|
Card: 1 / 40 |
Sustainable development is defined in the Brundtland Report as meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of ___ to meet their own needs. |
|
Card: 3 / 40 |
True or False: The Stockholm Declaration explicitly mentions sustainable development. |
|
Card: 4 / 40 |
False; it implies the integration of economic development with environmental protection.  |
|
Card: 5 / 40 |
What are the three new principles added to the concept of sustainable development? |
|
Card: 6 / 40 |
Obligation to assist and cooperate, eradication of poverty, financial assistance to developing countries.  |
|
Card: 7 / 40 |
Short Answer: Why is environmental protection considered crucial in sustainable development? |
|
Card: 8 / 40 |
It is essential to maintain a stable resource base and avoid over-exploitation of renewable resources.  |
|
Card: 9 / 40 |
True or False: The Rio Declaration suggests that environmental protection should be treated separately from the development process. |
|
Card: 10 / 40 |
False; it emphasizes that environmental protection is integral to development. |
|
Card: 11 / 40 |
What is the primary objective of sustainable development related to economic activity? |
|
Card: 12 / 40 |
To ensure continuous production of goods and services while maintaining manageable levels of government and avoiding imbalances that could harm agriculture and industry. |
|
Card: 13 / 40 |
The Precautionary Principle asserts that development should be halted if it leads to ___ and ___ environmental harm. |
|
Card: 15 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The new principles of sustainable development include the obligation to assist and cooperate, the eradication of poverty, and financial assistance to ___ countries. |
|
Card: 17 / 40 |
What is the main goal of integrating environmental considerations into economic and developmental plans? |
|
Card: 19 / 40 |
True or False: The principle of intergenerational equity focuses on the exploitation of natural resources without regard for future generations. |
|
Card: 21 / 40 |
List the five key elements of the Precautionary Principle aimed at preventing irreversible harm. |
|
Card: 22 / 40 |
1. Taking preventive action in the face of uncertainty, 2. Shifting the burden of proof to the proponents of an activity, 3. Exploring a wide range of alternatives to potentially harmful actions, 4. Involving the public in decision-making, 5. Considering the cumulative impacts of actions. 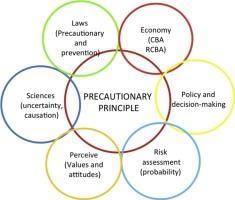 |
|
Card: 24 / 40 |
It refers to the sustainable and prudent exploitation of natural resources to ensure their availability for future generations. |
|
Card: 25 / 40 |
What does the Precautionary Principle advocate for in the face of incomplete scientific evidence? |
|
Card: 26 / 40 |
The Precautionary Principle advocates for taking protective measures even in the absence of full scientific evidence of risks, emphasizing that actions should not be delayed solely due to incomplete scientific information. |
|
Card: 27 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The obligation to take preventive measures against potential harm is known as ___. |
|
Card: 29 / 40 |
What is the purpose of Alternatives Assessments under the Precautionary Principle? |
|
Card: 30 / 40 |
Alternatives Assessments aim to evaluate a range of options and select the one with the least potential impact on human health and the environment.  |
|
Card: 31 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The community's right to access complete and accurate information regarding possible impacts on human health and the environment is referred to as ___. |
|
Card: 33 / 40 |
True or False: Full Cost Accounting involves only considering the immediate financial implications of an action. |
|
Card: 34 / 40 |
False. Full Cost Accounting involves conducting cost-benefit analyses to consider all costs associated with an action, including long-term effects. |
|
Card: 35 / 40 |
What is meant by the term 'Participatory Decision Process' in the context of the Precautionary Principle? |
|
Card: 36 / 40 |
Participatory Decision Process refers to ensuring transparency and public participation in decisions made under the Precautionary Principle. |
|
Card: 37 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: Precautionary measures should be taken when there is a lack of complete information about the potential for ___ and ___ damage. |
|
Card: 39 / 40 |
The Precautionary Principle suggests that action should be taken when there are threats of ___ or ___ damage. |





























