|
What is the significance of social stratification in understanding individual access to social resources? |
Card: 1 / 50 |
|
Social stratification highlights how individuals' positions in the social hierarchy influence their access to resources, which can vary based on socioeconomic class.  |
Card: 2 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The three essential concepts discussed in sociology to understand the interaction between individuals and society are structure, stratification, and ___. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
True or False: The dialectical relationship between the individual and society is not important in sociology. |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
Socioeconomic class refers to a group of individuals sharing similar economic status, which affects their access to resources such as education, healthcare, and employment opportunities.  |
Card: 8 / 50 |
|
Social structure consists of recurring patterns in human behavior and relationships, sustained over time through institutions like schools, ensuring social reproduction. |
Card: 10 / 50 |
|
True or False: Karl Marx believed that social structures are entirely constraining and do not allow for human agency. |
Card: 11 / 50 |
|
False. Karl Marx recognized that while social structures constrain individuals, there is also room for human agency and creativity to maintain and transform these structures.  |
Card: 12 / 50 |
|
Social stratification refers to ___ between social classes in terms of access to rewards. |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
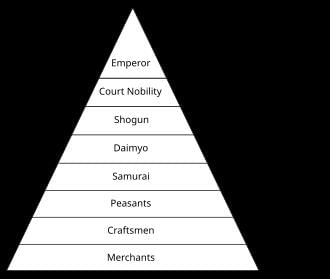
What are the most apparent forms of social stratification in contemporary societies? |
Card: 15 / 50 |
|
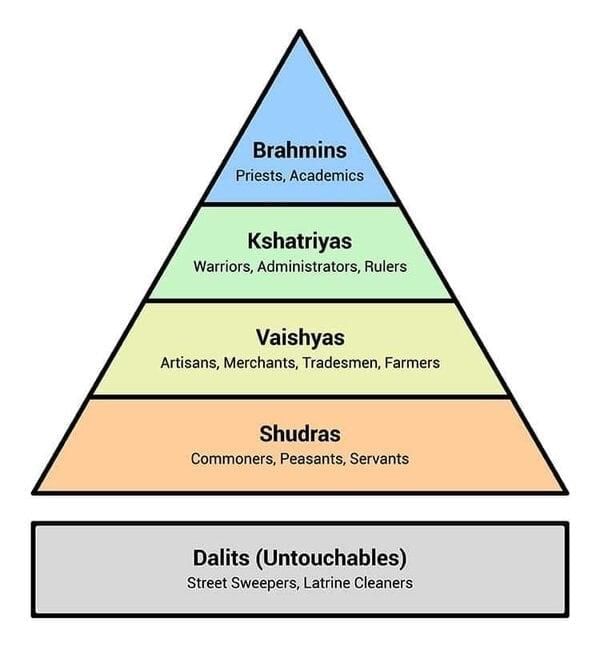
Fill in the blank: The caste system is a form of social stratification characterized by ___ and ___ characteristics. |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
Which sociologist emphasized the idea that society has a solidity similar to physical structures? |
Card: 19 / 50 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which of the following factors is NOT commonly associated with social stratification? A) Race B) Gender C) Height D) Class |
Card: 21 / 50 |
|
The needs of different groups, as no single individual can fulfill all demands alone. 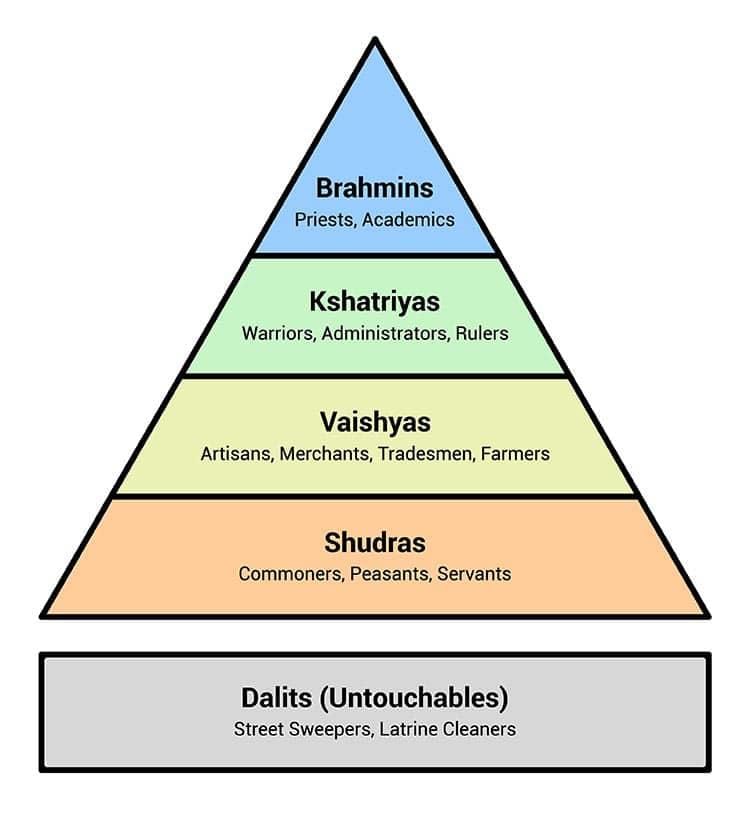 |
Card: 24 / 50 |
|
Life chances are defined as the tangible benefits that enhance a person's ___ and include factors such as wealth and job stability. |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
