|
Card: 1 / 50 |
The emergence of sociology was significantly influenced by which three major historical events? |
|
Card: 3 / 50 |
Fill in the blanks: The Enlightenment led to a shift away from reliance on ___, ___, and divine intervention. |
|
Card: 5 / 50 |
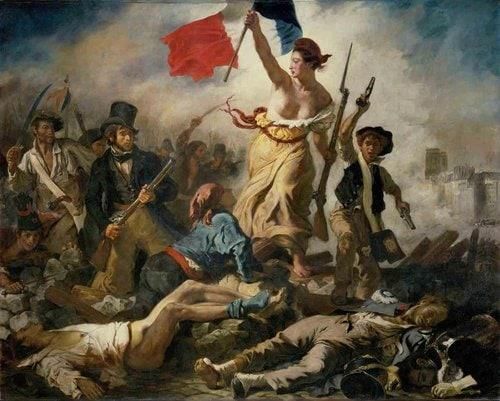
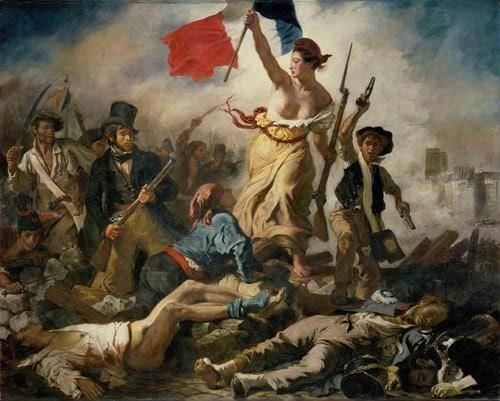
True or False: The French Revolution represented a movement towards increased monarchy and centralized power. |
|
Card: 7 / 50 |
What were the main processes that shaped modernity in Europe and influenced classical sociological theorists? |
|
Card: 8 / 50 |
The onset of the Age of Reason or Enlightenment, the political changes from the French Revolution, and the economic transformations brought by the Industrial Revolution.  |
|
Card: 9 / 50 |
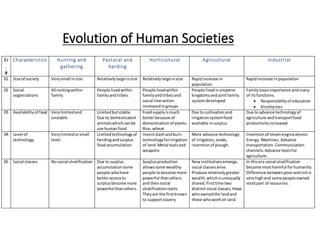
Fill in the blank: The Industrial Revolution introduced ___ production, which changed the social landscape of Europe. |
|
Card: 11 / 50 |
Which sociological theorists were primarily influenced by the changes brought about during the emergence of modernity? |
|
Card: 13 / 50 |
The Enlightenment emphasized the importance of ___ in understanding human existence. |
|
Card: 15 / 50 |
True or False: The Enlightenment contributed to the rise of both secular and religious worldviews. |
|
Card: 19 / 50 |
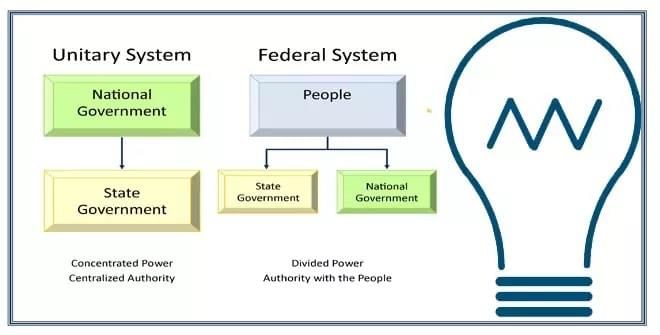
Fill in the blank: The political changes during the French Revolution led to the introduction of political sovereignty for both individuals and ___-states. |
|
Card: 21 / 50 |
What major societal change did the French Revolution bring to peasants previously bound to feudal lords? |
|
Card: 23 / 50 |
The shift towards secularism during the Enlightenment was necessary to move ___, religion, and divine intervention out of focus. |
|
Card: 25 / 50 |
Multiple Choice: Which of the following best describes a key aspect of the Enlightenment? A) Emphasis on divine rights B) Importance of reason C) Focus on religious authority D) Belief in inherited privileges |
|
Card: 27 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The division between the public sphere of the state and the private sphere of the family was a significant ideological shift during the ___ period. |
