|
Individuals join groups for social support and companionship, shared interests and goals, information and knowledge sharing, identity formation and validation, and power and influence.  |
Card: 2 / 36 |
|
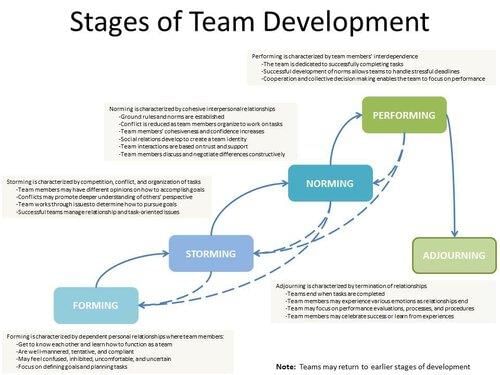
The stages of group formation include forming, storming, norming, and performing. 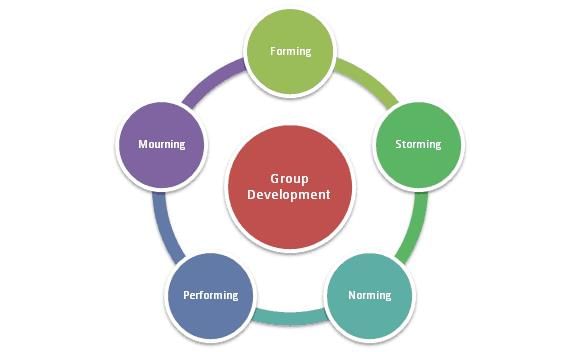 |
Card: 4 / 36 |
|
Groups can have both positive and negative impacts on individuals. Provide an example of each. |
Card: 5 / 36 |
|
A positive impact can be a supportive and cohesive group providing a sense of social identity; a negative impact can be a group with harmful goals leading to negative behaviors.  |
Card: 6 / 36 |
|
Fill in the blank: Group formation is the process by which individuals come together to form a ___ unit. |
Card: 7 / 36 |
|
True or False: Belonging to a group with negative goals can enhance an individual's social identity. |
Card: 9 / 36 |
|
False: Belonging to a group with negative goals can lead to harmful behaviors and attitudes, not enhance social identity. 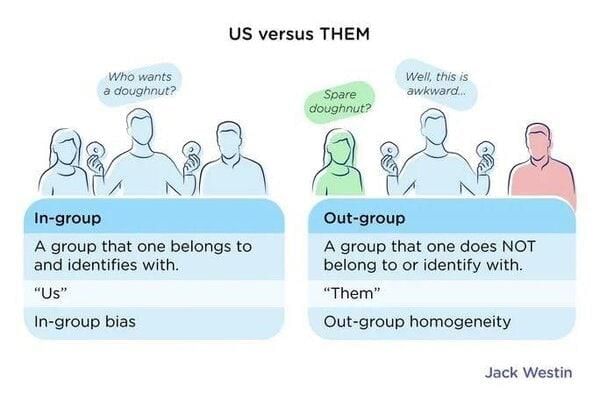 |
Card: 10 / 36 |
|
Fill in the blank: The norming stage is where the group begins to establish its own ___ and expectations. |
Card: 11 / 36 |
|
Groups contribute to identity formation by providing individuals with a sense of belonging and validation through shared values and beliefs.  |
Card: 14 / 36 |
|
The four stages of group development are Forming, Storming, Norming, and Performing. 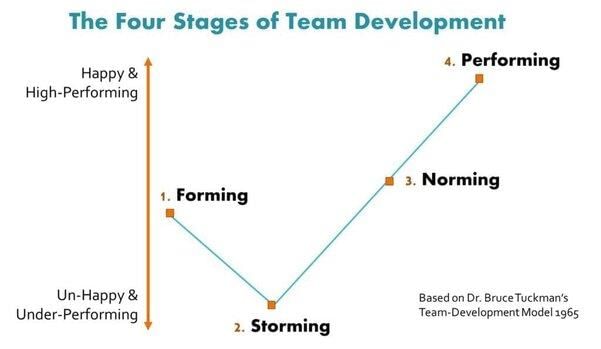 |
Card: 16 / 36 |
|
Fill in the blank: In the Storming stage, conflicts and disagreements may arise as individuals start to ___ their opinions. |
Card: 17 / 36 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
True or False: Cohesiveness refers to the division and lack of attraction among group members. |
