|
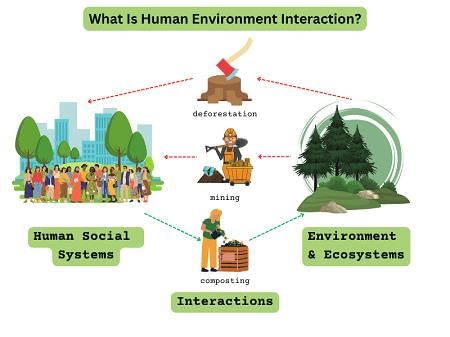
Human intervention and ecological change are mutually influencing; society affects the natural environment, and in turn, the natural environment shapes societal structures. |
Card: 2 / 48 |
|
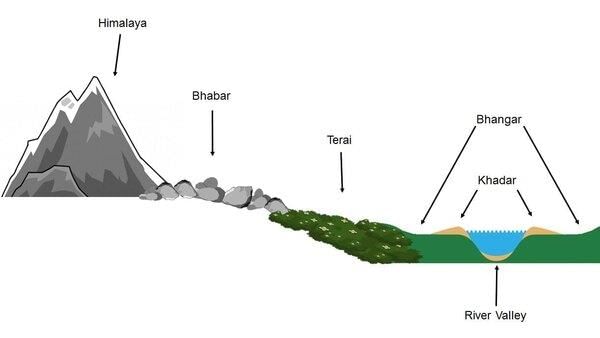
Fill in the blanks: The Indo-Gangetic floodplain is known for its ___ soil that supports ___ settlements. |
Card: 3 / 48 |
|
Capitalism has led to various environmental impacts such as urban air pollution, resource conflicts, and global warming, affecting ecosystems and biodiversity.  |
Card: 8 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The high productivity of the Indo-Gangetic floodplain leads to surpluses that can sustain ___ activities. |
Card: 9 / 48 |
|
Fertile soil enables extensive agricultural productivity, which supports larger populations and allows for the development of complex hierarchical societies and states.  |
Card: 12 / 48 |
|
True or False: The 'nature-nurture' debate suggests that genetics alone shapes individual behavior. |
Card: 15 / 48 |
|
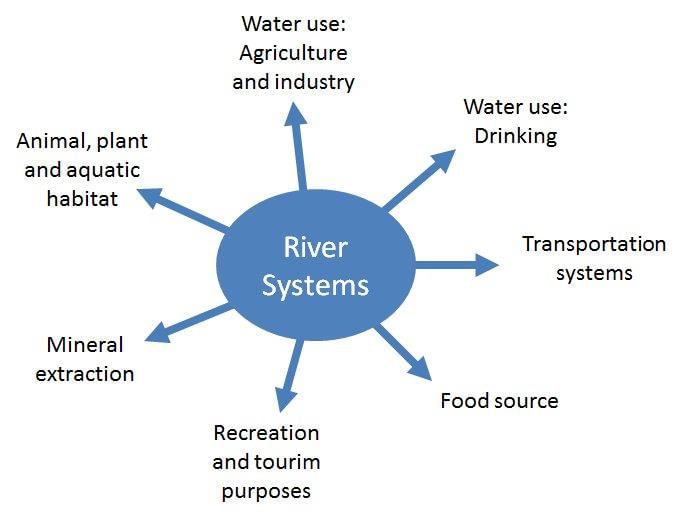
What multifaceted aspects of a river's cultural significance can be reduced to a single calculation for entrepreneurs? |
Card: 17 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: Social organization plays a significant role in determining how society interacts with the ___. |
Card: 19 / 48 |
|
True or False: Historical social upheavals had no impact on the perception of women's and Black people's capabilities. |
Card: 21 / 48 |
|
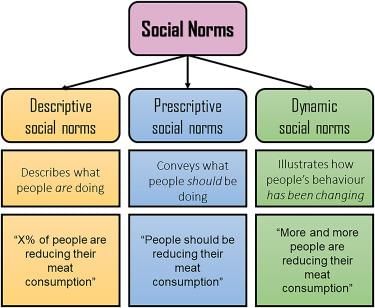
How do social norms and values affect the interaction between society and the environment? |
Card: 23 / 48 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
What are the primary resources being depleted due to intensive agriculture, industry, and urbanization? |
Card: 25 / 48 |
|
Water and land resources, including aquifers and habitats for biodiversity such as forests and wetlands. 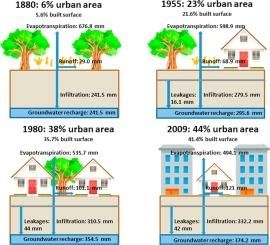 |
Card: 26 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: Air pollution contributes to respiratory problems and is a critical concern in both ___ and ___ areas. |
Card: 27 / 48 |
|
True or False: Global warming is primarily caused by the depletion of fossil fuels. |
Card: 29 / 48 |
|
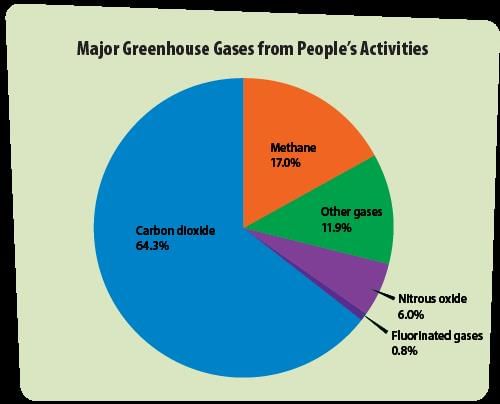
