|
Card: 1 / 102 |
True or False: Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty discovered that protein was responsible for the transformation in Griffith's experiment. |
|
Card: 3 / 102 |
Fill in the blank: The number of base pairs in human DNA (haploid) is ___ x 10^9. |
|
Card: 5 / 102 |
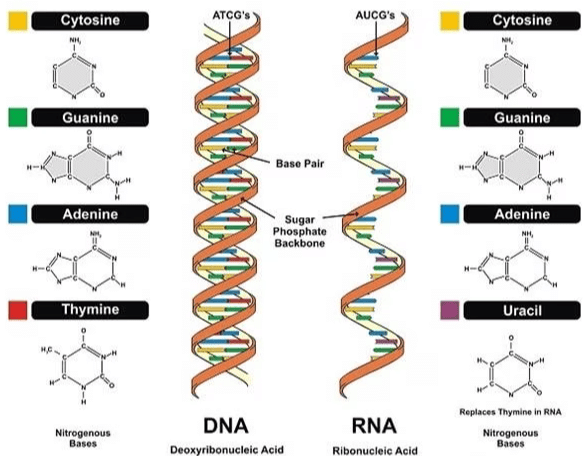
What are the two types of nitrogenous bases found in nucleic acids, and which bases belong to each type? |
|
Card: 6 / 102 |
The two types of nitrogenous bases are purines and pyrimidines. Purines include Adenine (A) and Guanine (G), while pyrimidines include Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) in DNA, and Uracil (U) in RNA. 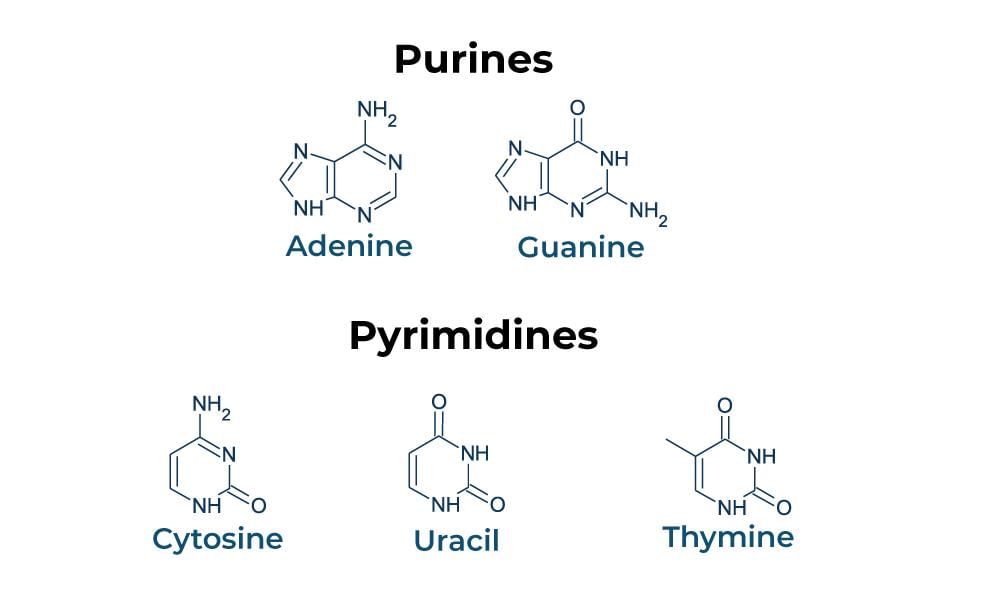 |
|
Card: 9 / 102 |
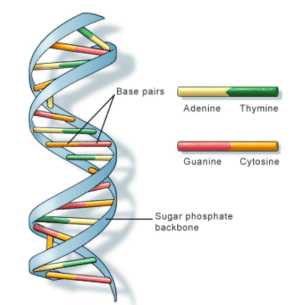
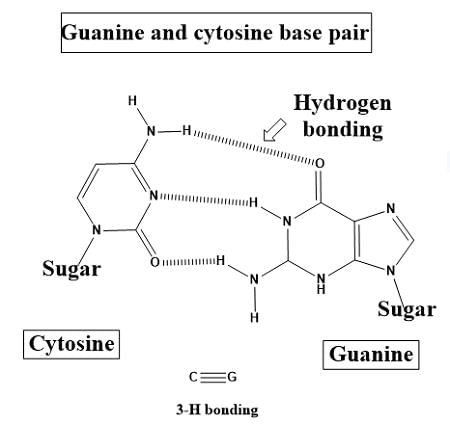
In the double helix structure of DNA, Adenine pairs with ___ and Guanine pairs with ___. |
|
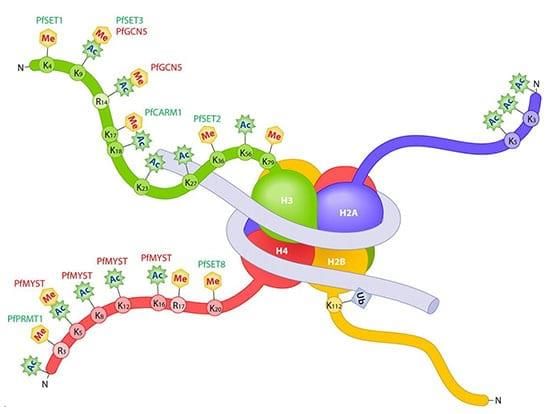
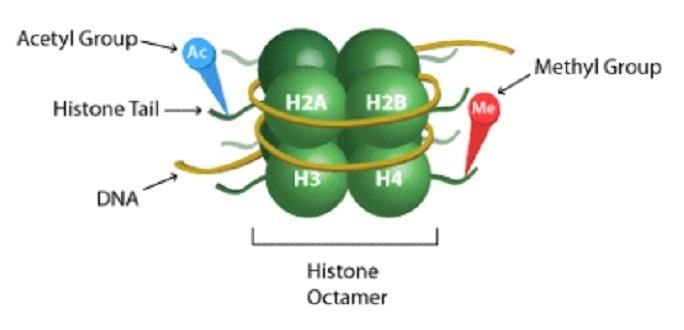
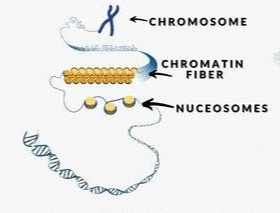
Card: 11 / 102 |
In eukaryotes, DNA is organized into structures called ___ which consist of DNA wrapped around histone proteins. |
|
Card: 13 / 102 |
True or False: Heterochromatin is transcriptionally active and appears lightly stained under a microscope. |
|
Card: 14 / 102 |
False. Heterochromatin is transcriptionally inactive and appears densely packed and darkly stained. 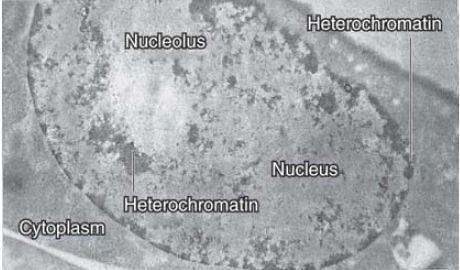 |
