|
Card: 2 / 50 |
The cascading effect refers to the situation where both the central and state governments tax the same goods, leading to VAT being applied on the excise duty component without allowing credit for it, thereby increasing the total tax burden on consumers. |
|
Card: 5 / 50 |
True or False: In the old tax system, the state government allowed manufacturers to credit the excise duty paid when calculating VAT. |
|
Card: 6 / 50 |
False. The state government did not allow credit for the excise duty paid by the manufacturer. |
|
Card: 8 / 50 |
1. Cascading effect due to double taxation on goods; 2. Lack of input tax credit for manufacturers. |
|
Card: 9 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The central government taxed the ___ of goods, while the state government levied tax on their ___. |
|
Card: 12 / 50 |
It led to higher prices for goods, as multiple layers of tax were applied, increasing the overall tax burden. |
|
Card: 13 / 50 |
True or False: The old indirect tax system allowed for seamless input tax credit across different levels of taxation. |
|
Card: 14 / 50 |
False. The old system did not allow for seamless input tax credit, which contributed to the cascading effect. |
|
Card: 15 / 50 |
The imposition of service tax on the provision of services without credit for input services contributed to ___ by taxing tax. |
|
Card: 17 / 50 |
True or False: Prior to GST, the taxation system in India was characterized by a single tax structure that was easy to navigate. |
|
Card: 18 / 50 |
False. The taxation system was cumbersome due to multiple taxes like Excise duty, VAT, and Service tax. |
|
Card: 19 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: Overlapping of jurisdiction became a challenge due to the unclear distinction between ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 21 / 50 |
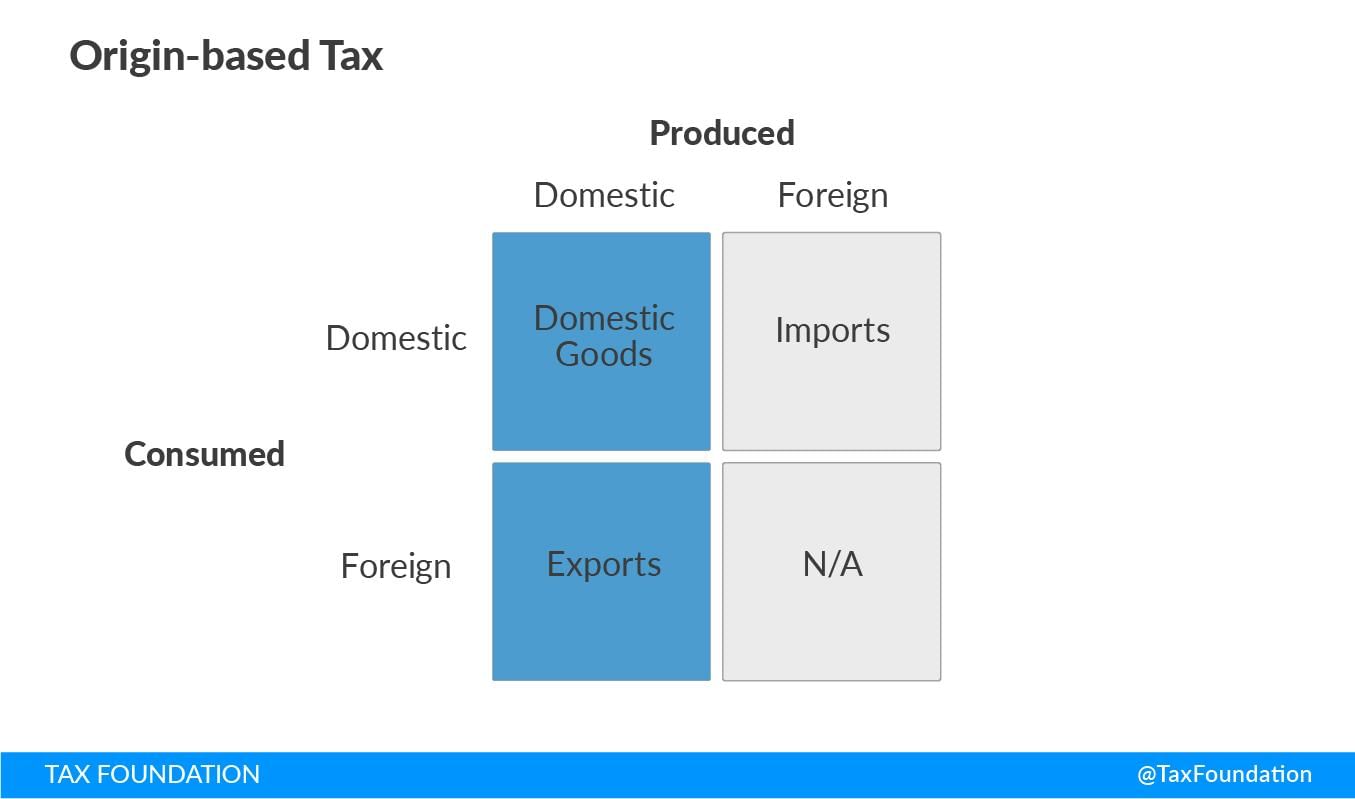
What was the impact of the origin-based tax system on inter-state commerce in India before GST? |
|
Card: 22 / 50 |
It encouraged states to offer tax relief to attract industries and imposed entry taxes on goods from other states, hindering an integrated market. |
|
Card: 23 / 50 |
True or False: The introduction of GST has resolved all issues related to overlapping tax jurisdictions in India. |
|
Card: 24 / 50 |
False. While GST aimed to simplify the tax structure, some complexities remain. |
|
Card: 25 / 50 |
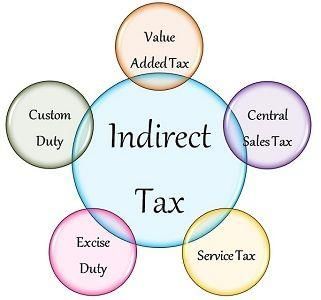
Fill in the blank: The multiplicity of taxes prior to GST included Excise duty, VAT, Entry tax, luxury tax, and ___ tax. |
|
Card: 27 / 50 |
How did the tax structure before GST affect the development of a national market in India? |
|
Card: 28 / 50 |
It created barriers such as Central State tax and entry tax, preventing the establishment of a seamless national market. |
|
Card: 29 / 50 |
The implementation of GST aimed to reduce the loss of man-hours and truck hours caused by ___ at state boundaries. |
|
Card: 31 / 50 |
True or False: The pre-GST regime had a single tax authority that simplified compliance for taxpayers. |
|
Card: 32 / 50 |
False. The pre-GST regime had multiple tax authorities, complicating compliance. |
|
Card: 33 / 50 |
GST is a form of ___ tax that is applied at various stages of the supply chain. |
|
Card: 35 / 50 |
What major issue did the multiplicity of tax laws create for taxpayers under the pre-GST regime? |
|
Card: 37 / 50 |
The lack of online data hindered the ability of tax departments to verify input tax credit claims, leading to ___ by some dealers. |
|
Card: 39 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The burden of compliance and multiple tax laws led to increased ___ among taxpayers. |
|
Card: 41 / 50 |
True or False: One of the consequences of the overlapping jurisdictions in the pre-GST system was increased efficiency in tax collection. |
|
Card: 42 / 50 |
False. Overlapping jurisdictions created confusion and inefficiencies in tax collection. |
|
Card: 45 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The various tax laws and differing taxable events led to a huge amount of ___ in the tax system. |
|
Card: 49 / 50 |
The GST system operates on a principle of ___ taxation, meaning it is levied based on the destination of goods and services rather than the origin. |