|
What is the primary moral and political significance of the concept of equality? |
Card: 1 / 44 |
|
The primary significance of equality is that it asserts every individual possesses equal worth, regardless of gender, race, color, or nationality. |
Card: 2 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: The paradox of equality highlights that while the ideal of equality is widely accepted, ___ still persists in various forms. |
Card: 3 / 44 |
|
False. The ideal of equality is not fully realized, as inequality is still prevalent in various aspects of life.  |
Card: 6 / 44 |
|
Forms of inequality include unequal distribution of wealth, limited opportunities, discriminatory work practices, and unequal distribution of power. |
Card: 8 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: Efforts to address the paradox of equality must involve a comprehensive approach that promotes ___ and justice. |
Card: 9 / 44 |
|
The principle of equality emphasizes that human beings merit equal consideration and regard due to their shared humanity. 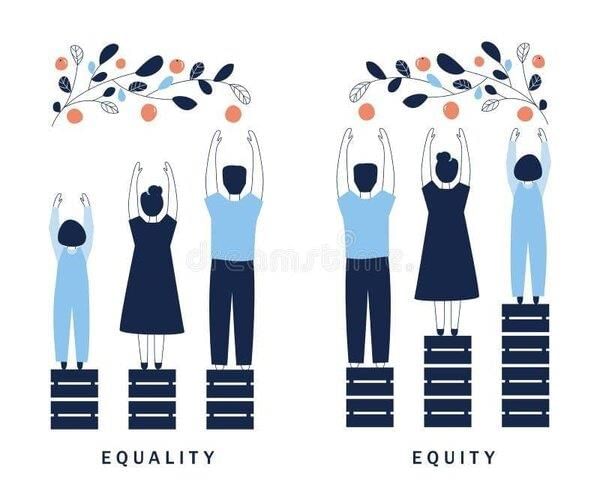 |
Card: 12 / 44 |
|
What does treating people with equal respect imply in the context of equality? |
Card: 13 / 44 |
|
It implies that while individuals may be treated differently based on their roles or contributions, such treatment should not be based on unacceptable factors like religion, race, caste, or gender. |
Card: 14 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: The commitment to the ideal of equality does not entail the elimination of all differences; it simply means that treatment must not be predetermined by ___ or ___ circumstances. |
Card: 15 / 44 |
|
True or False: Equality of opportunity means that all individuals must achieve the same level of success in their careers. |
Card: 17 / 44 |
|
False: Equality of opportunity means that all individuals have the same rights and opportunities to pursue their goals, not that they will achieve the same outcomes. |
Card: 18 / 44 |
|
When individuals are treated differently solely based on their religion, race, caste, or gender. |
Card: 20 / 44 |
|
List two basic goods that access to which can create an unjust and unequal society. |
Card: 21 / 44 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Fill in the blank: A smoothly functioning society requires the division of labor and functions, which often leads to individuals having different ___ and ___ because of it. |
Card: 23 / 44 |
|
Natural inequalities are based on inherent characteristics and abilities, while socially produced inequalities arise from disparities in opportunity and exploitation within society. |
Card: 28 / 44 |
|
True or False: Socially produced inequalities are justified if they are based on natural differences. |
Card: 29 / 44 |
|
False. Justification of socially produced inequalities based on natural differences is often contested and can be viewed as unjust. |
Card: 30 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: Certain societies may reward ___ work more highly than ___ labor. |
Card: 31 / 44 |
|
What has made it possible for many individuals with disabilities to function effectively in society? |
Card: 33 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: The belief that women were the weaker sex justified denying them ___ rights. |
Card: 35 / 44 |
|
Short Answer: Why is the distinction between natural and socially produced inequalities complex? |
Card: 37 / 44 |
|
Because long-standing inequalities may appear justifiable based on natural differences, and advancements in technology challenge the idea that certain characteristics are immutable. |
Card: 38 / 44 |
|
What are the three main dimensions of equality identified by various thinkers and ideologies? |
Card: 39 / 44 |
|
Political equality in democratic societies grants citizens equal access to what fundamental rights? |
Card: 41 / 44 |
|
The right to vote, freedom of expression, movement and association, and freedom of belief. |
Card: 42 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: Economic inequality exists when there are significant differences in ___, ___, or ___ between individuals or classes. |
Card: 43 / 44 |