|
Card: 17 / 102 |
I am the repeating unit that prevents DNA from tangling and consists of DNA and histone proteins. What am I? |
|
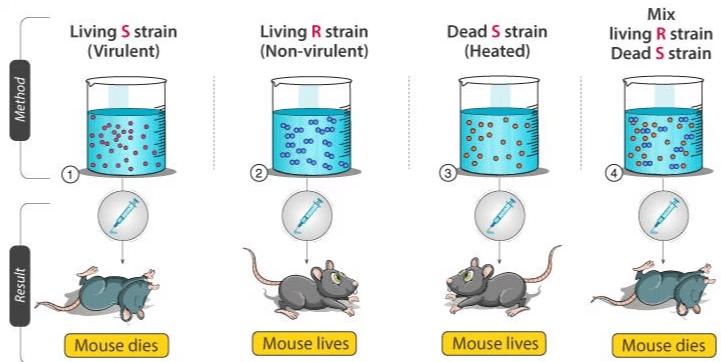
Card: 19 / 102 |
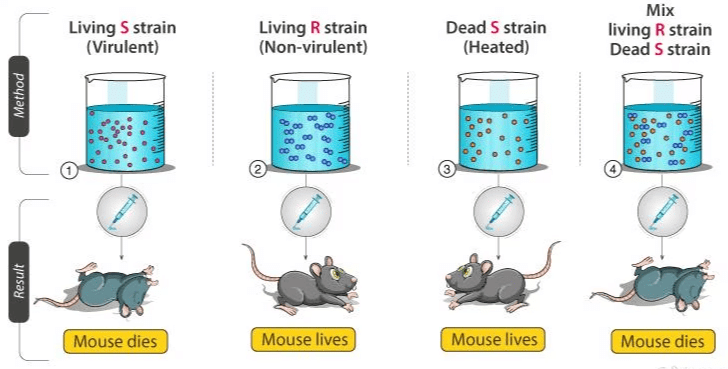
Frederick Griffith's experiment demonstrated that heat-killed S strain bacteria could transform R strain bacteria into a virulent form through a process called ___. |
|
Card: 21 / 102 |
True or False: Friedrich Miescher discovered DNA as the genetic material immediately after Gregor Mendel established his principles of inheritance. |
|
Card: 22 / 102 |
False. Miescher discovered nuclein, which laid the groundwork for understanding DNA, but it took time for DNA to be established as the genetic material. |
|
Card: 23 / 102 |
What did Griffith conclude about the 'transforming principle' observed in his experiments? |
|
Card: 24 / 102 |
Griffith concluded that some transforming principle from the heat-killed S strain was transferred to the R strain, enabling it to synthesize a smooth coat and become virulent. |
|
Card: 25 / 102 |
What did Oswald Avery and his colleagues conclude about the transforming principle in Griffith's experiment? |
|
Card: 26 / 102 |
They concluded that DNA is the hereditary material responsible for the transformation of R bacteria into S bacteria. |
|
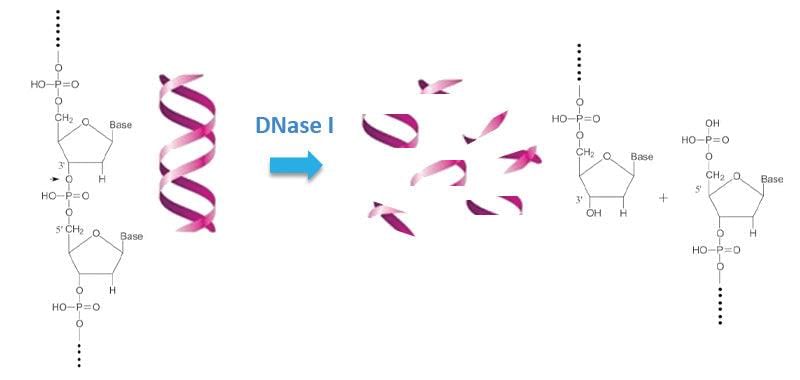
