|
Card: 2 / 50 |
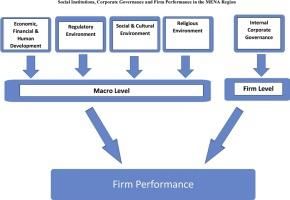
Social change refers to the transformation of people's attitudes and behaviors in society. Its main drivers include environmental, technological, economic, political, and cultural factors.  |
|
Card: 3 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Internal change occurs when the ideals and values of a particular period significantly differ from those of the ___ age. |
|
Card: 5 / 50 |
True or False: External change refers to changes in people's attitudes and behaviors. |
|
Card: 6 / 50 |
False. External change refers to changes in the structures and foundations of society, such as family and marriage.  |
|
Card: 8 / 50 |
Endogenous change refers to changes that originate from within a society, while exogenous change involves influences from outside the society.  |
|
Card: 9 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Structural change refers to alterations in the institutions that constitute a society or in the rules that govern these ___. |
|
Card: 12 / 50 |
The introduction of paper currency significantly shifted the organization of financial markets and transactions, altering the economic structure of society. |
|
Card: 13 / 50 |
Multiple Choice: Which of the following is NOT considered a main driver of societal change? A) Technological B) Cultural C) Historical D) Environmental |
|
Card: 16 / 50 |
The two types of changes are internal change and external change (or structural change).  |
|
Card: 17 / 50 |
What distinguishes endogenous change from exogenous change in sociological contexts? |
|
Card: 18 / 50 |
Endogenous change originates from within a society, while exogenous change comes from outside influences.  |
|
Card: 19 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Darwin's theory of evolution emphasizes the concept of ____, where only the most adaptable organisms survive. |
|
Card: 21 / 50 |
True or False: The Industrial Revolution is an example of radical change that significantly transformed societal values and practices. |
|
Card: 24 / 50 |
Environmental changes can have irreversible effects on society, leading to new social dynamics and job opportunities, or causing destruction that alters societal structures permanently. 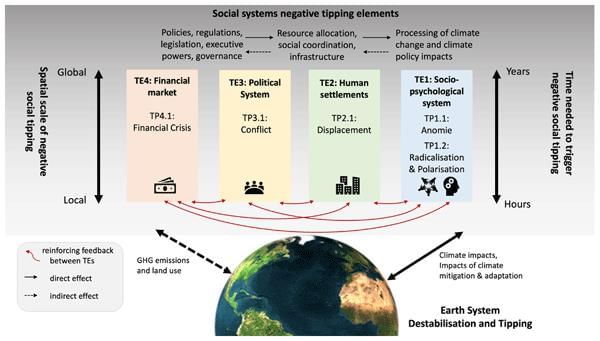 |
|