True or False: Social status refers to the financial resources a person possesses. |
Card: 27 / 50 |
|
False. Social status refers to the level of respect or importance a person holds in society. |
Card: 28 / 50 |
|
The ability of one group to exert power and control over another group is known as ___ influence. |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Social structure and stratification impact the opportunities and resources available to individuals and groups, shaping their ability to ___, collaborate, and engage in conflict. |
Card: 31 / 50 |
|
Which of the following is NOT a benefit that advantaged groups may enjoy? A) Job stability B) Limited leisure time C) Health insurance D) Wealth |
Card: 33 / 50 |
|
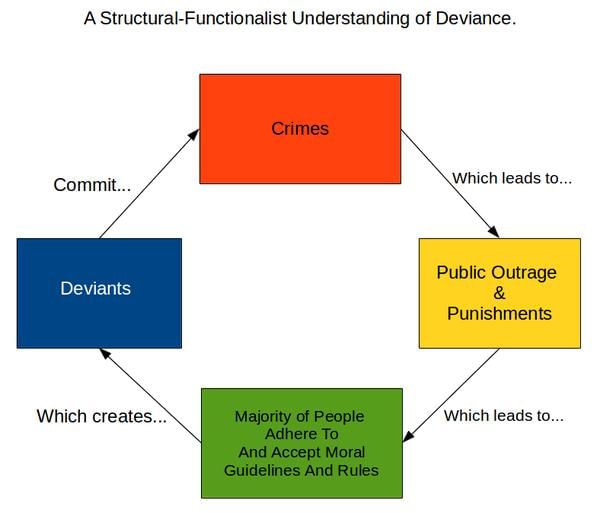
What does the conflict perspective in sociology emphasize regarding social interactions? |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
The conflict perspective examines how cooperation varies across societies and how production relations generate conflicts, revealing hidden power struggles and discrimination based on caste, class, or patriarchy. |
Card: 36 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The functionalist perspective assumes that different components of society have a role in ___ and ___ society. |
Card: 37 / 50 |
|
True or False: According to MacIver and Page, social processes are static and do not involve change within the social structure. |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
False. Social processes are described as the continuous change that takes place within the social structure.  |
Card: 40 / 50 |
|
What do both Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim assert about human collaboration in society? |
Card: 41 / 50 |
|
They assert that humans must collaborate to meet their basic needs and to produce and reproduce themselves and their environment.  |
Card: 42 / 50 |
|
What are the universal characteristics of societies according to the functionalist approach? |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
Collaboration, competition, and conflict are recognized as universal characteristics of all societies. 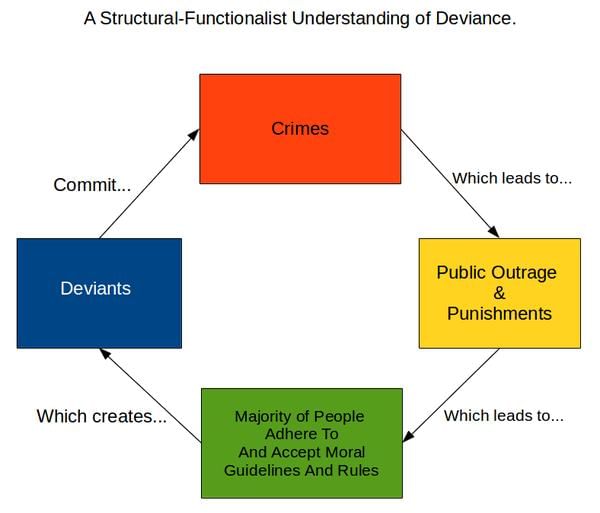 |
Card: 46 / 50 |
|
What is the primary assumption underlying the process of cooperation among individuals? |
Card: 47 / 50 |
|
Cooperation assumes that individuals will act with sympathy and empathy towards one another, working together voluntarily towards common objectives. |
Card: 48 / 50 |
|
Competition can be defined as a struggle between individuals or groups vying for ___ resources. |
Card: 49 / 50 |