|
Card: 30 / 50 |
The systematic application of science and technology to industrial production and the development of new methods of organizing markets and labor.  |
|
Card: 31 / 50 |
The principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity emerged from ___ and became foundational values of the modern state. |
|
Card: 33 / 50 |
True or False: The Industrial Revolution led to improved working conditions and higher wages for factory workers. |
|
Card: 34 / 50 |
False. The Industrial Revolution caused low wages and hazardous working conditions.  |
|
Card: 37 / 50 |
The redefinition of the nation-state involved the establishment of ___ governance. |
|
Card: 39 / 50 |
Karl Marx believed that human society evolved through several stages, including feudalism, primitive communism, slavery, and ___. |
|
Card: 41 / 50 |
True or False: Karl Marx thought that capitalism would ultimately hinder humanity's progress towards equality and freedom. |
|
Card: 42 / 50 |
False. Marx believed capitalism played a crucial role in advancing humanity towards equality and freedom despite its flaws.  |
|
Card: 44 / 50 |
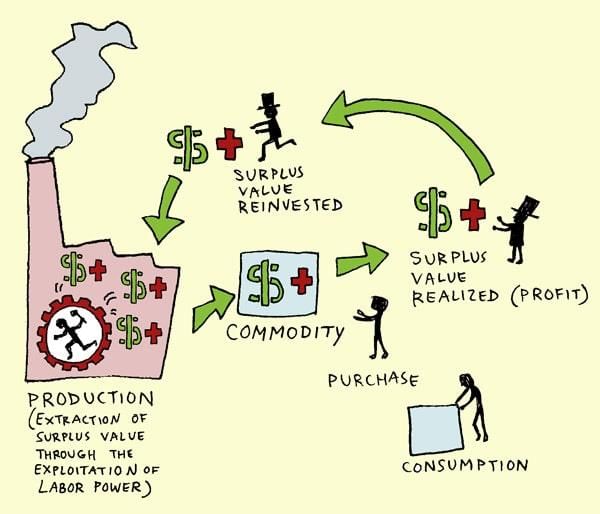
Alienation refers to the increasing distance between people and the natural world, the individualization of social structures mediated by market forces, and the lack of ownership over the goods produced by employees.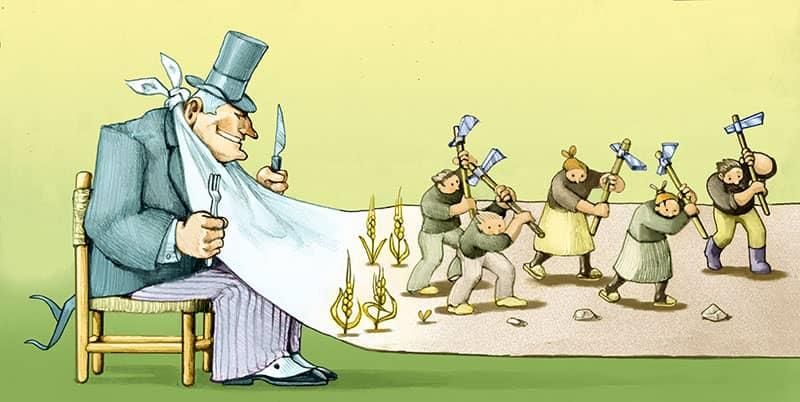  |
|
Card: 45 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Marx's theory posited that the working class would eventually band together to lead a revolution and establish a ___ society. |
|
Card: 47 / 50 |
Which of the following best describes Marx's view on the role of capitalism in society? A) It is purely exploitative B) It is a necessary stage towards achieving equality C) It has no impact on social structures D) It only benefits the ruling class. |
|
Card: 50 / 50 |
The economic base consists of the productive forces and production relations that shape society, including means of production, labor organization, and economic ties. 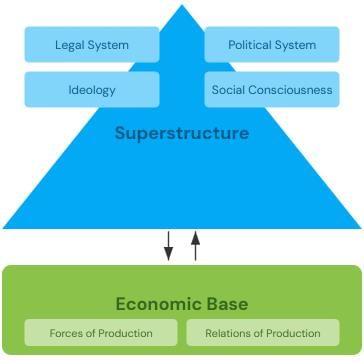 |