Card: 27 / 102 |
Fill in the blank: DNase is an enzyme that ___ DNA by cutting the bonds between nucleotides. |
|
Card: 29 / 102 |
True or False: Avery's findings were universally accepted by biologists at the time. |
|
Card: 30 / 102 |
False; not all biologists accepted the idea that DNA was the hereditary material. 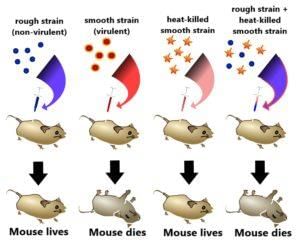 |
|
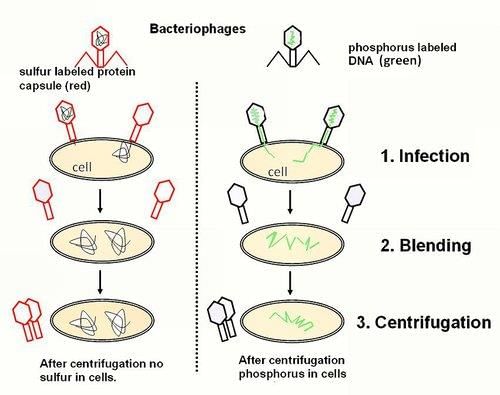
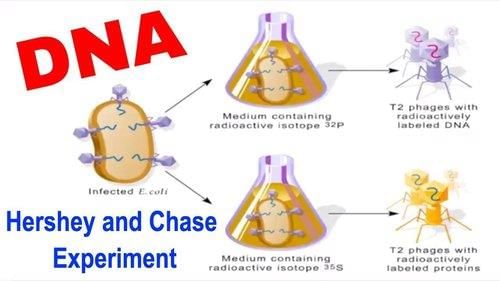
Card: 32 / 102 |
To determine whether DNA or protein was the genetic material in bacteriophages. |
|
Card: 33 / 102 |
Fill in the blank: Hershey and Chase used radioactive ___ to label DNA and radioactive ___ to label protein. |
|
Card: 35 / 102 |
True or False: The results of Hershey and Chase's experiment showed that protein entered bacterial cells during infection. |
|
Card: 37 / 102 |
What crucial experiment proved that DNA, rather than proteins, carries genetic information? |
|
Card: 39 / 102 |
Fill in the blank: RNA is more prone to ___ and evolves faster compared to DNA. |
|
Card: 41 / 102 |
True or False: DNA is less stable than RNA due to its structural composition. |
|
Card: 42 / 102 |
False. DNA is more stable than RNA because it lacks the 2'-OH group that makes RNA chemically reactive. 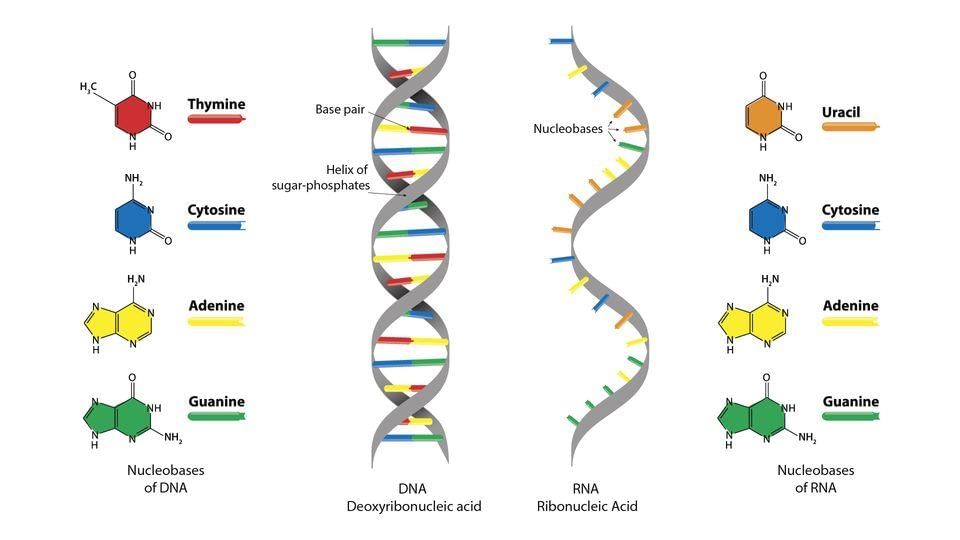 |
|
Card: 43 / 102 |
What experimental method did Meselson and Stahl use to demonstrate the semi-conservative replication of DNA? |
