NEET Exam > NEET Questions > What is the main contributing structure to th...
Start Learning for Free
What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole?
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof...
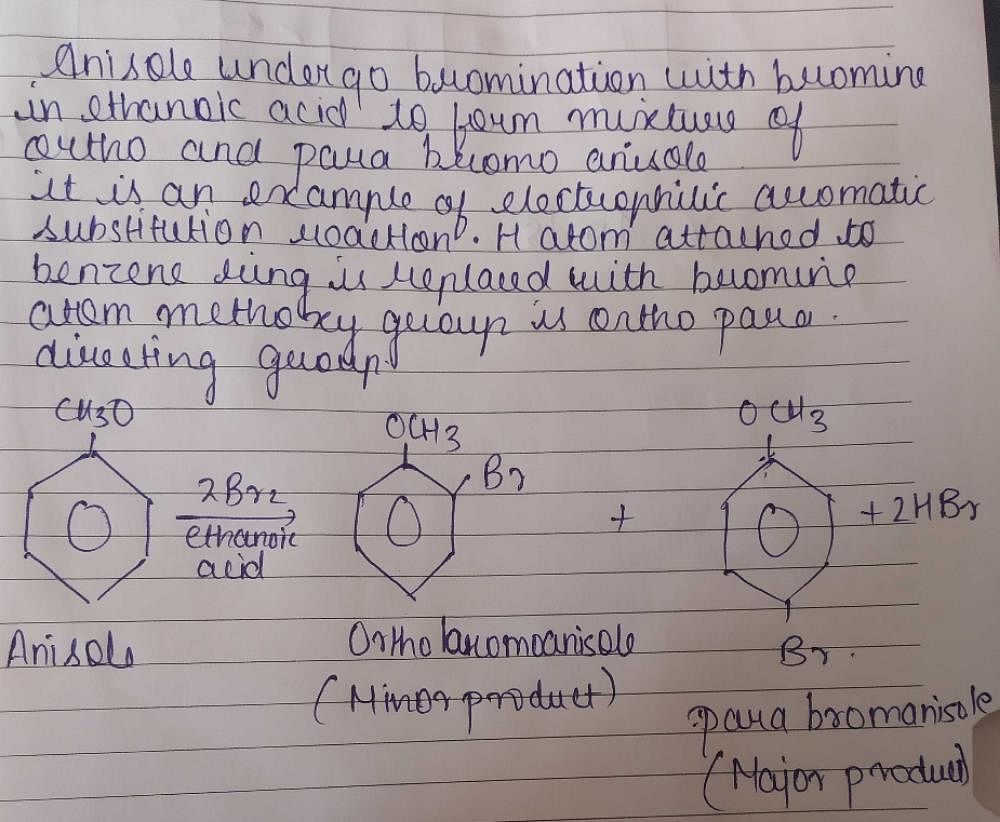
Community Answer
What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof...
Contributing Structure to the Cation Intermediate in the Bromination of Anisole
The bromination of anisole involves the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the aromatic ring with a bromine atom. This reaction proceeds through the formation of a cation intermediate. The main contributing structure to this cation intermediate can be explained as follows:
Formation of the Cation Intermediate:
1. Initially, anisole (methoxybenzene) undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) with bromine in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst, such as iron(III) bromide (FeBr3).
2. The Lewis acid catalyst facilitates the generation of an electrophilic bromonium cation (Br+). The FeBr3 coordinates with the bromine molecule, polarizing the Br-Br bond and generating an electrophilic bromine species.
3. The electrophilic bromonium cation then attacks the electron-rich aromatic ring of anisole, leading to the formation of a cation intermediate.
Main Contributing Structure to the Cation Intermediate:
The cation intermediate in the bromination of anisole can be represented by the resonance structures, with the positive charge localized on different carbon atoms on the aromatic ring:
- The positive charge can be delocalized onto the carbon atom ortho to the methoxy group (OCH3) present on the ring.
- The positive charge can also be delocalized onto the carbon atom para to the methoxy group.
- The positive charge can also be partially delocalized onto the oxygen atom of the methoxy group.
Resonance Structure 1:
In this structure, the positive charge is localized on the carbon atom ortho to the methoxy group. This carbon atom is directly bonded to the bromine atom, making it a highly electrophilic site.
Resonance Structure 2:
In this structure, the positive charge is localized on the carbon atom para to the methoxy group. This carbon atom is also directly bonded to the bromine atom, making it another highly electrophilic site.
Resonance Structure 3:
In this structure, the positive charge is partially delocalized onto the oxygen atom of the methoxy group. This oxygen atom can act as an electron-donating group, enhancing the stability of the cation intermediate.
These resonance structures indicate that the positive charge is delocalized over the aromatic ring, making the cation intermediate more stable. The presence of the electron-donating methoxy group increases the electron density on the ring, facilitating the attack of the electrophilic bromine species.
In summary, the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate in the bromination of anisole involves the delocalization of the positive charge onto the carbon atoms ortho and para to the methoxy group, as well as partial delocalization onto the oxygen atom of the methoxy group. These resonance structures enhance the stability of the cation intermediate and promote the bromination reaction.
The bromination of anisole involves the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the aromatic ring with a bromine atom. This reaction proceeds through the formation of a cation intermediate. The main contributing structure to this cation intermediate can be explained as follows:
Formation of the Cation Intermediate:
1. Initially, anisole (methoxybenzene) undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) with bromine in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst, such as iron(III) bromide (FeBr3).
2. The Lewis acid catalyst facilitates the generation of an electrophilic bromonium cation (Br+). The FeBr3 coordinates with the bromine molecule, polarizing the Br-Br bond and generating an electrophilic bromine species.
3. The electrophilic bromonium cation then attacks the electron-rich aromatic ring of anisole, leading to the formation of a cation intermediate.
Main Contributing Structure to the Cation Intermediate:
The cation intermediate in the bromination of anisole can be represented by the resonance structures, with the positive charge localized on different carbon atoms on the aromatic ring:
- The positive charge can be delocalized onto the carbon atom ortho to the methoxy group (OCH3) present on the ring.
- The positive charge can also be delocalized onto the carbon atom para to the methoxy group.
- The positive charge can also be partially delocalized onto the oxygen atom of the methoxy group.
Resonance Structure 1:
In this structure, the positive charge is localized on the carbon atom ortho to the methoxy group. This carbon atom is directly bonded to the bromine atom, making it a highly electrophilic site.
Resonance Structure 2:
In this structure, the positive charge is localized on the carbon atom para to the methoxy group. This carbon atom is also directly bonded to the bromine atom, making it another highly electrophilic site.
Resonance Structure 3:
In this structure, the positive charge is partially delocalized onto the oxygen atom of the methoxy group. This oxygen atom can act as an electron-donating group, enhancing the stability of the cation intermediate.
These resonance structures indicate that the positive charge is delocalized over the aromatic ring, making the cation intermediate more stable. The presence of the electron-donating methoxy group increases the electron density on the ring, facilitating the attack of the electrophilic bromine species.
In summary, the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate in the bromination of anisole involves the delocalization of the positive charge onto the carbon atoms ortho and para to the methoxy group, as well as partial delocalization onto the oxygen atom of the methoxy group. These resonance structures enhance the stability of the cation intermediate and promote the bromination reaction.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole?
Question Description
What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole?.
What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole?.
Solutions for What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole?, a detailed solution for What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole? has been provided alongside types of What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the main contributing structure to the cation intermediate bof bromination of anisole? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























