|
Card: 1 / 50 |
Article 265 of the Constitution prohibits arbitrary tax collection, stating that ___ shall be levied or collected except by authority of law. |
|
Card: 3 / 50 |
True or False: The power to levy Goods and Services Tax (GST) is exclusively granted to the Centre according to Article 246A. |
|
Card: 5 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: If any tax law does not align with the Constitution, it is considered ___ and deemed illegal. |
|
Card: 8 / 50 |
It implies that the tax must be within the legislative competence of the body imposing it.  |
|
Card: 9 / 50 |
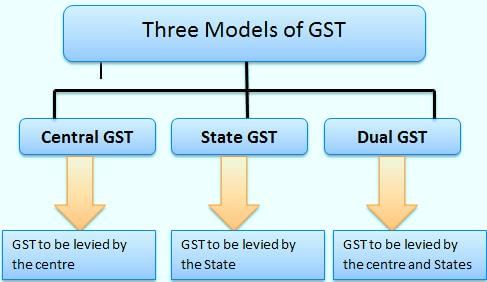
According to Article 246A, the power to levy GST was introduced by the ___ Amendment Act of 2016. |
|
Card: 13 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The powers of taxation, whether direct or indirect, stem from the ___ of India. |
|
Card: 17 / 50 |
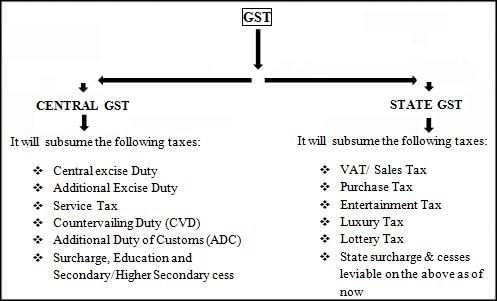
The Constitution (101st Amendment) Act, 2016 was enacted to empower both the Centre and the States to levy and collect ___. |
|
Card: 19 / 50 |
True or False: The Centre exclusively levied taxes on services before the introduction of GST. |
|
Card: 21 / 50 |
Before GST, the Centre imposed excise duty on goods produced in India, while the States levied ___ once goods entered the stream of trade. |
|
Card: 25 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: For inter-State sales, the Centre could levy Central Sales Tax, but the revenue was entirely retained by ___. |
|
Card: 27 / 50 |
True or False: The introduction of GST removed the ability of States to levy any form of tax on goods. |
|
Card: 28 / 50 |
False. The introduction of GST allowed both the Centre and the States to levy and collect a unified tax. |
|
Card: 29 / 50 |
Short Answer: What type of tax did the Centre impose on all goods produced or manufactured in India prior to GST? |
|
Card: 31 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The introduction of GST integrated various taxes, including excise duty and ___. |
|
Card: 33 / 50 |
Article 246A of the Constitution of India grants power to which entities regarding Goods and Services Tax? |
|
Card: 34 / 50 |
It grants power to both the Centre and State Governments to make laws regarding GST.  |
|
Card: 35 / 50 |
True or False: The Centre has exclusive power to legislate on GST for intra-State supply of goods and/or services. |
|
Card: 36 / 50 |
False. The Centre has exclusive power to legislate on GST for inter-State supply of goods and/or services.  |
|
Card: 38 / 50 |
GST on inter-State supplies is levied and collected by the Government of India. 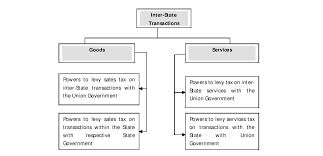 |
|
Card: 39 / 50 |
Fill in the blank: The collected GST tax is apportioned between the Union and the States as per the law made by Parliament on the recommendations of the ___ . |
|
Card: 42 / 50 |
'Goods' includes all materials, commodities, and articles as defined under Article 366. |
|
Card: 45 / 50 |
True or False: The import of goods or services into India is considered as supply in the course of inter-State trade or commerce. |
|
Card: 47 / 50 |
What is excluded from the definition of 'goods and services tax' as per Article 366? |
|
Card: 49 / 50 |
What is the primary purpose of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council as established by Article 279A? |
|
Card: 50 / 50 |
The primary purpose of the GST Council is to recommend important issues such as tax rates, exemptions, threshold limits, and dispute resolution to the Union and the States. |