|
Card: 2 / 34 |
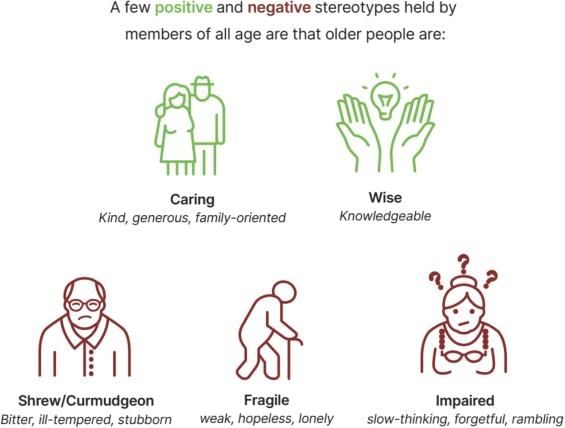
Social cognition is the process of perceiving, interpreting, and understanding the social world around us, influencing our judgments, decisions, and interactions with others.  |
|
Card: 3 / 34 |
True or False: Stereotypes are always negative and based on accurate information. |
|
Card: 4 / 34 |
False. Stereotypes can be positive or negative and are often based on oversimplified or inaccurate information. 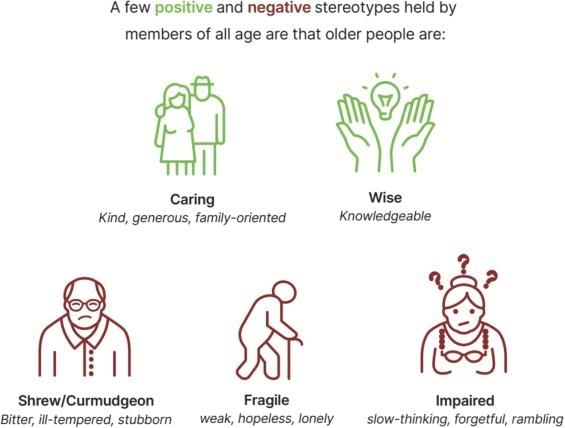 |
|
Card: 6 / 34 |
Stereotypes can lead to prejudice, discrimination, and unfair treatment of individuals or groups. 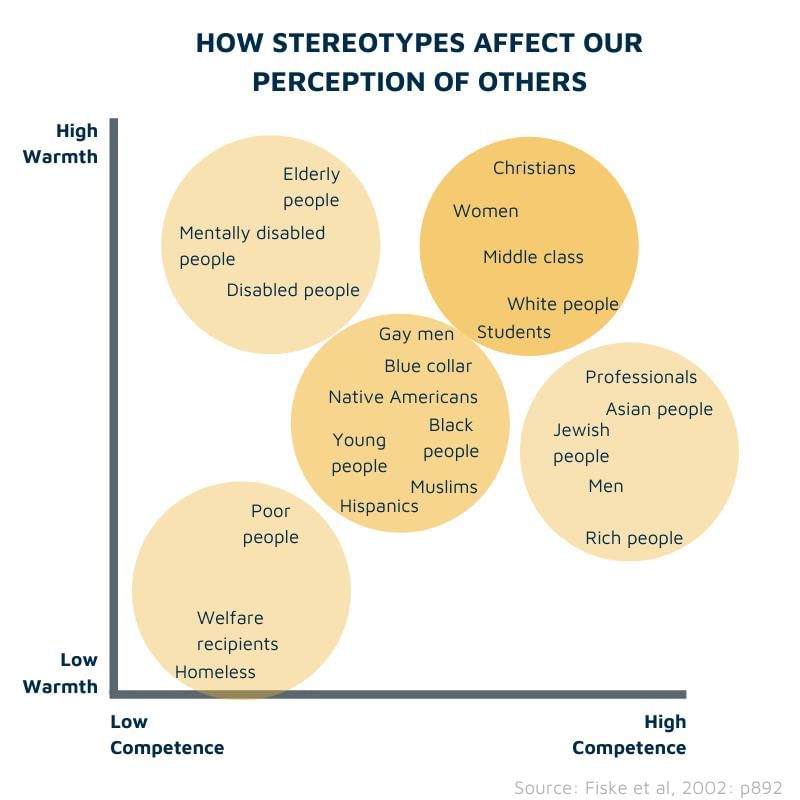 |
|
Card: 7 / 34 |
Fill in the blank: It is important to challenge negative ___ to reduce prejudice and discrimination. |
|
Card: 10 / 34 |
Social cognition influences behavior by shaping our attitudes and judgments about ourselves and others, which in turn affects how we interact and respond in social situations.  |