Card: 19 / 36 |
|
False. Cohesiveness refers to the unity and mutual attraction among group members. |
Card: 20 / 36 |
|
Ascribed status is a social position assigned at birth or involuntarily acquired, while achieved status is a position earned through individual effort or accomplishments. 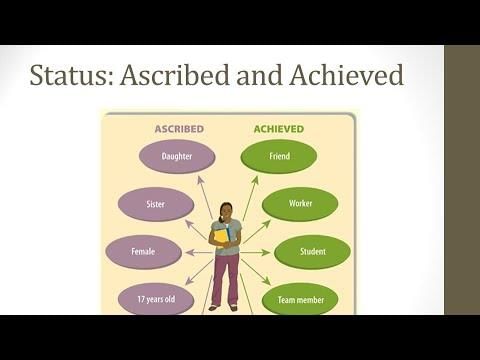 |
Card: 22 / 36 |
|
Fill in the blank: Norms are standards of behavior and beliefs agreed upon by a group, acting as ___ rules guiding the behavior of members. |
Card: 23 / 36 |
|
What is the primary outcome of highly cohesive groups, and what potential issue can arise from excessive cohesion? |
Card: 25 / 36 |
|
Highly cohesive groups exhibit strong team spirit and a reluctance to leave the group; however, excessive cohesion can lead to groupthink.  |
Card: 26 / 36 |
|
Fill in the blank: In the Norming stage, group members start to understand each other's ___ and responsibilities. |
Card: 27 / 36 |
|
In-group bias refers to the tendency for individuals to favor members of their own group over members of other groups. This bias can lead to discrimination, prejudice, and the reinforcement of social inequality.  |
Card: 30 / 36 |
|
True or False: Informal groups are bound by explicit rules and designated roles. |
Card: 31 / 36 |
|
False. Informal groups are not bound by rules or laws and are characterized by close relationships among members.  |
Card: 32 / 36 |
|
Formal groups are established based on explicit rules and laws, with designated roles and established norms, whereas informal groups lack strict regulations and are based on personal relationships among members. 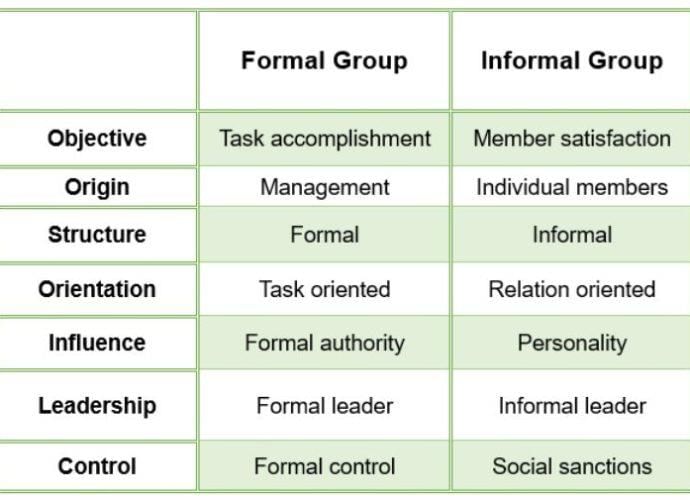 |
Card: 34 / 36 |
|
Fill in the blank: Members of out-groups may be viewed as ___ or ___ compared to in-group members. |
Card: 35 / 36 |