those with refined tastes from the ___ masses. |
Card: 11 / 48 |
|
True or False: Culture is solely associated with high art forms such as classical music and dance. |
Card: 13 / 48 |
|
False. Culture encompasses a way of life that includes all members of society and is not limited to high art forms.  |
Card: 14 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blanks: Culture is not something that divides people based on their ___. |
Card: 15 / 48 |
|
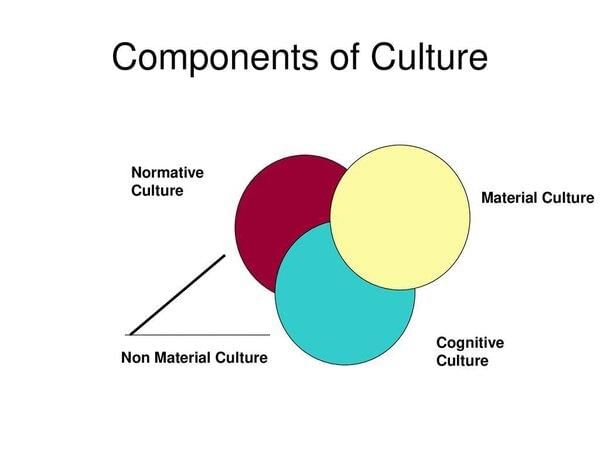
Fill in the blank: The cognitive dimension of culture deals with how we ___ and make sense of information. |
Card: 21 / 48 |
|
True or False: In non-literate societies, knowledge is primarily transmitted through written texts. |
Card: 23 / 48 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Writing allows for more elaborate expression and documentation of art, whereas oral traditions emphasize repetition for memorization. |
Card: 26 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The normative dimension of culture includes the ___ we follow in our behavior. |
Card: 27 / 48 |
|
It raises questions about how new forms of communication affect our attention span and cognitive processes. 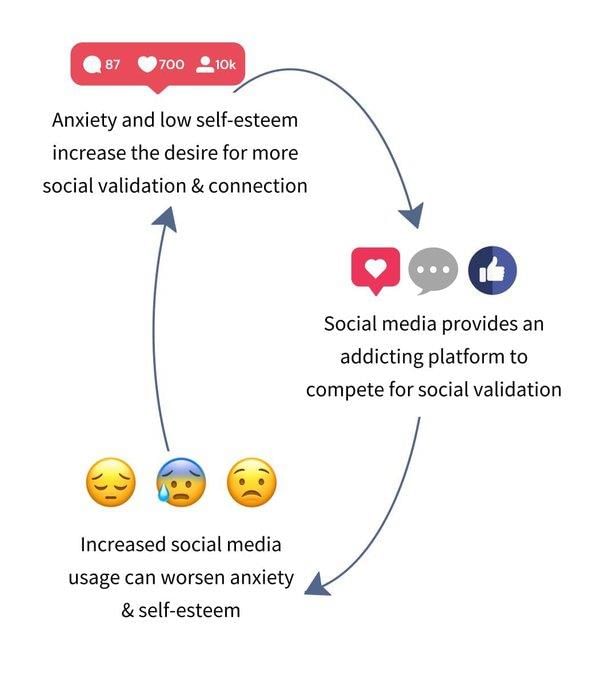 |
Card: 30 / 48 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which dimension of culture involves the use of tools and materials? A) Cognitive B) Normative C) Material D) Social |
Card: 31 / 48 |
|
Societal literacy determines access to written knowledge, which shapes cultural practices and can create disparities in how different communities understand and engage with their culture. |
Card: 34 / 48 |
|
Norms are unwritten rules that guide behavior and can vary from one group to another, while laws are official rules established by the government that apply uniformly to everyone.  |
Card: 36 / 48 |
|
False. Norms vary between different cultures and social groups, while laws are enforced uniformly. 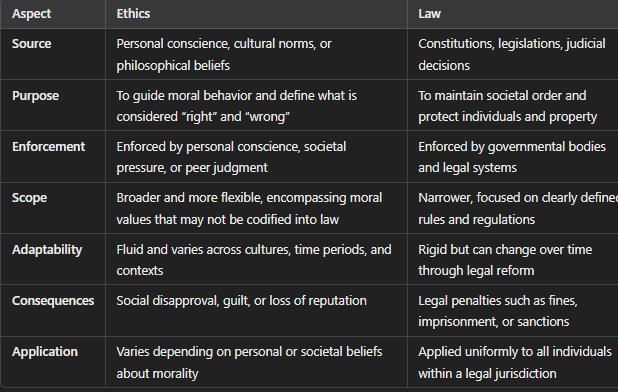 |
Card: 40 / 48 |
|
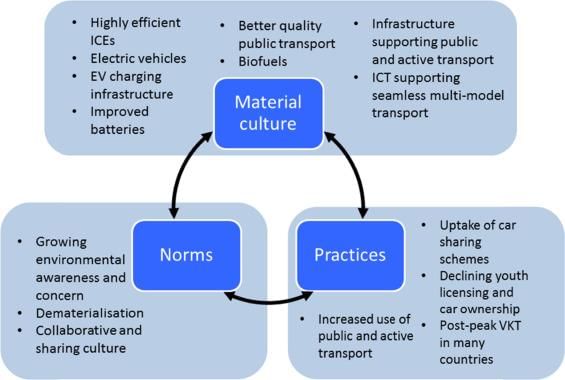
Fill in the blank: The material aspect of culture includes ___, ___, and modes of transportation. |
Card: 41 / 48 |
|
True or False: Laws can sometimes be discriminatory, favoring certain groups over others. |
Card: 45 / 48 |
|
True. Laws are meant to be universal, but their enforcement can sometimes be biased. |
Card: 46 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: Norms can be seen as ___ rules that dictate how we should act in specific contexts. |
Card: 47 / 48 |