|
Card: 11 / 34 |
What is the process of forming an overall impression of someone based on available information called? |
|
Card: 13 / 34 |
Impression formation can be influenced by ___ and pre-existing ___ and stereotypes. |
|
Card: 17 / 34 |
True or False: The fundamental attribution error refers to the tendency to attribute one's own behavior to internal factors. |
|
Card: 18 / 34 |
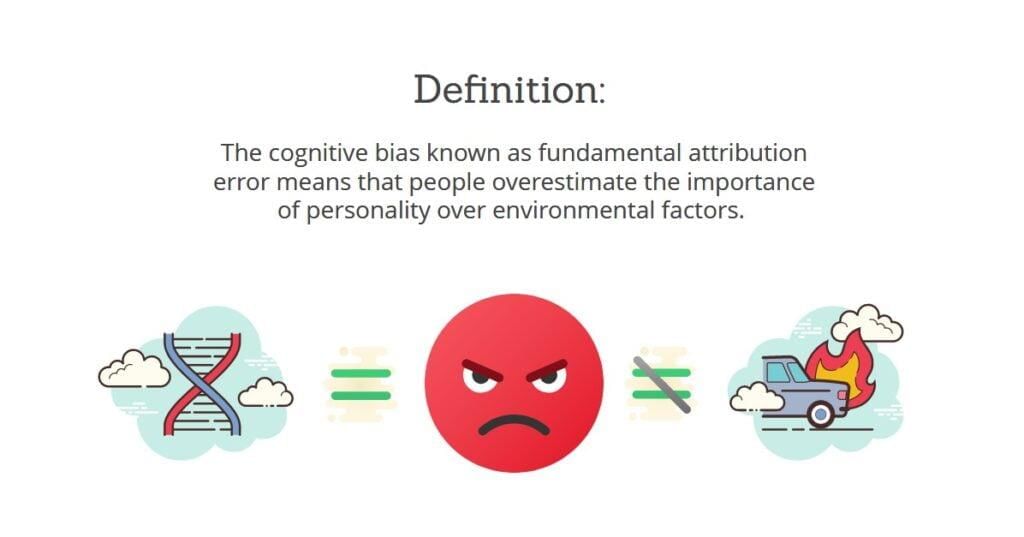
False. The fundamental attribution error refers to attributing others' behavior to internal traits rather than the situation. 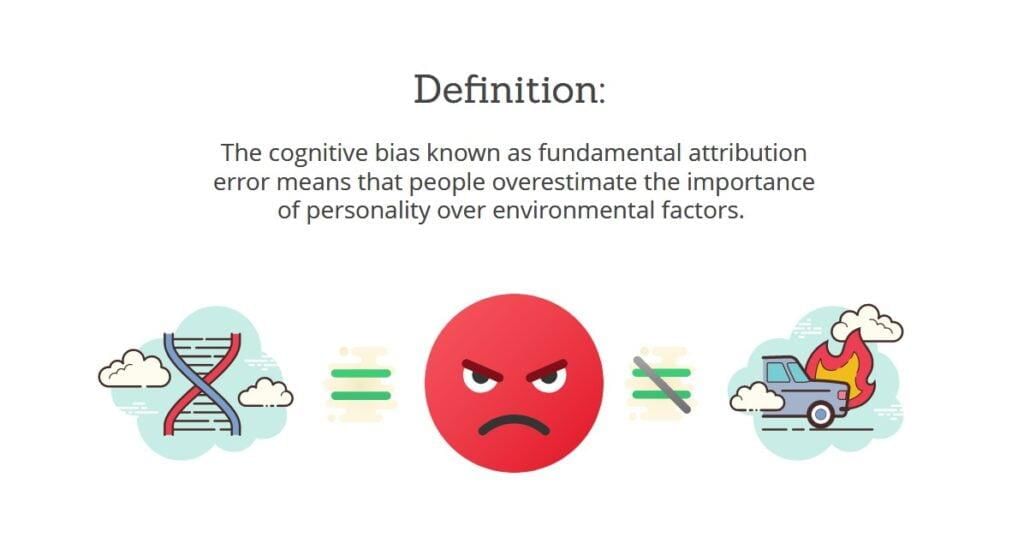 |
|
Card: 20 / 34 |
Internal attribution attributes behavior to personal traits, while external attribution attributes behavior to situational factors. 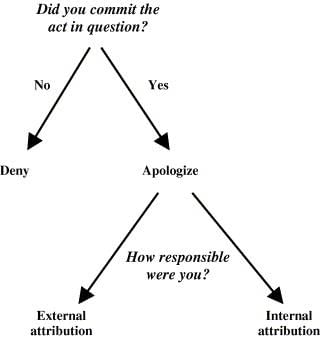 |
|
Card: 21 / 34 |
Which bias describes the tendency to emphasize personal characteristics in explaining others' behavior? |
|
Card: 24 / 34 |