False. Global warming is primarily caused by greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane trapping heat in the atmosphere. 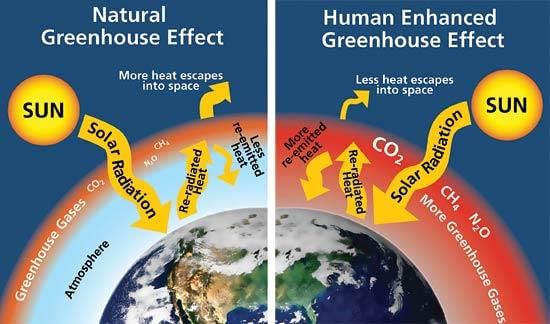 |
Card: 30 / 48 |
|
What long-term effects of genetically altered organisms are still not well understood? |
Card: 31 / 48 |
|
The long-term effects of consuming genetically modified foods on human health and their impact on ecological systems. 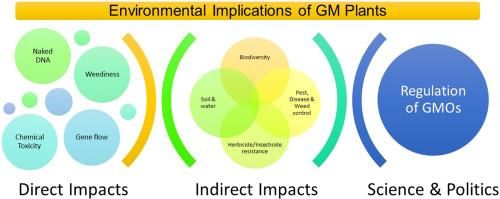 |
Card: 32 / 48 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which of the following gases is NOT a contributor to the greenhouse effect? A) Carbon Dioxide B) Methane C) Oxygen D) Nitrous Oxide |
Card: 33 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The expansion of agricultural land is primarily responsible for the destruction of ___ and ___ habitats. |
Card: 35 / 48 |
|
Cooking fires pose a significant risk of indoor air pollution, leading to respiratory and other health issues. |
Card: 38 / 48 |
|
The primary goal of the Chipko Movement was to protect trees and forests by advocating for sustainable forestry practices and preventing deforestation.  |
Card: 40 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Narmada Bachao Andolan primarily focused on issues related to ___ and ___ of displaced communities due to dam construction. |
Card: 41 / 48 |
|
True or False: The Bhopal industrial accident had no significant impact on the community's health. |
Card: 43 / 48 |
|
False. The Bhopal industrial accident resulted in thousands of deaths and long-term health issues for the surrounding population.  |
Card: 44 / 48 |
|
Explain how social status affects the ability to cope with environmental disasters. |
Card: 45 / 48 |
|
Social status affects the ability to cope with environmental disasters because those with higher social status often have better access to resources, information, and support systems, whereas marginalized groups may lack these advantages, making recovery more difficult. |
Card: 46 / 48 |
|
In the context of environmental issues, what does the social ecology school emphasize? |
Card: 47 / 48 |
|
The social ecology school emphasizes the impact of social relationships, especially regarding property and production arrangements, on how individuals perceive and interact with the environment. |
Card: 48 / 48 |