|
Card: 44 / 102 |
They used centrifugation in a caesium chloride density gradient to differentiate between heavy DNA (with 15N) and normal DNA (with 14N). |
|
Card: 45 / 102 |
Fill in the blank: RNA is believed to have acted as both ___ and a ___ in early life forms. |
|
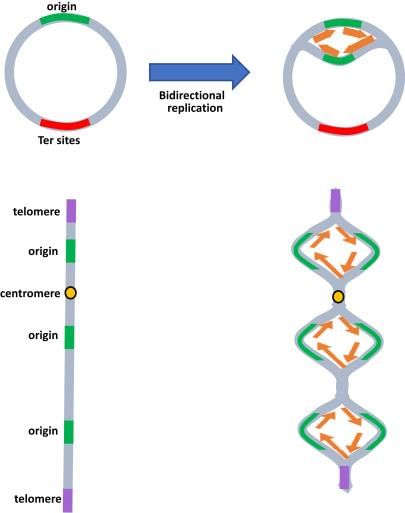
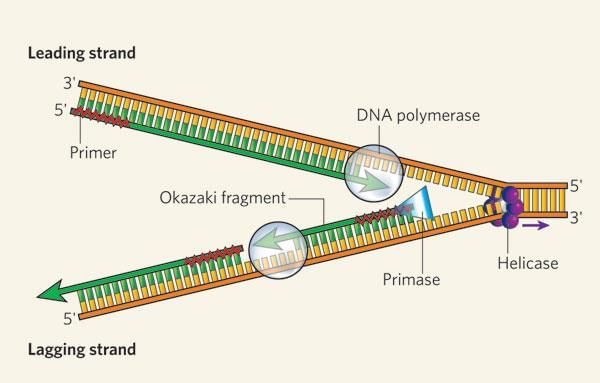
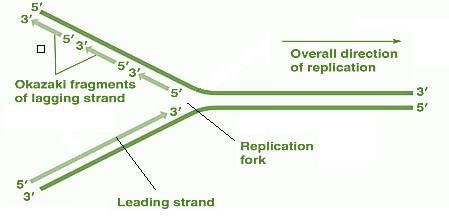
Card: 51 / 102 |
What are the short fragments formed on the lagging strand during DNA replication called? |
|
Card: 53 / 102 |
In eukaryotic cells, DNA replication occurs during which phase of the cell cycle? |
|
Card: 55 / 102 |
The process of transcription involves copying genetic information from ___ to ___. |
|
Card: 57 / 102 |
True or False: In eukaryotic cells, structural genes are typically polycistronic. |
|
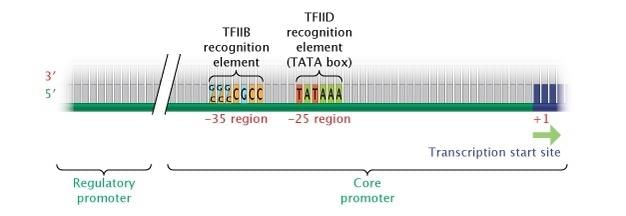
Card: 59 / 102 |
Fill in the blank: The region of DNA that initiates transcription is called the ___. |
|
Card: 61 / 102 |
What are the two types of sequences found in eukaryotic genes, and what distinguishes them? |
|
Card: 62 / 102 |
Exons (coding sequences) and introns (non-coding sequences), where introns are removed in mature RNA. 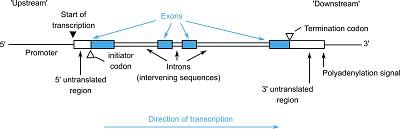 |
|
Card: 64 / 102 |
The three main steps of transcription are initiation, elongation, and termination. 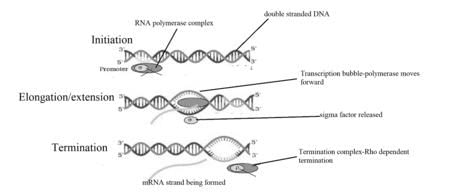 |