Context can alter the significance of certain cues, leading to different impressions based on the situation. 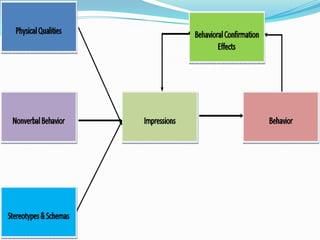 |
|
Card: 25 / 34 |
Fill in the blank: Social loafing occurs when individuals exert ___ effort in a group compared to working alone. |
|
Card: 27 / 34 |
What does the diffusion of responsibility explain in the context of group performance? |
|
Card: 28 / 34 |
Diffusion of responsibility explains why individuals may feel less accountable for the outcome of the group's performance, leading to social loafing. 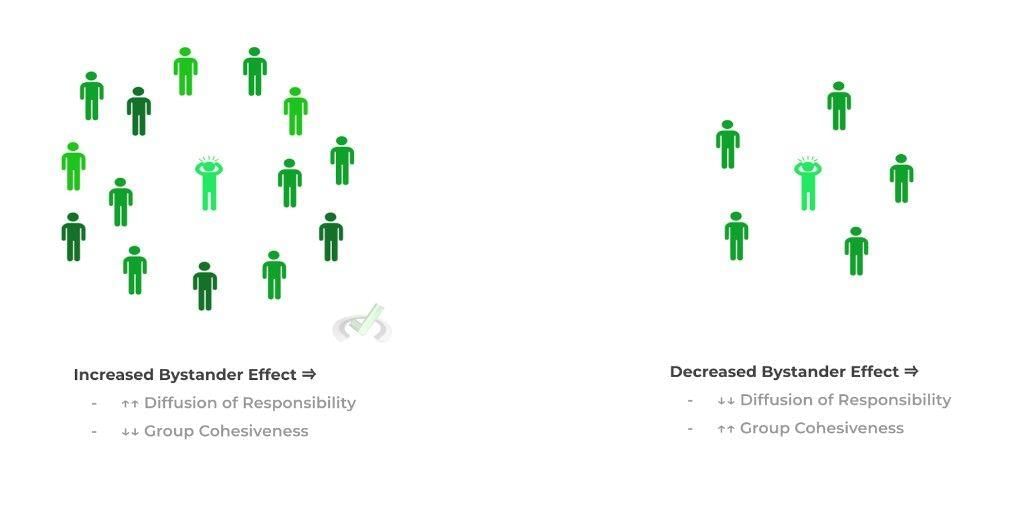 |
|
Card: 29 / 34 |
Fill in the blank: Group polarization leads to more extreme opinions due to ___ with the views of group members. |
|
Card: 32 / 34 |
Donating to charity, volunteering, helping a stranger, and cooperating to achieve a common goal.  |
|
Card: 33 / 34 |
True or False: Anti-social behavior includes actions like helping others and volunteering. |