|
Card: 2 / 28 |
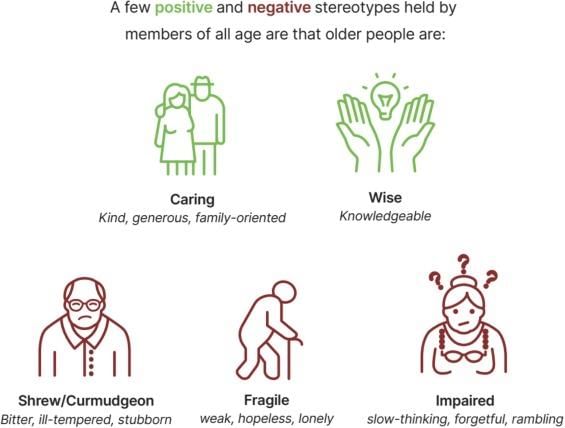
The key components that influence social behaviour include social perception, social cognition, attitudes, prejudice, discrimination, aggression, altruism, and interpersonal relationships.  |
|
Card: 3 / 28 |
Fill in the blanks: Prejudice and discrimination are negative attitudes based on ___. |
|
Card: 6 / 28 |
Social cognition involves how individuals interpret and process social information, while social perception refers specifically to the process of forming impressions of other people.  |
|
Card: 7 / 28 |
Which of the following is NOT a component of social behaviour? A) Aggression B) Altruism C) Solitude D) Prejudice |
|
Card: 10 / 28 |
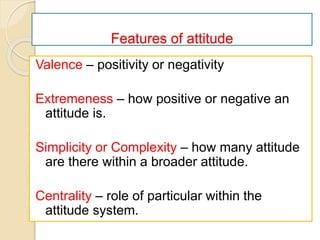
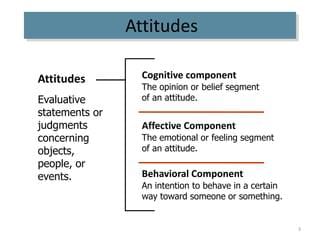
The three components of attitude are the affective component, the behavioral component, and the cognitive component. 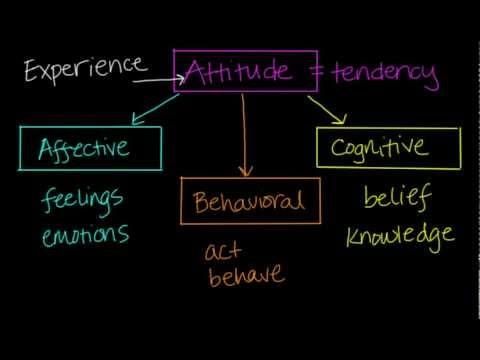 |
|
Card: 13 / 28 |
Fill in the blank: An attitude system is considered simple if it has only a few ___ and complex if it has many. |
|
Card: 15 / 28 |
Which component of attitude refers to our emotions towards the attitude object? |
|
Card: 17 / 28 |
In the context of health and well-being, what are examples of member attitudes? |
|
Card: 18 / 28 |
Examples include views on physical health, mental health, happiness, and strategies for achieving well-being.  |
|
Card: 20 / 28 |
Attitudes can be formed through direct contact, personal values, socialization, and media exposure. 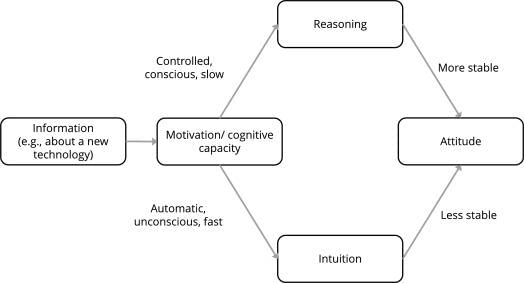 |
|
Card: 21 / 28 |
Fill in the blank: Attitude formation can occur through ___, where a person's positive attitude is shaped by their liking for the teacher of a subject. |
|
Card: 24 / 28 |
False. Attitudes can change due to new experiences, social norms, and information.  |
|
Card: 26 / 28 |
Modeling influences attitude formation by allowing individuals to learn attitudes by observing the behaviors and attitudes of others. 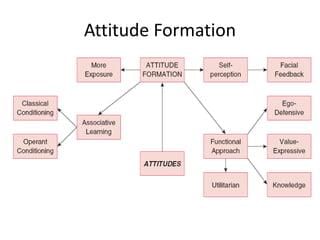 |
|
Card: 27 / 28 |
The Family and School Environment significantly influence ___ formation in childhood and adolescence. |