IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > The first step of urea cycle involves the com...
Start Learning for Free
The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound is
- a)Citrulline
- b)Carbamoyl phosphate
- c)Ornithine
- d)Arginosuccinate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with ...
Carbamoyl phosphate is the first compound that is formed from the reaction of bicarbonate and ammonia in mitochondria by the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1. Another isoform of this enzyme is present in the cytosol that forms the same compound which is involved in biosynthesis of nucleotides (pyrimidine biosynthesis).

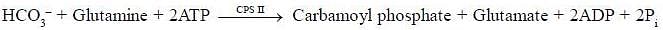

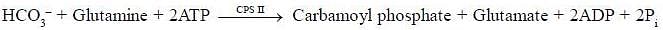
Most Upvoted Answer
The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with ...
The first step of the urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate.
The urea cycle is a crucial metabolic pathway that takes place in the liver and helps to eliminate toxic ammonia from the body. Ammonia is produced as a byproduct of amino acid metabolism and needs to be converted into urea, a less toxic compound that can be excreted in urine.
The first step of the urea cycle:
1. Combination of Ammonia and Bicarbonate: In the first step of the urea cycle, ammonia (NH3) and bicarbonate (HCO3-) combine together in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPSI). This reaction occurs in the mitochondria of liver cells.
2. Conversion of ATP to ADP and Pi: The combination of ammonia and bicarbonate requires the input of energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). One molecule of ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) during this step.
3. Formation of Carbamoyl Phosphate: The reaction between ammonia and bicarbonate results in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate. This compound is an important intermediate in both the urea cycle and nucleotide biosynthesis.
Role of Carbamoyl Phosphate:
Carbamoyl phosphate serves as a precursor for the synthesis of both urea and pyrimidine nucleotides, which are essential components of DNA and RNA. In the context of the urea cycle, carbamoyl phosphate is further utilized in subsequent steps to produce citrulline, argininosuccinate, and eventually urea.
Significance of the Urea Cycle:
The urea cycle plays a vital role in maintaining nitrogen balance in the body. Ammonia, a toxic substance, is converted into urea, which is less toxic and can be safely excreted by the kidneys. This process prevents the accumulation of ammonia in the bloodstream, which can lead to neurological damage.
In conclusion, the first step of the urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia and bicarbonate, resulting in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate. This compound serves as an important intermediate in both the urea cycle and nucleotide biosynthesis.
The urea cycle is a crucial metabolic pathway that takes place in the liver and helps to eliminate toxic ammonia from the body. Ammonia is produced as a byproduct of amino acid metabolism and needs to be converted into urea, a less toxic compound that can be excreted in urine.
The first step of the urea cycle:
1. Combination of Ammonia and Bicarbonate: In the first step of the urea cycle, ammonia (NH3) and bicarbonate (HCO3-) combine together in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPSI). This reaction occurs in the mitochondria of liver cells.
2. Conversion of ATP to ADP and Pi: The combination of ammonia and bicarbonate requires the input of energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). One molecule of ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) during this step.
3. Formation of Carbamoyl Phosphate: The reaction between ammonia and bicarbonate results in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate. This compound is an important intermediate in both the urea cycle and nucleotide biosynthesis.
Role of Carbamoyl Phosphate:
Carbamoyl phosphate serves as a precursor for the synthesis of both urea and pyrimidine nucleotides, which are essential components of DNA and RNA. In the context of the urea cycle, carbamoyl phosphate is further utilized in subsequent steps to produce citrulline, argininosuccinate, and eventually urea.
Significance of the Urea Cycle:
The urea cycle plays a vital role in maintaining nitrogen balance in the body. Ammonia, a toxic substance, is converted into urea, which is less toxic and can be safely excreted by the kidneys. This process prevents the accumulation of ammonia in the bloodstream, which can lead to neurological damage.
In conclusion, the first step of the urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia and bicarbonate, resulting in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate. This compound serves as an important intermediate in both the urea cycle and nucleotide biosynthesis.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound isa)Citrullineb)Carbamoyl phosphatec)Ornithined)ArginosuccinateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
