Card: 25 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The introduction of universal adult suffrage, allowing voting for those at least ___ years old, marked a significant political shift. |
|
Card: 27 / 50 |
How did technological advancements during the Industrial Revolution influence social change? |
|
Card: 28 / 50 |
Technological advancements catalyzed social change by transforming economic systems, improving productivity, and altering labor dynamics. 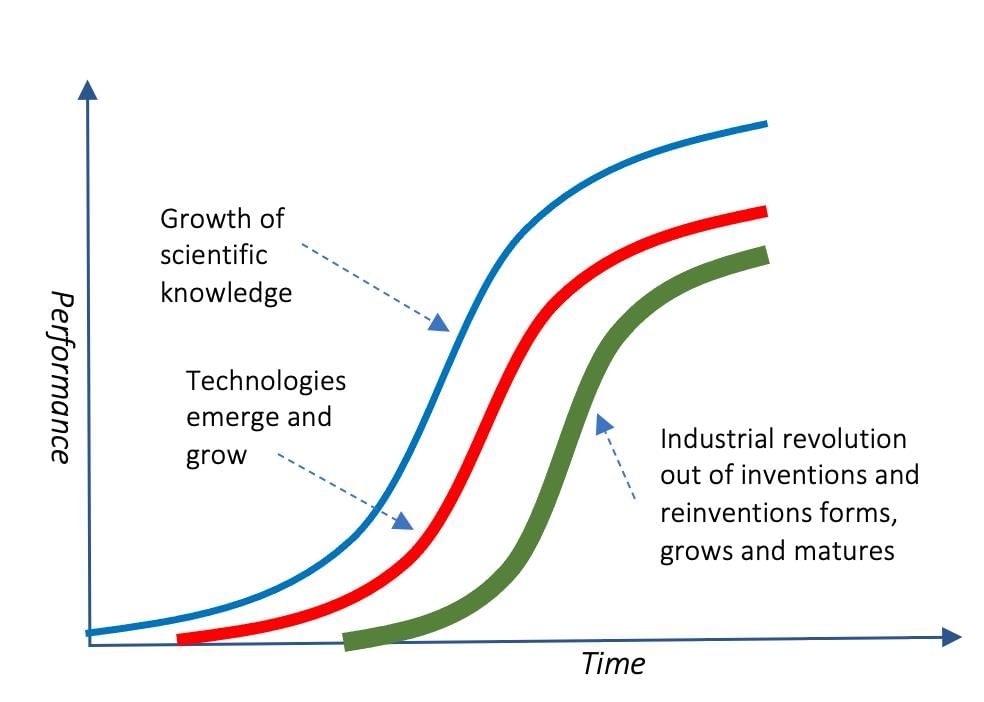 |
|
Card: 29 / 50 |
True or False: Cultural change only occurs through technological advancements. |
|
Card: 30 / 50 |
False: Cultural change can also occur through shifts in behavior, religious beliefs, and social norms.  |
|
Card: 31 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The bhakti movement significantly impacted the social structure of medieval India by influencing ___ norms. |
|
Card: 36 / 50 |
Societies use a combination of forced obedience and voluntary consent to maintain social order.  |
|
Card: 37 / 50 |
True or False: The dominant group in society often embraces changes that challenge their norms and values. |
|
Card: 38 / 50 |
False. The dominant group typically resists changes that could destabilize their social standing.  |
|
Card: 39 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Social control refers to the intentional maintenance and promotion of particular social patterns, values, and ___. |
|
Card: 42 / 50 |
Power is the ability to influence someone to act in your favor, even against their will. 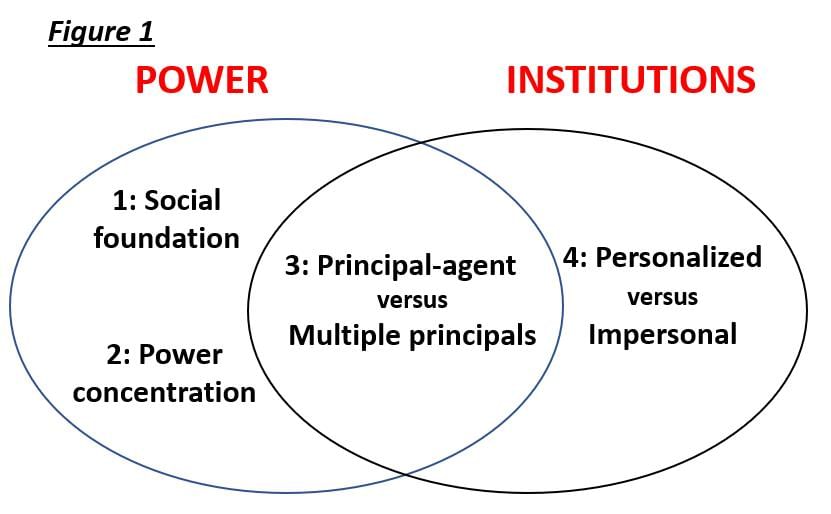 |
|
Card: 43 / 50 |
Which type of power is described as being based on influence rather than legal authority? |
|
Card: 45 / 50 |
True or False: Social control is always implemented through coercive measures. |
|
Card: 46 / 50 |
False. Social control can also be achieved through internalized pressure and voluntary compliance.  |
|
Card: 47 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Members of society should have the freedom to choose whether to follow the rules and values of their ___. |
|
Card: 49 / 50 |
What is the main characteristic of the power dynamic described in the content? |
|
Card: 50 / 50 |
It is a stable relationship where the dominant group significantly influences societal behaviors, often leading to forced cooperation without confrontation. |