|
Card: 65 / 102 |
True or False: In eukaryotic cells, the primary transcript is functional and does not require further processing. |
|
Card: 66 / 102 |
False. The primary transcript is non-functional and requires splicing to remove introns and join exons. |
|
Card: 67 / 102 |
Fill in the blank: RNA polymerase II is responsible for the transcription of ___ in eukaryotic cells. |
|
Card: 69 / 102 |
I am a factor that binds with RNA polymerase to begin transcription, and I am found at the promoter site. What am I? |
|
Card: 71 / 102 |
What is the significance of the term 'degenerate' in the context of the genetic code? |
|
Card: 72 / 102 |
The term 'degenerate' refers to the fact that multiple codons can code for the same amino acid, meaning that the genetic code has redundancy. 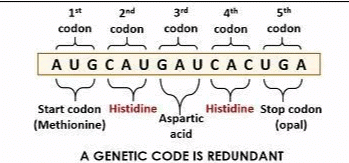 |
|
Card: 73 / 102 |
Fill in the blank: The start codon is ___ and it codes for the amino acid ___ . |
|
Card: 75 / 102 |
True or False: There are 64 codons in total, of which all code for amino acids. |
|
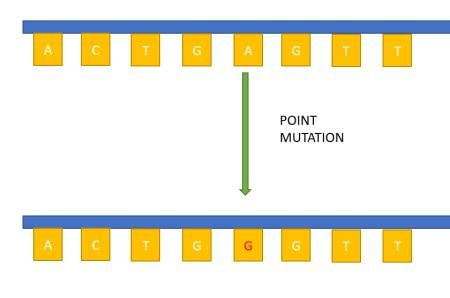
Card: 77 / 102 |
Riddle: I am a type of mutation where the change is small, just a single base pair, causing problems for all. What am I? |
|
Card: 79 / 102 |
The process of translation begins with the presence of ___ in the small subunit of ribosomes. |
|
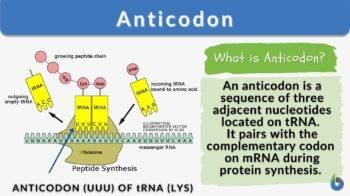
Card: 81 / 102 |
True or False: tRNA has an anticodon loop that is complementary to the codon on mRNA. |
|
Card: 84 / 102 |
The release factor binds to the stop codon, terminating the translation process and releasing the polypeptide from the ribosome. |
|
Card: 87 / 102 |
True or False: In prokaryotes, gene expression is primarily regulated at the level of translation. |
|
Card: 88 / 102 |
False. Gene expression is primarily regulated at the initiation of transcription. 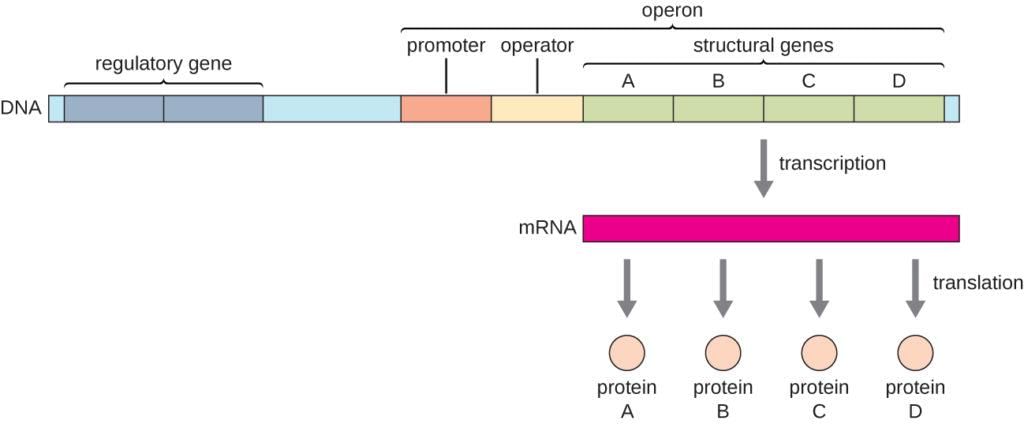 |
|
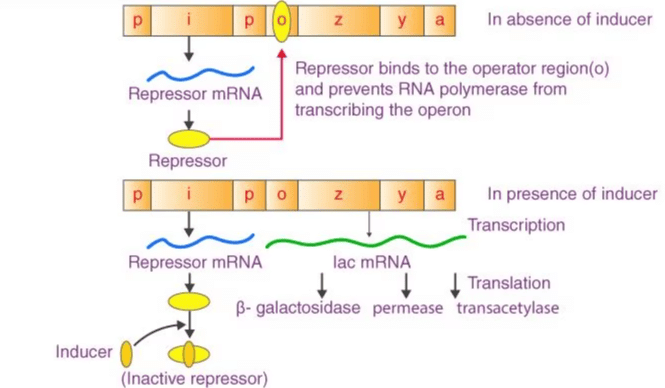
Card: 90 / 102 |
The three structural genes are z, y, and a. The z gene codes for β-galactosidase, which hydrolyzes lactose; the y gene codes for permease, which increases cell permeability to β-galactosides; and the a gene codes for transacetylase. 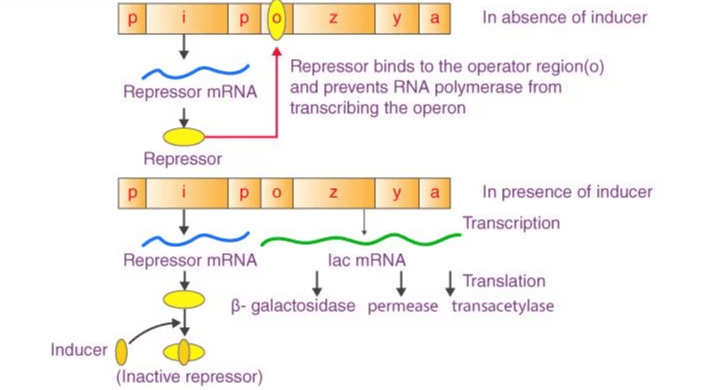 |
|
Card: 91 / 102 |
The Human Genome Project aimed to decipher the complete DNA sequence of the human genome and was launched in ___ and completed in ___. |
|
Card: 97 / 102 |
DNA fingerprinting is primarily based on the variability of ___ in the human genome. |
|
Card: 99 / 102 |
True or False: DNA fingerprinting can only be used for criminal investigations. |
|
Card: 100 / 102 |
False. It can also be used for paternity testing and determining genetic diversity. |
|
Card: 101 / 102 |
What are the two main classifications of satellite DNA based on their length? |